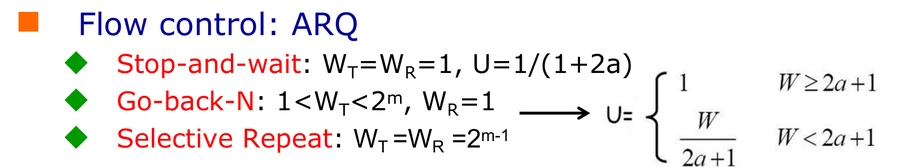应用层-传输层
Application Layer
Principles of Network Applications
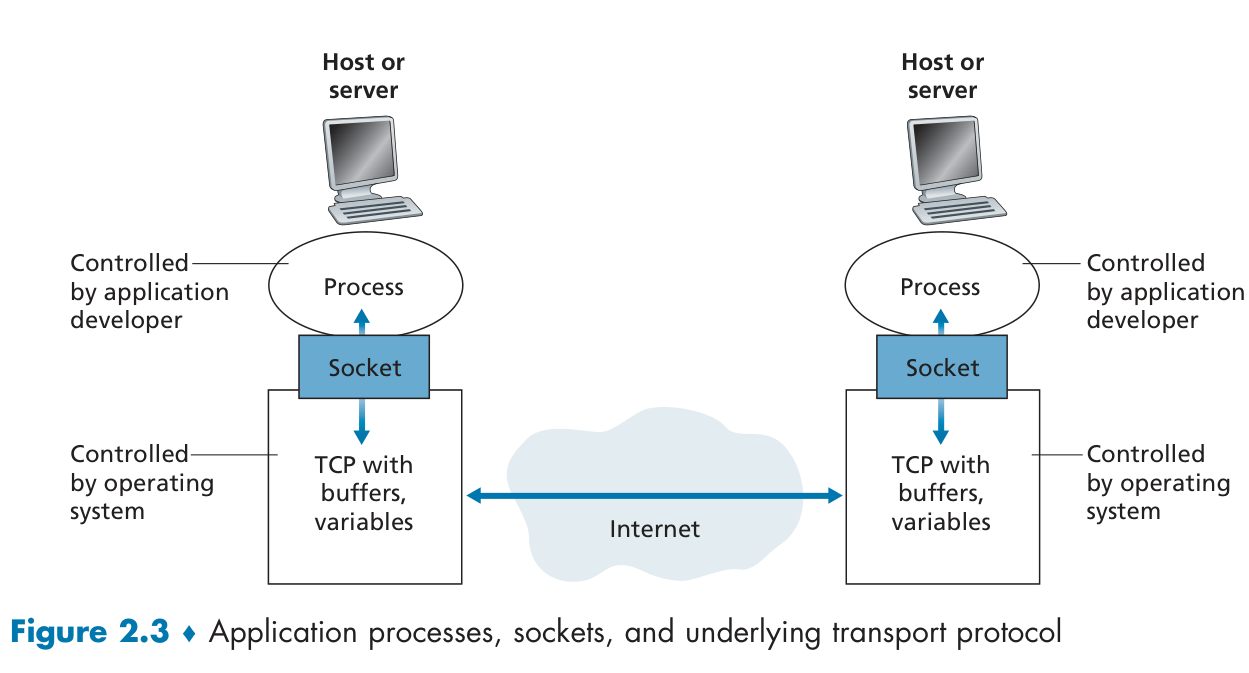
进行通信的双方都是进程 。
Socket(套接字)是应用程序和网络之间的应用程序编程接口(API).
