计算机网络
本系列笔记以《计算机网络-自顶向下方法》为纲,结合配套视频、北邮教学PPT、《图解HTTP》、优秀博客等形成。致谢如上。
COMPUTER NETWORKS AND THE INTERNET
Internet
概念
什么是计算机网络? Billions of connected computing devices.
running network apps at Internet’s “edge”
End systems(端系统) are connected together by a network of communication links(通信链路) and packet switches(分组交换机).
A packet switch takes a packet arriving on one of its incoming communication links and forwards that packet on one of its outgoing communication links. The two most prominent types in today’s Internet are routers and link-layer switches(交换机).
End systems access the Internet through Internet Service Providers (ISP,因特网服务提供商) .
End systems, packet switches, and other pieces of the Internet run protocols(协议) that control the sending and receiving of information within the Internet. The Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and the Internet Protocol (IP) are two of the most important protocols in the Internet.
Internet: “network of networks”
Service
End systems attached to the Internet provide a socket interface(套接字接口) that specifies how a program running on one end system asks the Internet infrastructure to deliver data to a specific destination program running on another end system.
QoS - Quality of Service:latency, bandwidth, bit-error-rate.
传输机会TXOP:每个站获得相同的传输时间,而不是相同数量的帧,解决速率异常(每个站点得到相同的平均数据率)
SDU服务数据单元:为完成用户所要求的功能而应传送的数据。
PCI协议控制信息:控制协议操作的信息。
PDU协议数据单元:该层同层之间传送的数据单位。(如网络层是包)
协议
A protocol defines the format and the order of messages exchanged between two or more communicating entities, as well as the actions taken on the transmission and/or receipt of a message or other event.
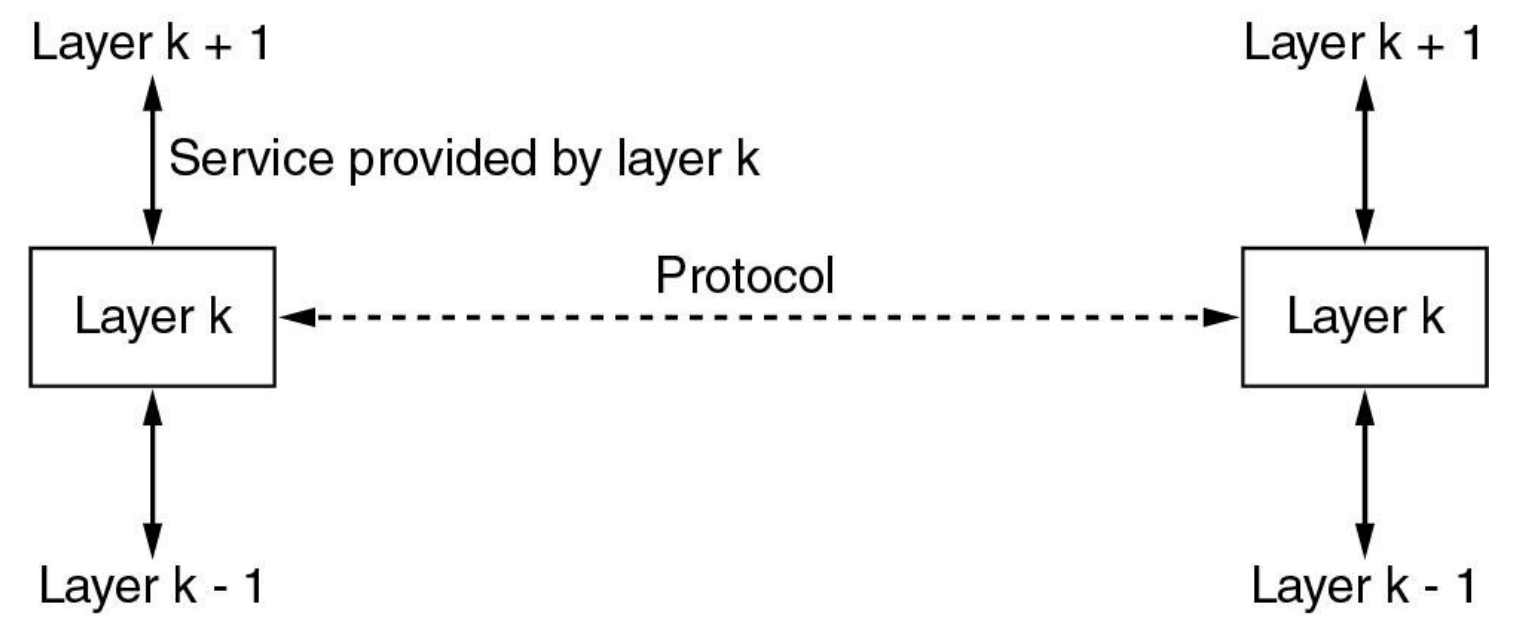
The Network Edge
End systems are also referred to as hosts because they host(主机) (that is, run) application programs.
