网络层
The Network Layer: Data Plane
Overflow
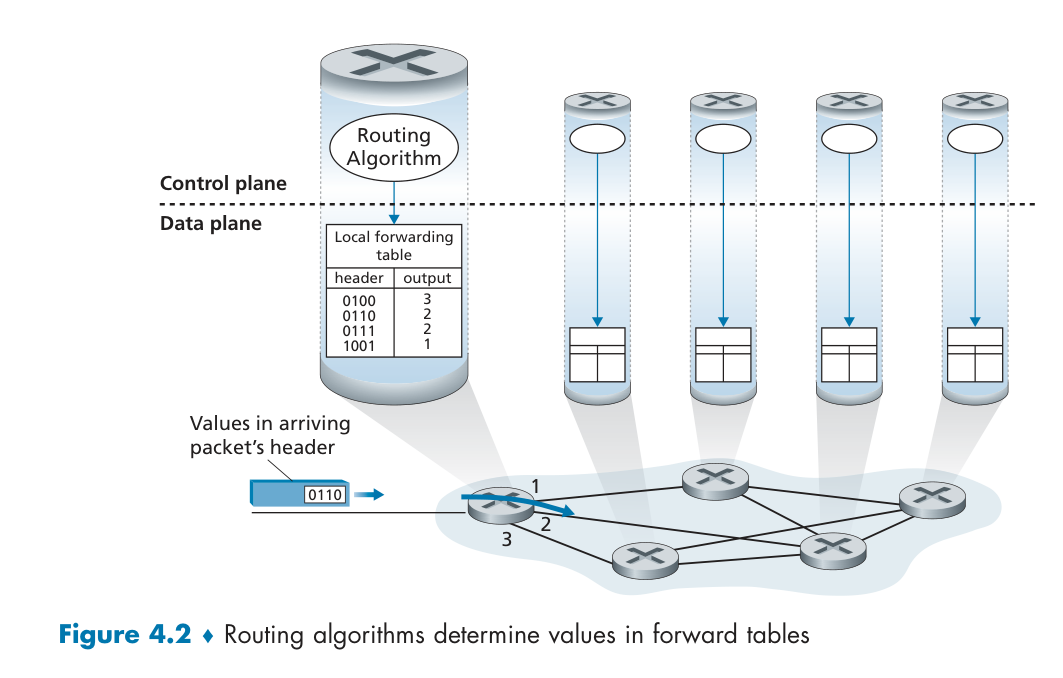
(数据平面:转发)Forwarding:the router-local action of transferring a packet from an input link interface to the appropriate output link interface.
(控制平面:路由)Routing: the network-wide process that determines the end-to-end paths that packets take from source to destination routers:
examines header fields in all IP datagrams passing through it.
moves datagrams from input ports to output ports to transfer datagrams along end-end path
Network Service Model
The network service model defines the characteristics of end-to-end delivery of packets.
best-effort service to:
Guaranteed delivery (with guaranteed delivery).
In-order packet delivery.
Guaranteed minimal bandwidth.
Security.
No guarantees on:
i.successful datagram delivery to destination
ii.timing or order of delivery
iii.bandwidth available to end-end flow
其实服务模型有很多种,其机制和复杂度的权衡,难以辨明优劣。尽力而为即可。
即分成两种网络服务方式--数据报(无连接)和虚电路(面向连接)方式。
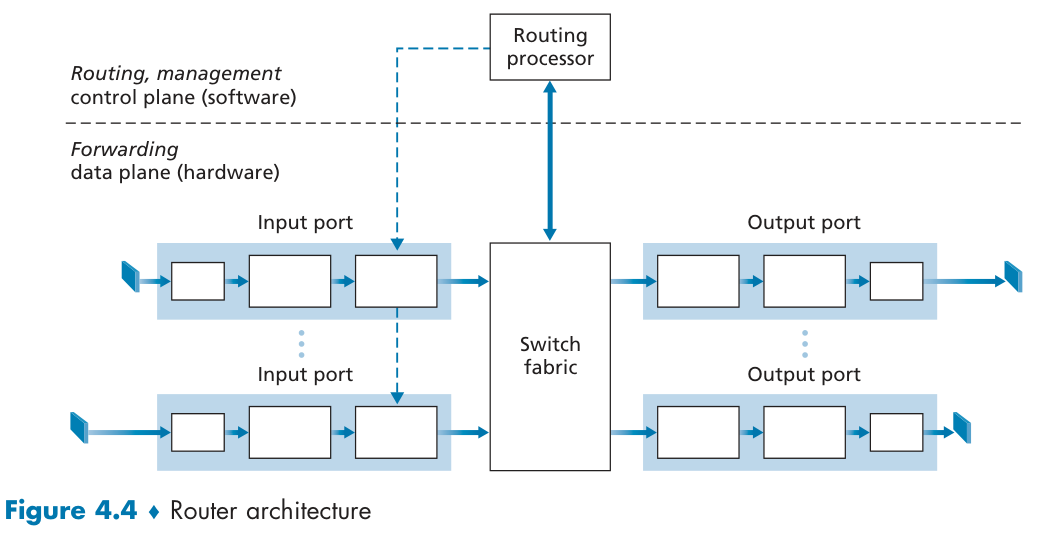
What's Inside a Router?