Web Http
Non-persistent HTTP
RTT(round-trip time) : time for a small packet to travel from client to server and back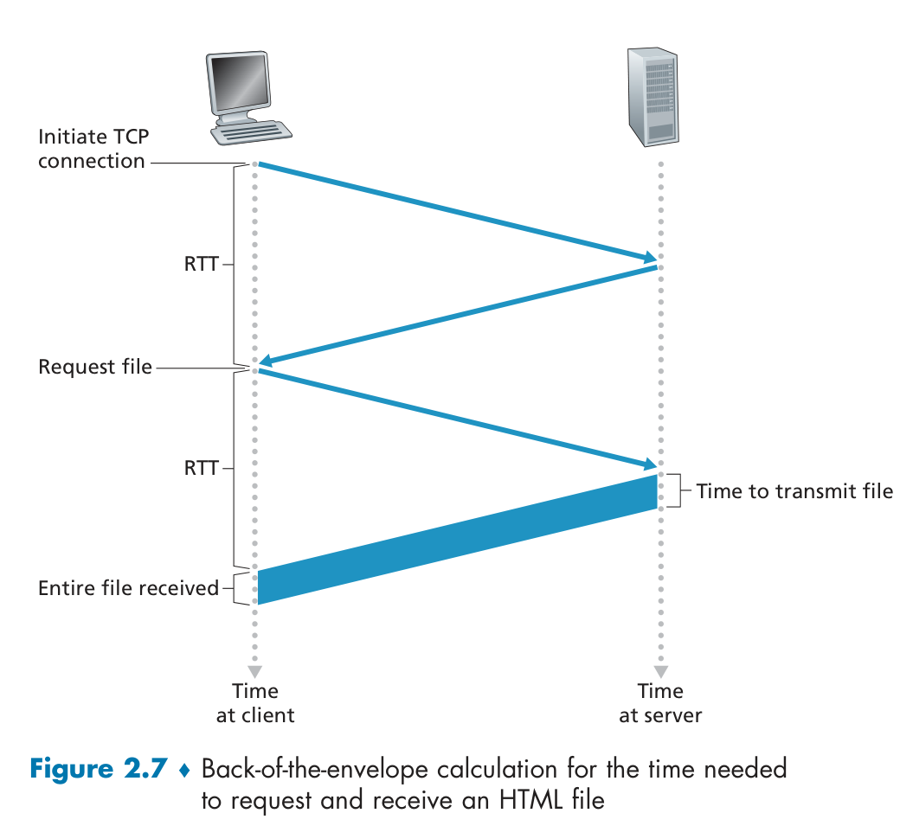
Persistent(HTTP1.1): introduced multiple, pipelined GETs over single TCP connection. Subsequent requests and responses between the same client and server can be sent over the same connection.
HTTP 通信时,除客户端和服务器以外,还有一些用于通信数据转发的应用程序配合服务器工作。
代理:接收由客户端发送的请求并转发给服务器,接收服务器返回的响应并转发给客户端。
网关:转发其他服务器通信数据的服务器,就像自己拥有资源的源服务器一样处理请求。
隧道:是在客户端和服务器两者之间进行中转,并保持双方通信连接。
HTTP Method
GET
user input sent from client to server in entity body of POST request message
POST
include user data in URL field of HTTP GET request message (following a ‘?’),语义是请求服务器处理指定资源
HEAD
requests headers (only,不返回报文主体) that would be returned if specified URL were requested with an HTTP GET method.
PUT