host = end system. Hosts are sometimes further divided into two categories: clients and servers.
Access Networks
Home Access: DSL, Cable, FTTH, and 5G Fixed Wireless
The two most prevalent types of broadband residential access are digital subscriber line (DSL,数字用户线) and cable(电缆)。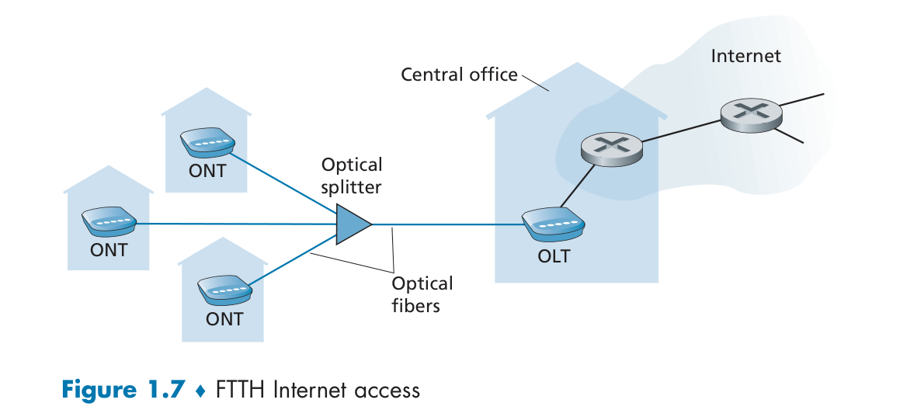
5G fixed wireless not only promises high-speed residential access, but will do so without installing costly and failure-prone cabling from the telco’s CO to the home.
Access in the Enterprise (and the Home): Ethernet and WiFi
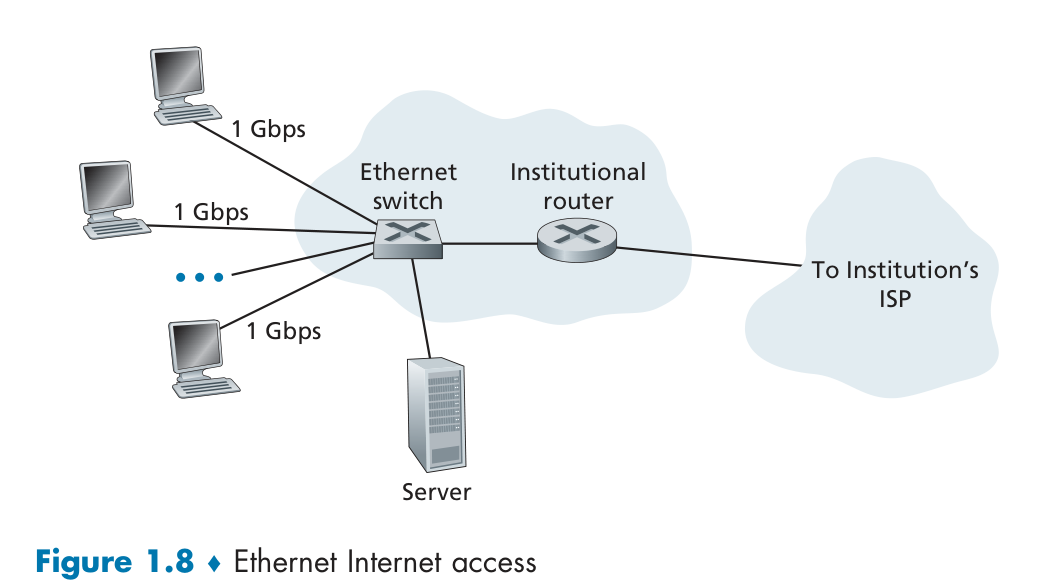
802.11 today provides a shared transmission rate of up to more than 100 Mbps.