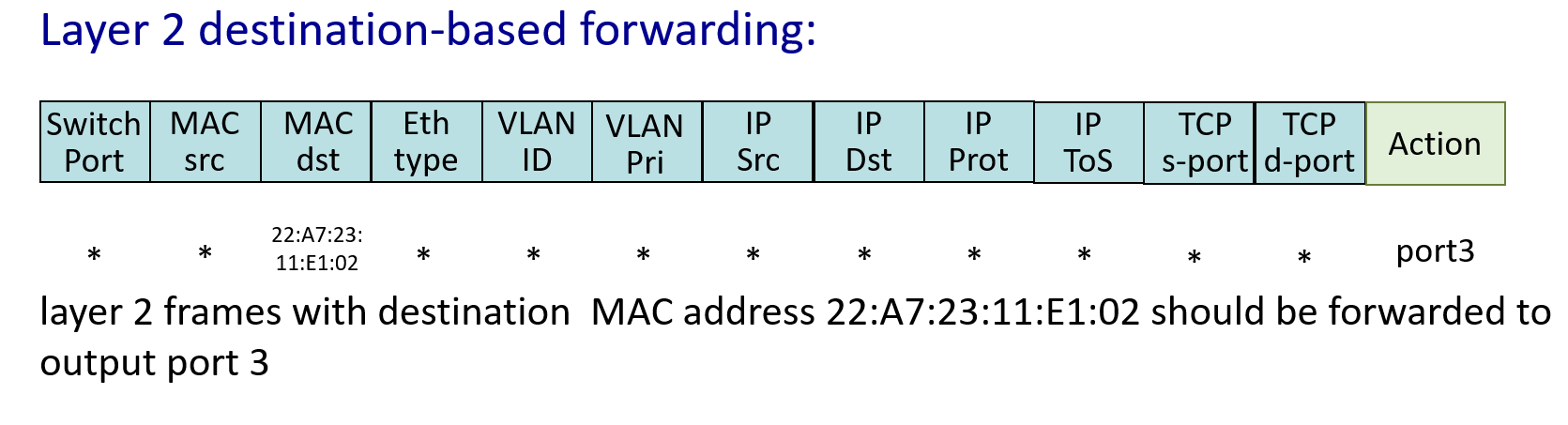
Destination-based forwarding
Generalized forwarding
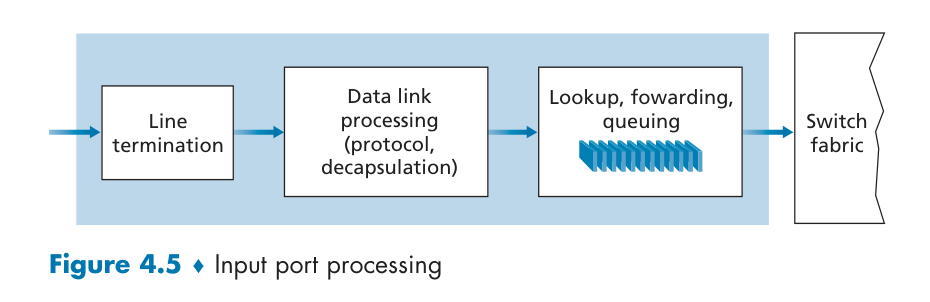
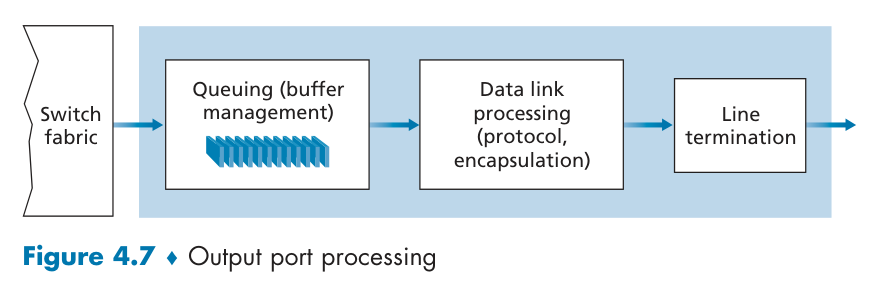
IO Port Processing
the router uses the longest prefix matching rule in lookup table to decide the dest.
Switching
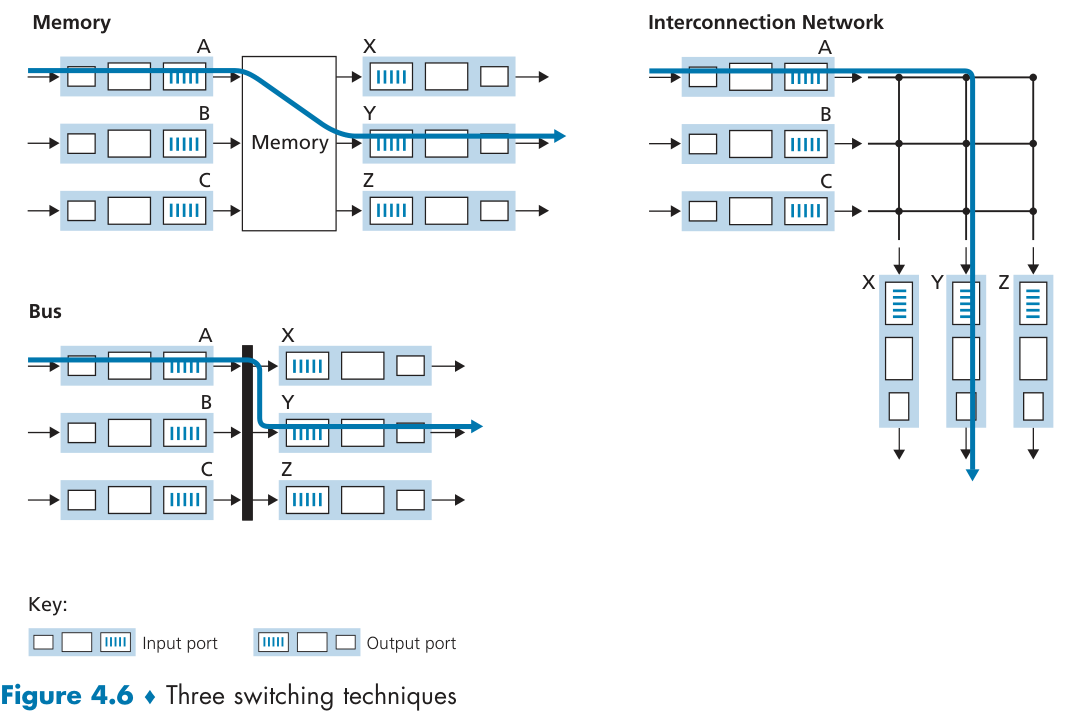
Switching via a bus: must wait since only one packet can cross the bus at a time.
Switching via an interconnection network: parallel(fragment datagram), A crossbar switch is non-blocking
More sophisticated interconnection networks use multiple stages of switching elements to allow packets from different input ports to proceed towards the same output port at the same time through the multi-stage switching fabric.
Queuing
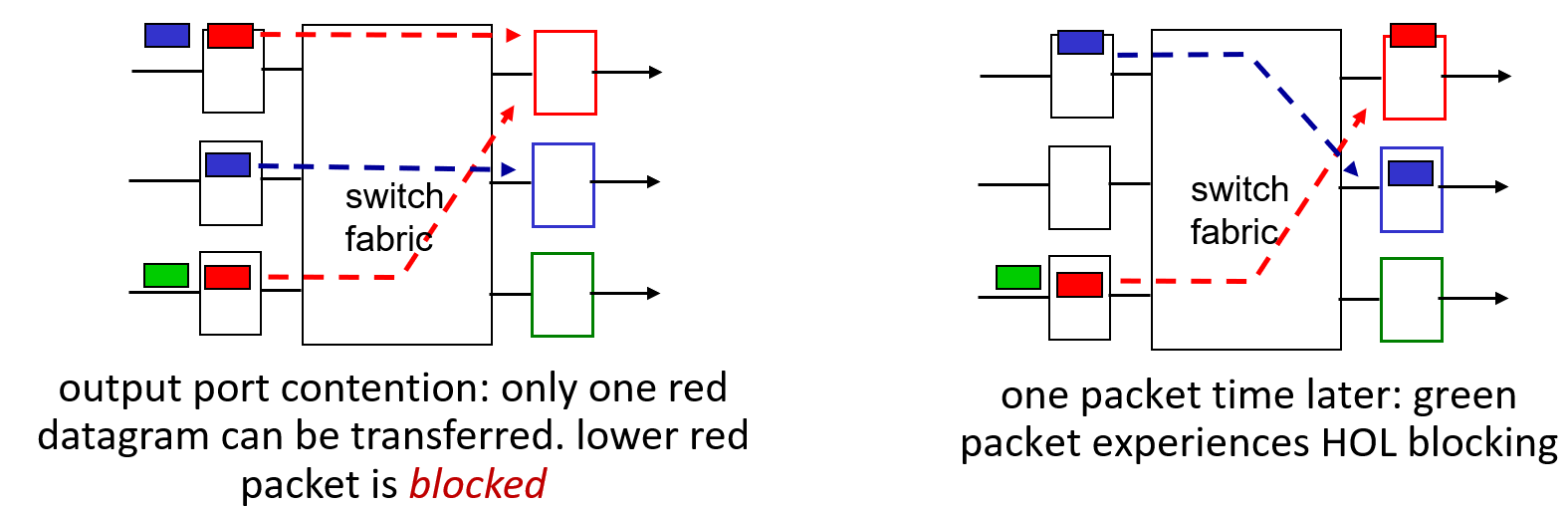
Head-of-the-Line (HOL) blocking: queued datagram at front of queue prevents others in queue from moving forward
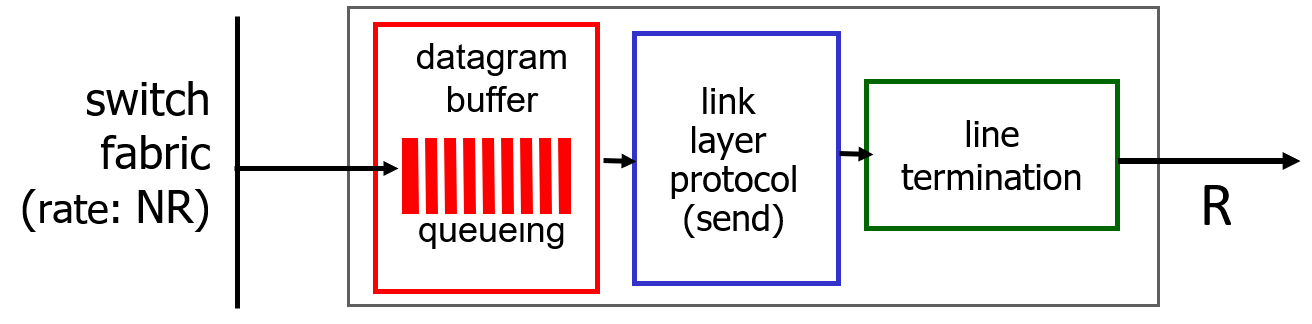
Datagrams can be lost due to congestion, lack of buffers(Buffering when arrival rate via switch exceeds output line speed )
The buffering size: (recommendation) $ \frac{RTT \times C}{\sqrt{n}} $
too much buffering can increase delays
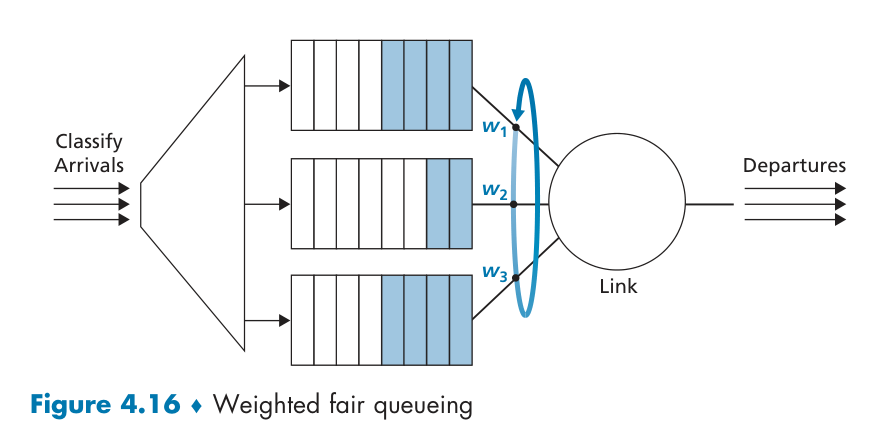
Packet Scheduling
FIFO
Priority Queuing
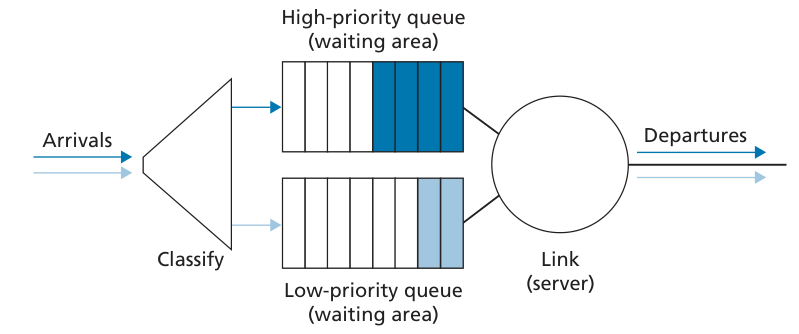
Round Robin and Weighted Fair Queuing (WFQ)
流量整形: 业务量突发:主机不规律地发送数据包,可能导致网络中出现拥塞,需要调整数据发送的平均速率.
令牌桶算法:在输出的数据流中允许一定的突发性,如果令牌桶是满的,并且到来的数据超过令牌桶容量,则:先以突发速率发送,利用公式
突发时长=桶容量 / (最大输出速率 - 令牌到达速率)计算出以最大速率发送的时间;当令牌桶中的令牌全部用完,而还有数据要发送,则剩下的数据将以令牌产生的速率匀速发送。
你可以使用Iptables在网络层按IP地址应用速率限制。
The Internet Protocol (IP)
IP是要设备接入网络后,根据上线的子网分配。在设备还没有IP地址时还需要用MAC地址(6 byte)来区分不同的设备。 总之,MAC地址就像自己的ID号,而IP地址就像带着邮政编码的住址。MAC可以在不依赖网络接入下区分设备。
IPv4
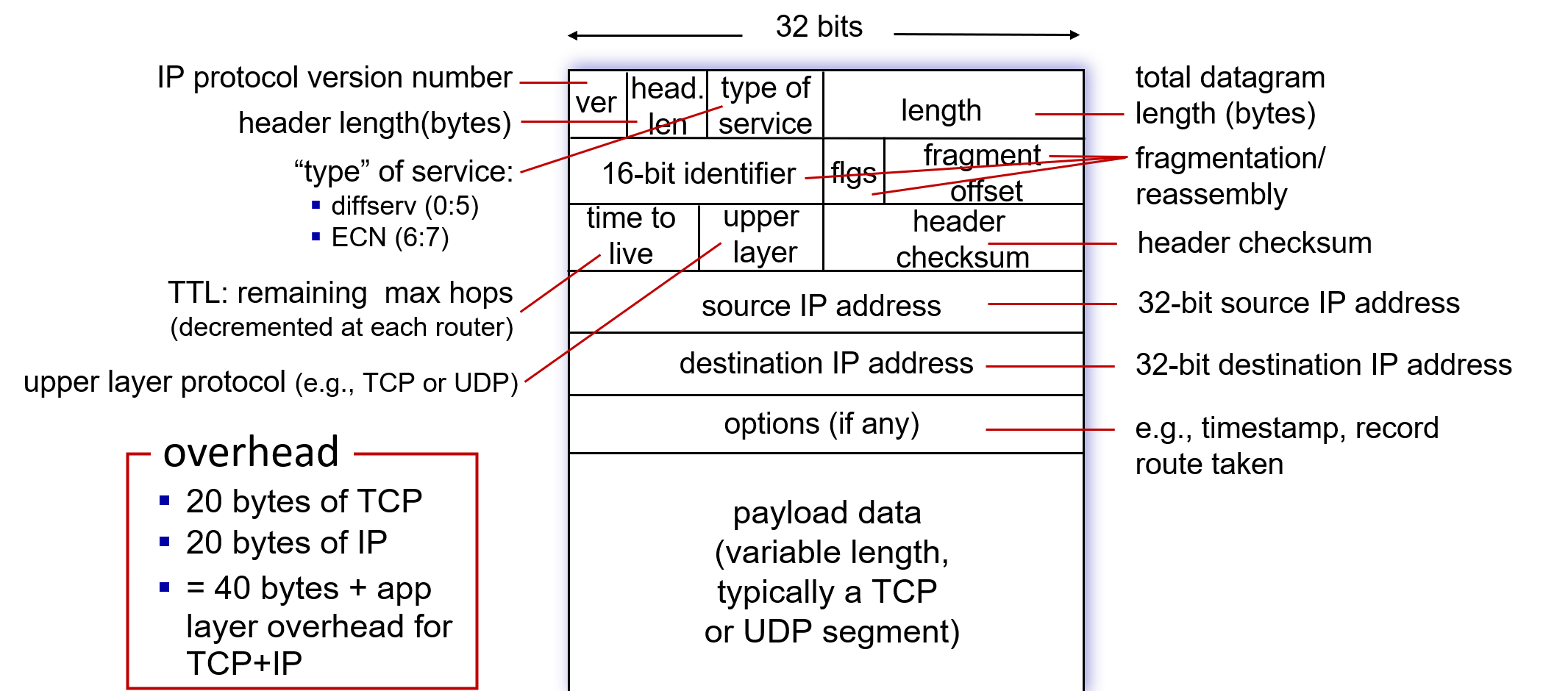
The boundary between the host and the physical link is called an interface.