Wide-Area Wireless Access: 3G and LTE 4G and 5G
Physical Media
For each transmitter-receiver pair,the bit is sent by propagating electromagnetic waves or optical pulses across a physical medium(物理媒介). Physical media fall into two categories: guided media(导引型媒介) and unguided media.
双绞线(TP):最常用的传输介质, 两根相互绝缘的铜线绞合,既可用于传输模拟信号也可用于传输数字信号。目前常用五类线。速度可达Mb/s
同轴电缆:更好的屏蔽特性和更大的带宽(3类 UTP: 16MHz;5类 UTP: 100MHz)。50欧姆电缆:常用于数字传输;75欧姆电缆:一般用于模拟传输和有线电视传输
光纤:有三种模式...
The Network Core
Packet Switching(分组交换)
在同一条传输线路上允许同时传输多个分组,也就是说分组交换不需要占用传输线路。
数据报方式:hosts break application-layer messages into packets (small, with header and footer). Between source and destination, each packet travels through communication links and packet switches (two predominant types: routers and link-layer switches). 提供无连接服务。
虚电路方式:维护虚电路表,提供网络层服务。要求设备高可靠。
Store-and-Forward Transmission(存储转发传输)
也称作报文交换。Entire packet must arrive at router before it can be transmitted on next link.