To determine the subnets, detach each interface from its host or router, creating islands of isolated networks. Each of these isolated networks is called a subnet.(不需要经过路由转发者) 
IPAddress=subnetpart+hostpart. 
The Internet's address assignment strategy is known as Classless Interdomain Routing (CIDR,无分类地址). 23 ABOVE.
Obtaining Address
How does host get IP address?
DHCP( Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) dynamically get address from as server, with plug-and-play or zeroconf.
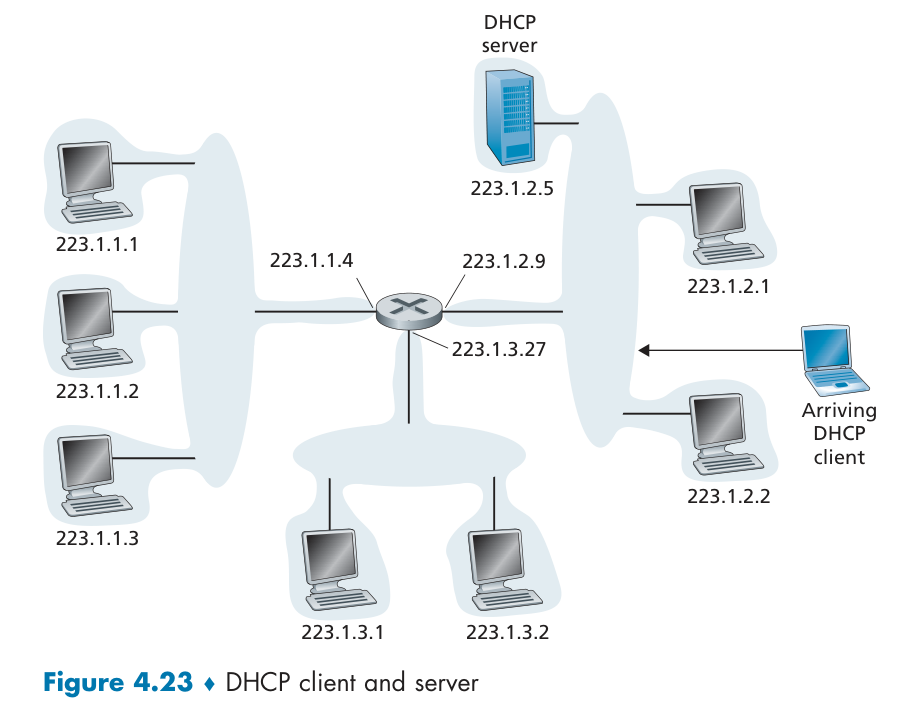
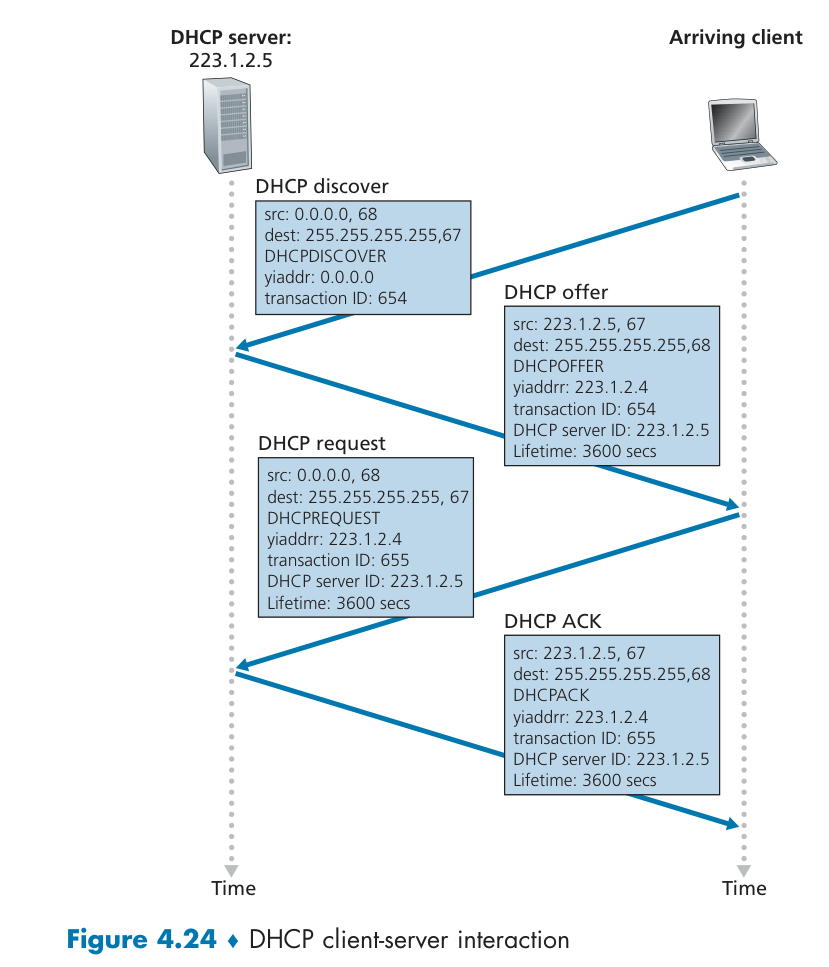
DHCP server can also formulates a encapsulated DHCP ACK containing client's IP address, IP address of first-hop router for client, name & IP address of DNS server。
以下是流程简介:
DHCP DISCOVER :使用 UDP 广播通信,DHCP 客户端将该 IP 数据报传递给链路层,链路层然后将帧广播到所有的网络设备。或者说,DHCP 客户端会向 DHCP 中继代理发送 DHCP 请求包,而 DHCP 中继代理在收到这个广播包以后,再以单播的形式发给 DHCP 服务器。因此,DHCP 服务器即使不在同一个链路上也可以实现统一分配和管理IP地址。
DHCP OFFER: 仍然使用 IP 广播地址 255.255.255.255,配置的内容不仅 是 IP 地址,还包括子网掩码、网关、租期、DNS。
DHCP REQUEST:客户端收到一个或多个服务器的 DHCP 提供报文后,选择一个回应,回显配置的参数。如果租约的 DHCP IP 地址即将过期,客户端也会向该服务器再次发送 DHCP REQUEST。
DHCP ACK:服务端返回。一旦客户端收到 DHCP ACK 后,交互便完成了。如果是 NACK 报文,客户端就要停止使用租约的 IP 地址。
IPv6(128b)
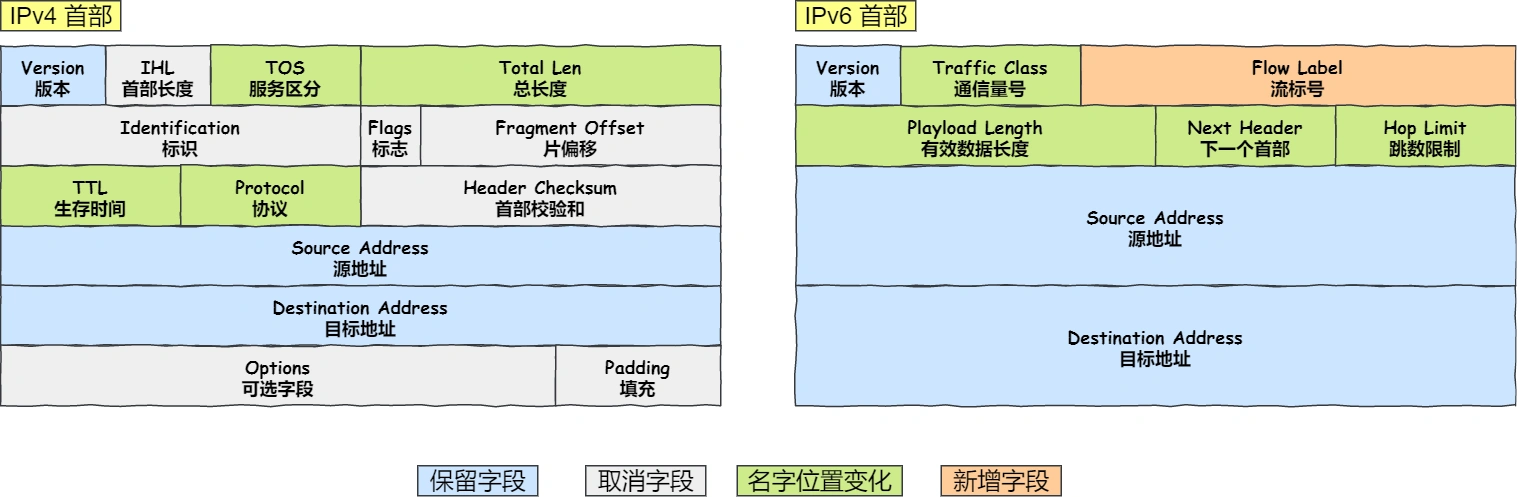
首部固定为40Byte。
取消了首部校验和字段。 因为在数据链路层和传输层都会校验。
取消选项字段。 若出现选项则通过 IPv6 首部中的「下一个首部」指出位置。
How will the public Internet based on IPv4 be transitioned to IPv6?
隧道技术 tunneling。 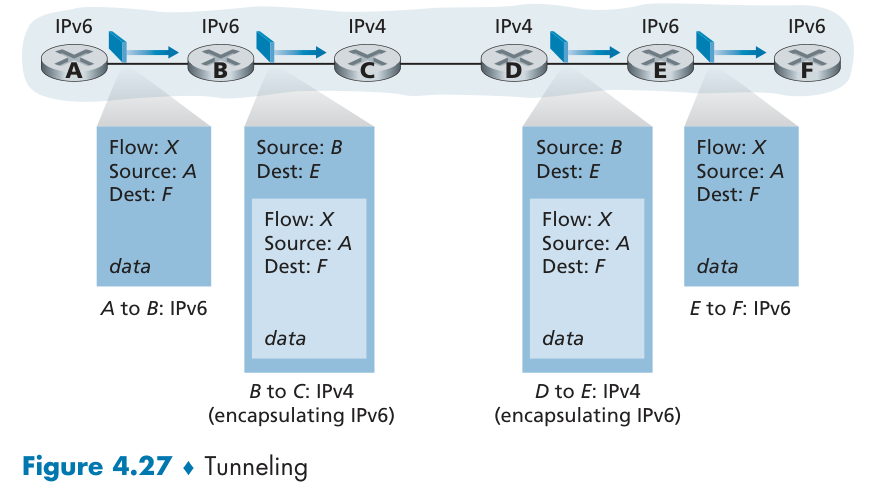
IP 分片与重组
每种数据链路的最大传输单元 MTU 都是不相同的,如以太网的 MTU 是 1500 字节。当 IP 数据包大小大于 MTU 时, IP 数据包就会被分片。经过分片之后的 IP 数据包在被重组的时候,由目标主机进行。(分片与重组是耗时的过程,在IPv6中禁止在网络层进行,所以 TCP 引入了 MSS ,也就是在 TCP 层进行分片)
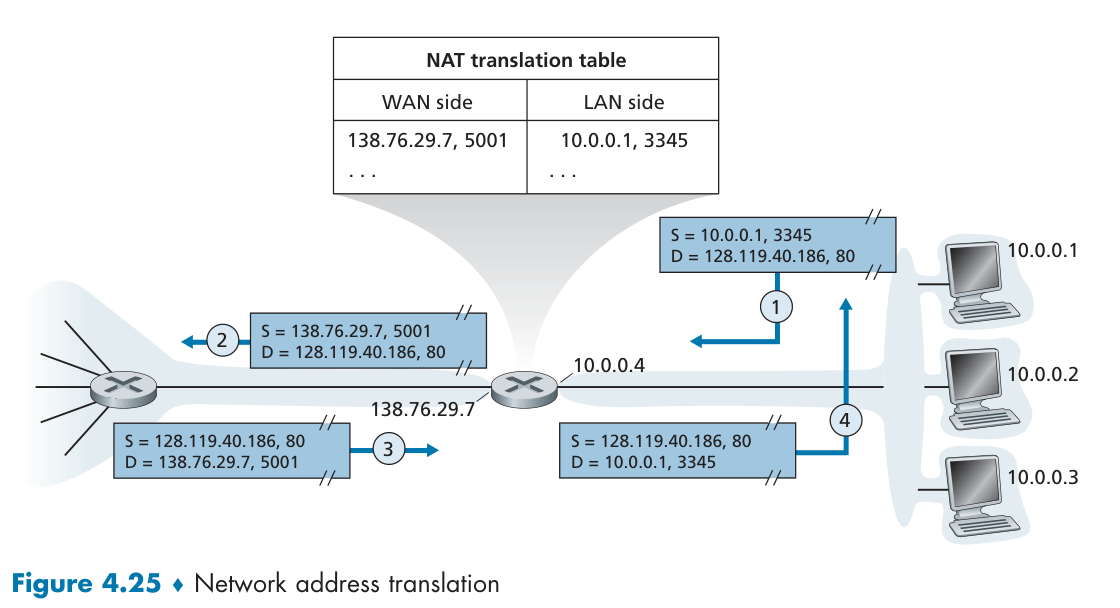
NAT
Network Address Translation. Widely used in SOHO to manage IP addresses.