Forwarding is the local action of moving arriving packets from router’s input link to appropriate router output link, while routing is the global action of determining the source-destination paths taken by packets.
中继转发时可以动态分配线路,利用率高,实时性差(特别是大包可能会填满缓冲区),只适用于数字信号。
Circuit Switching(电路交换)
In packet-switched networks, resources are not reserved; a session’s messages use the resources on demand and, as a consequence, may have to wait (that is, queue) for access to a communication link. Congestion loss and variable end-end delays are possible with this technique. 电路交换需要建立一条专用的物理链路,对线路的利用率很低。
Which of the characteristics below are associated with the technique of circuit switching?
Reserves resources needed for a call from source to destination.
Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) and Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) are two approaches for implementing this technique.
Performance
Delay
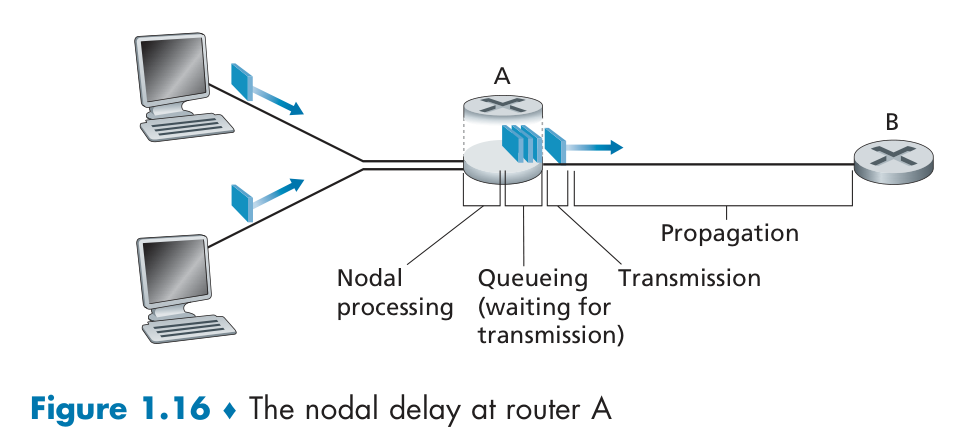
dnodal = dproc + dqueue + dtrans + dprop