private addresses refers to a network whose addresses only have meaning devices within that network
all devices in local network share just one IPv4 address as far as outside world is concerned.
now, map with port together. 现在当然不是一对一的,结合使用端口号的 NAT 也叫做网络地址与端口转换 NAPT,以传输层的端口号区分设备。
NAT 穿透技术:
该技术可以让外部也能主动与 NAT 内部服务器建立连接。简而言之,核心是:
发现自己的公网IP和Port。客户端主动从 NAT 设备获取公有 IP 地址,然后自己建立端口映射条目,然后用这个条目来对外通信,就不走NAT层了。(STUN协议)
将自己的IP和Port共享给对方。可以通过设计中继的方式, 进行交换。
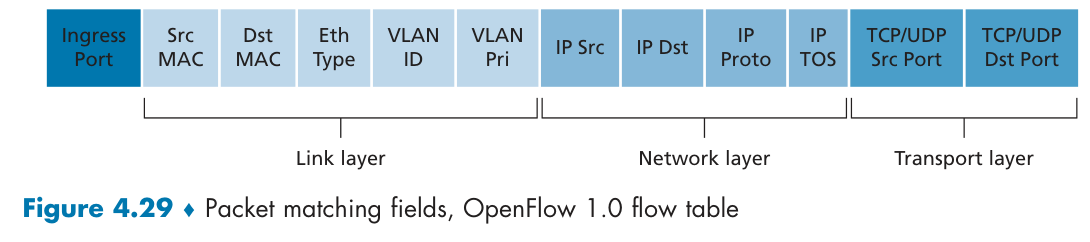
Generalized Forwarding
通过“匹配+动作”(match bits in arriving packet header(s) in any layers, take action),实现通用转发。下面是OpenFlow转发表的机制:
举例:
MiddleBox
we've also encountered other network equipment (“boxes”) within the network that sit on the data path and perform functions other than forwarding.
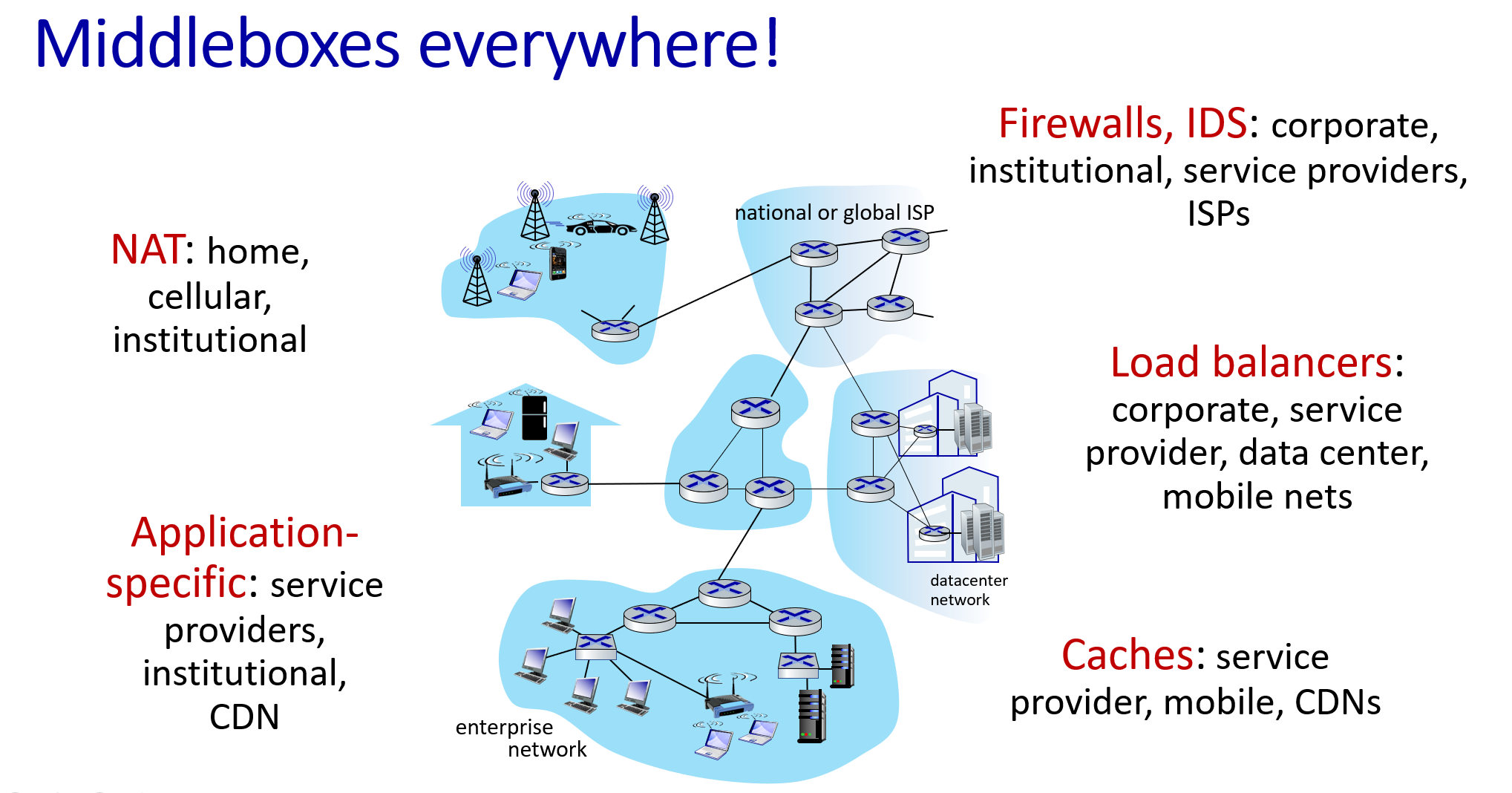
SDN(软件定义网络):centralize control and configuration management (logically) often in private/public cloud.