分组在路由器的输入队列和输出队列中排队等待的时间,取决于网络当前的通信量。
主机或路由器收到分组时进行处理需要时间
主机或路由器传输数据帧所需要的时间。
电磁波在信道中传播所需要花费的时间。
Packet Loss
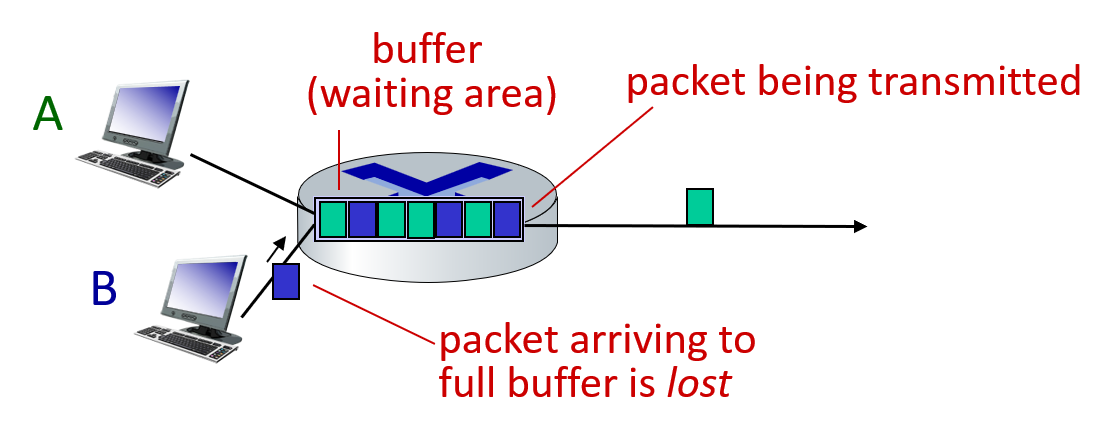
Throughput
throughput: rate (bits/time unit) at which bits are being sent from sender to receiver.
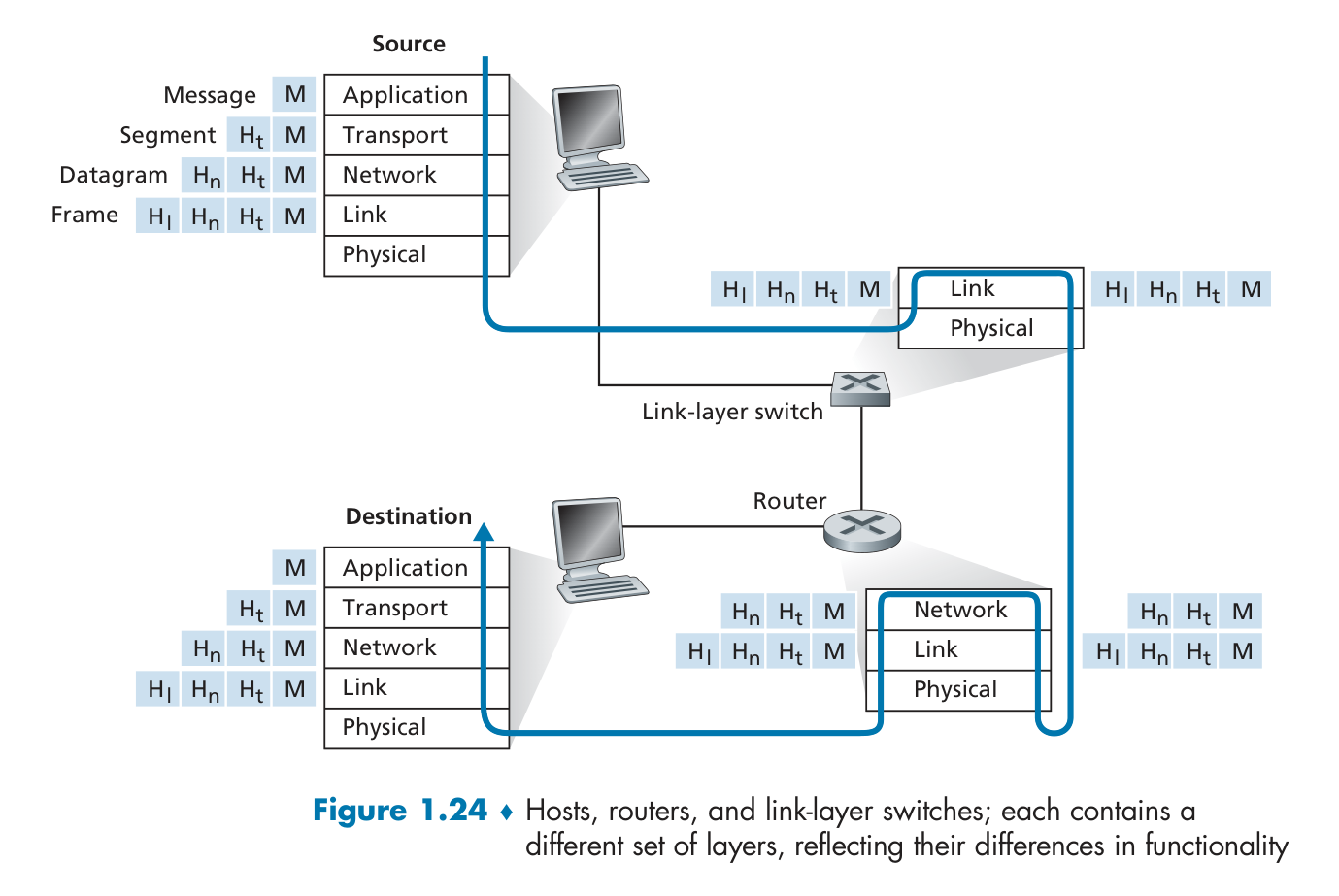
Protocol Layers and Service Models
Protocal Layers
Application
exchanges messages(报文) to implement some application service
HTTP, IMAP, SMTP, DNS
Transport
protocol creates segment and transfers M from one process to another
TCP, UDP
network
transfers datagram and transport-layer segment [Ht \ M] from one host to another
routing protocols,IP
link
creates frame and transfers datagram [Hn[Ht\M] from host to neighboring host, using network-layer services
Ethernet, 802.11 (WiFi), PPP
physical
bits “on the wire”
Models
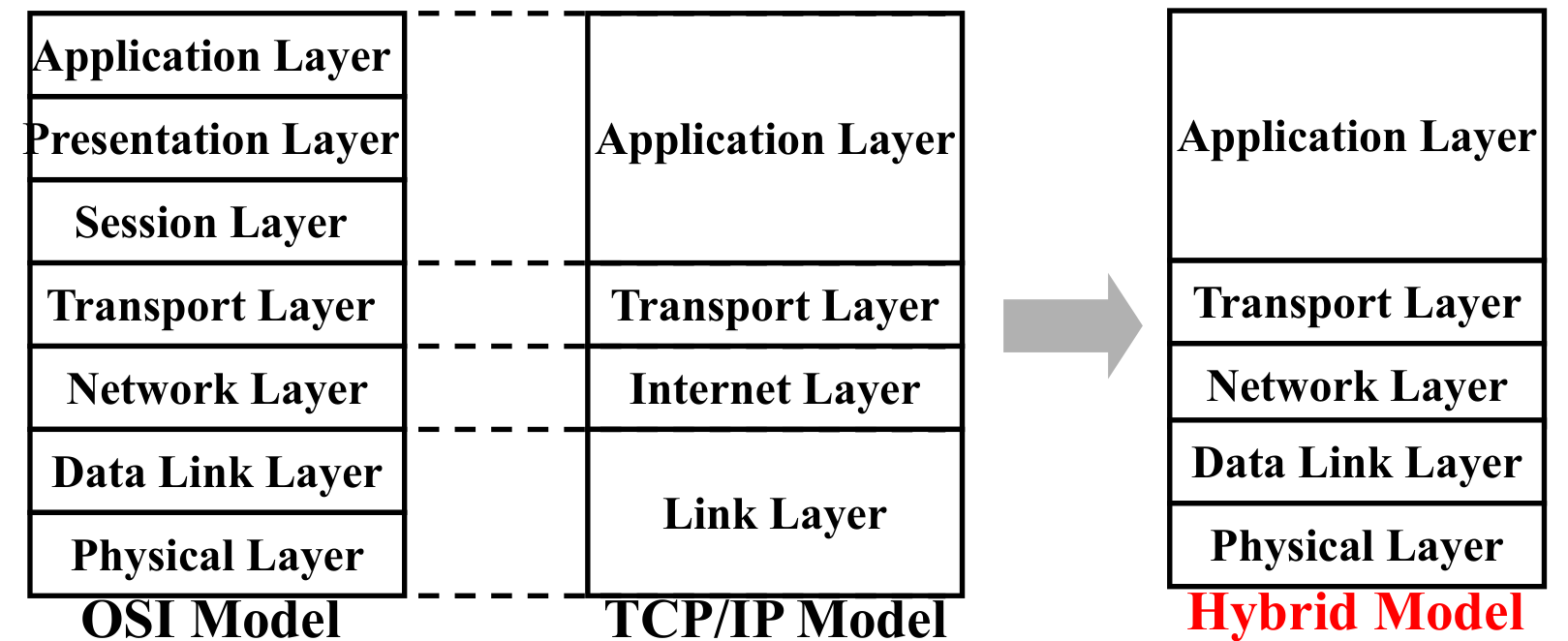
In OSI Model:
presentation: allow applications to interpret meaning of data, e.g., encryption, compression, machine-specific conventions