network functions virtualization (NFV): programmable services over white box networking, computation, storage
网络层控制平面
路由表选路算法
Dijkstra算法:从本地节点为初始节点集,不断迭代加入距离最小的节点集,直到所有节点均在节点集中。可以得到最短路径树。
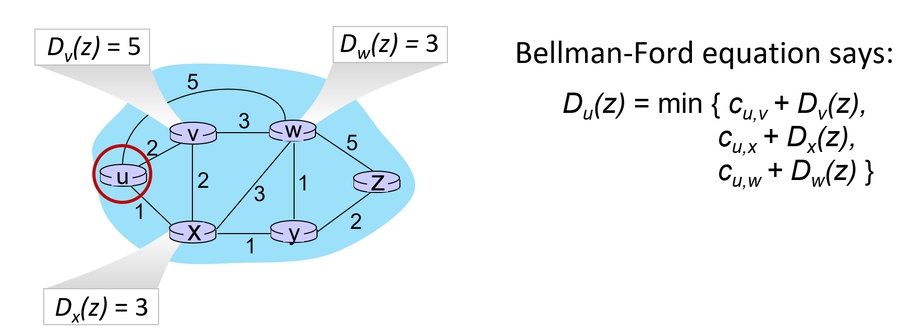
距离矢量算法:通过与邻居节点共享信息来更新路由表。(好消息扩散快,坏消息传播慢,且环路不友好)。eg:
链路状态选路(LSR):路由器与网络内的每一个路由器共享关于邻居的信息(链路状态包LSP。广播HELLO包,分发)
路由选择协议
互联网可以划分为许多较小的自治系统 AS(autonomous systems),每个管理机构在AS内部使用自己的选路协议,即内部选路协议;在AS之间,使用统一的选路协议,即外部选路协议。
RIP: Routing Information Protocol
classic DV: DVs exchanged every 30 secs
no longer widely used
距离是指跳数,直接相连的路由器跳数为 1。跳数最多为 15,上限是16(不可达), 可扩展性差。
RIP消息在 UDP 数据报中传输。
EIGRP: Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol(DV based)
OSPF: Open Shortest Path First
classic link-state routing (LSR)
each router floods OSPF link-state advertisements (directly over IP rather than using TCP/UDP) to all other routers in entire AS multiple link costs metrics possible: bandwidth, delay each router has full topology, uses Dijkstra’s algorithm to compute forwarding table.
只有当链路状态发生变化时,路由器才会洪泛向AS区内所有其他路由器通告自己的邻接情况。相比于 RIP,OSPF 的更新过程收敛的很快。
边界网关协议BGP:Border Gateway Protocol