session: synchronization, checkpointing, recovery of data exchange
访问一个网页的全流程
DHCP: Client now has IP address, knows name & addr of DNS server, IP address of its first-hop router
ARP:To send frame to first-hop router, need MAC address of router interface.
DNS:IP datagram may forwarded, routed (tables created by RIP, OSPF, IS-IS and/or BGP routing protocols) to DNS server
HTTP:mention that client first opens TCP socket to web server
web server responds with HTTP reply (containing web page). DONE!!
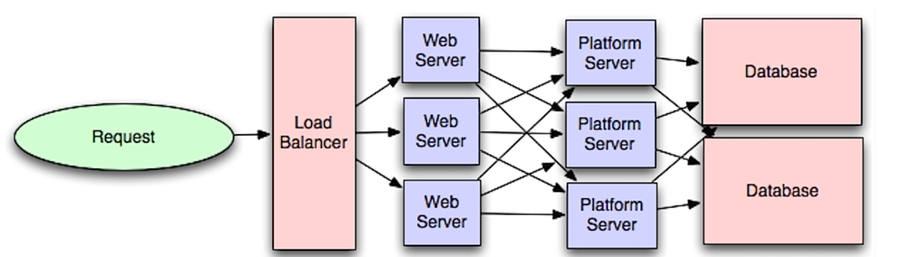
将 Web 服务层与应用层(也被称作平台层)分离,可以独立缩放和配置这两层。添加新的 API 只需要添加应用服务器,而不必添加额外的 web 服务器。
CDN
内容分发网络(CDN)是一个全球性的代理服务器分布式网络,它从靠近用户的位置提供内容。通常,HTML/CSS/JS,图片和视频等静态内容由 CDN 提供,CDN 的 DNS 解析会告知客户端连接哪台服务器。
当你服务器上内容发生变动时,推送 CDN 接受新内容。直接推送给 CDN 并重写 URL 地址以指向你的内容的 CDN 地址。你可以配置内容到期时间及何时更新(TTL)。流量最小化,但储存最大化。
CDN 拉取 是当第一个用户请求该资源时,从服务器上拉取资源。你将内容留在自己的服务器上并重写 URL 指向 CDN 地址,直到内容被缓存在 CDN 上为止。只有最近请求的内容保存在 CDN 中,流量才能更平衡地分散。
[[TDch2-3 Application&TransportLayer]]
参考:
最后更新于