May not the best route.
每个 AS 都必须配置 BGP 发言人,通过在两个相邻 BGP 发言人之间建立 TCP 连接来交换路由信息。
gateway receiving route advertisement uses import policy to accept/decline path.
eBGP:向邻居获取子网的可达性信息(spans two ASs )iBGP:向所有AS内部路由器传播可达信息(in the same AS)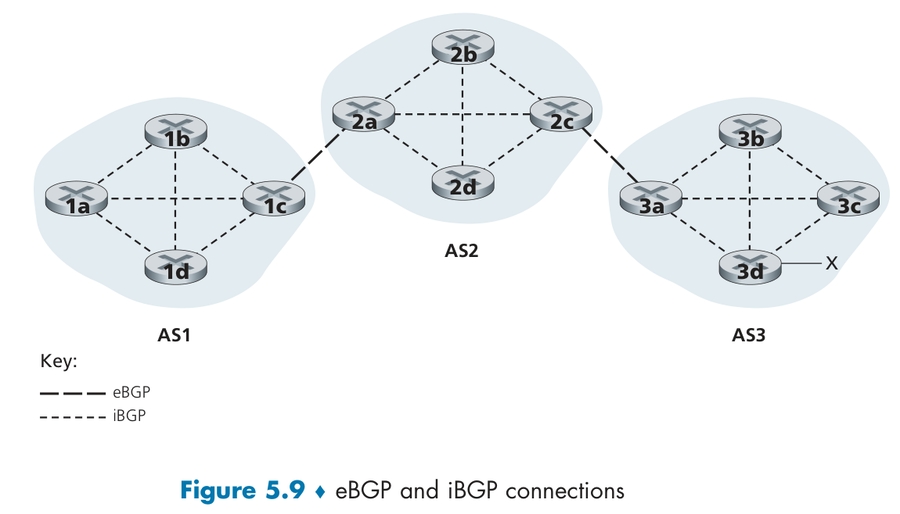
算法:热土豆算法 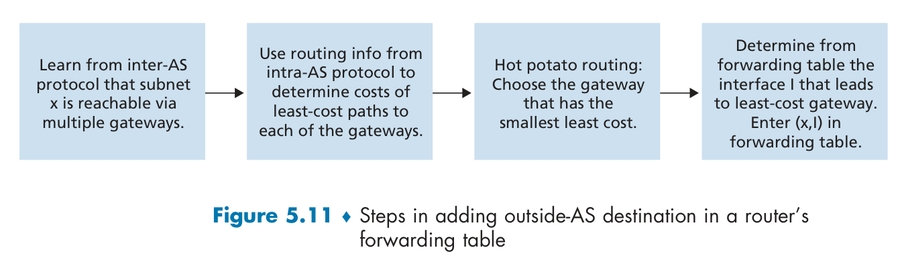
【选路四部曲】router may learn about more than one route to destination AS, selects route based on:
local preference value attribute: policy decision
shortest AS-PATH
closest NEXT-HOP router: hot potato routing
additional criteria
SDN 控制平面
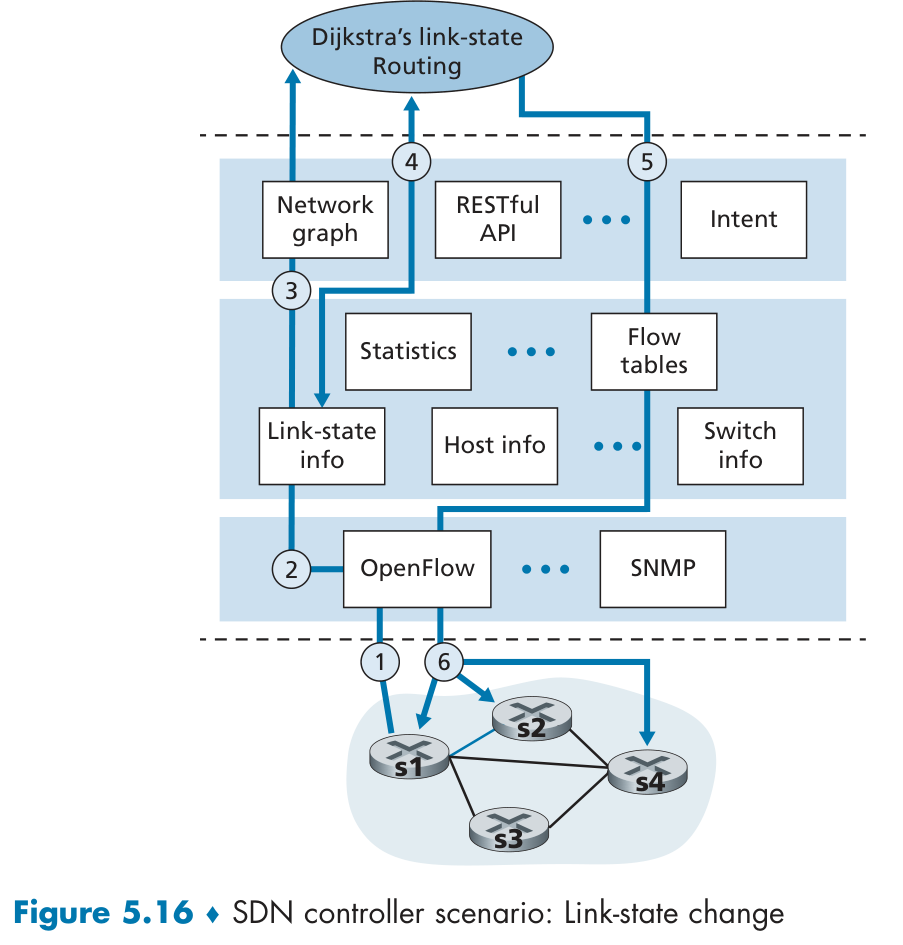
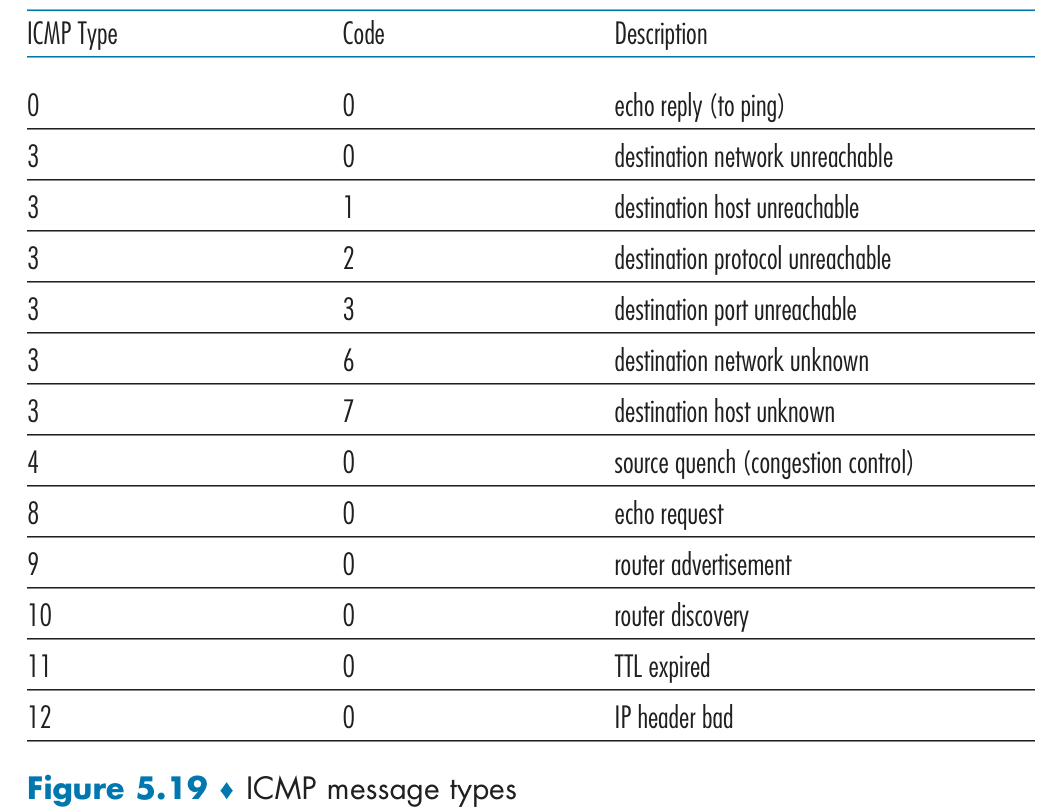
ICMP
ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol),称作互联网控制报文协议。ICMP 报文是封装在 IP 包里面,它工作在网络层,是 IP 协议的助手。可查询当前网络的控制信息状态。
Network Management
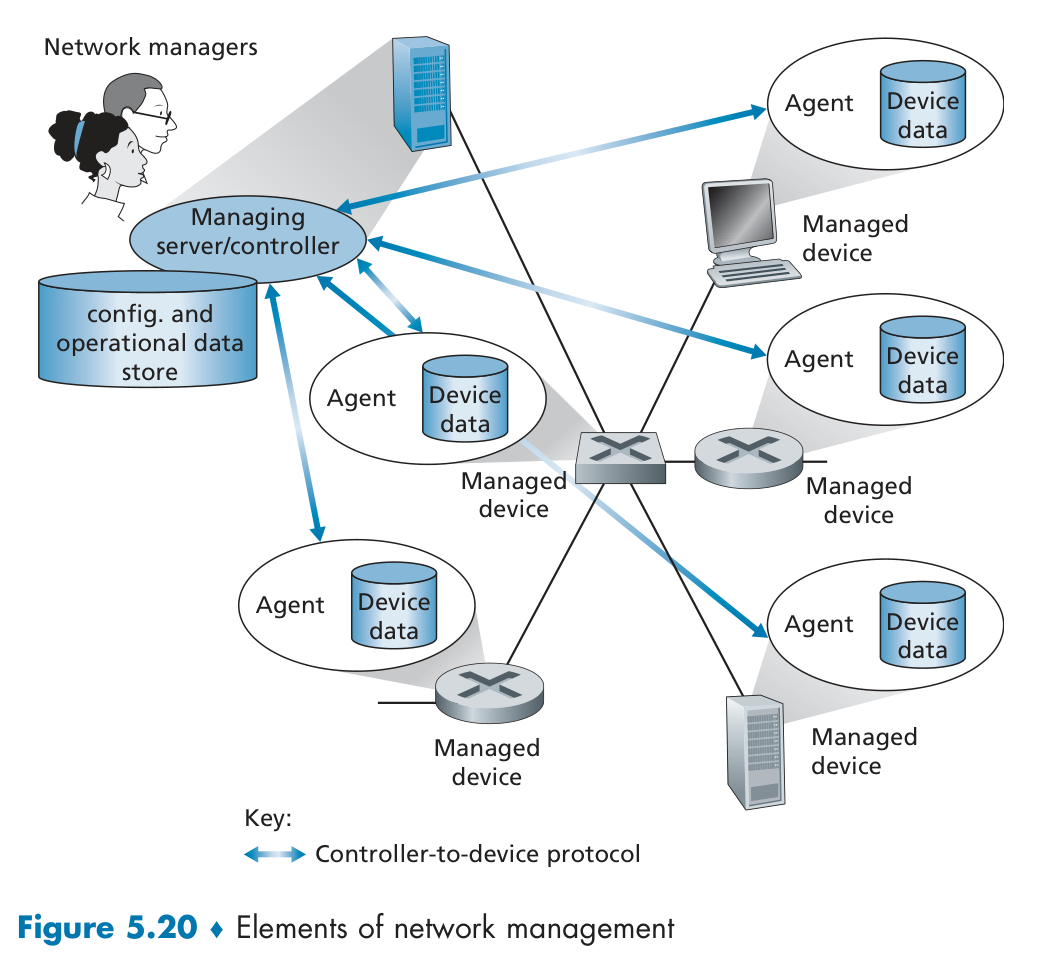
SNMP
An application-layer protocol used to convey network-management control and information messages between a managing server and an agent executing on behalf of that managing server.
参考材料:
[译] NAT 穿透是如何工作的:技术原理及企业级实践(Tailscale, 2020) (arthurchiao.art)
最后更新于