uploads new file (object) to server;completely replaces file that exists at specified URL with content in entity body of POST HTTP request message
DELETE
allows a user, or an application, to delete an object on a Web server.
状态码

Cookies
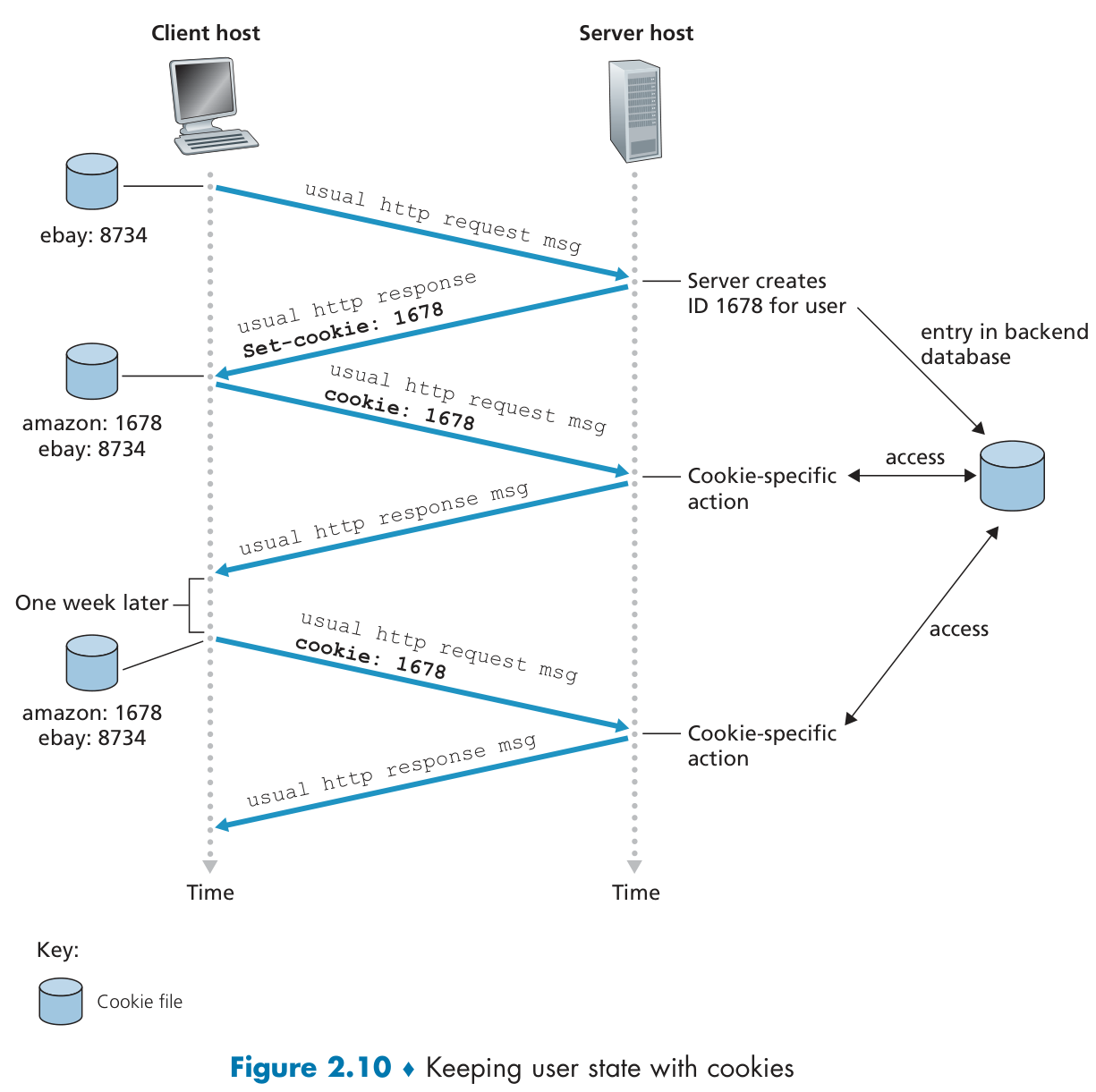
Cookies can be used to:
track user behavior on a given website (first party cookies)
track user behavior across multiple websites (third party cookies,第三方cookies) without user ever choosing to visit tracker site.
eg. Referer to ad host.
Web caches
HTTP GET/response interaction is stateless:
HTTP server does not remember anything about what happened during earlier steps in interacting with this HTTP client.
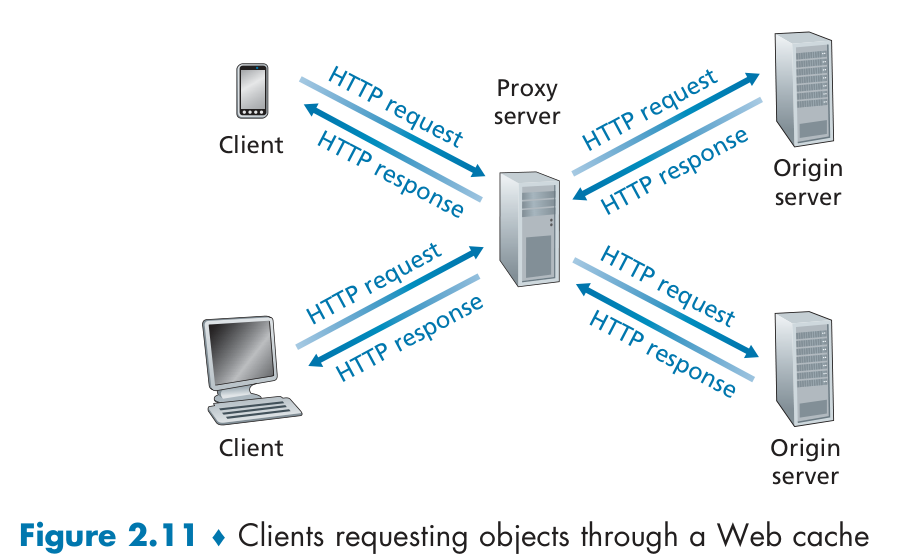
Web Cache is also called proxy server.
HTTP/2
HTTP/2: increased flexibility at server in sending objects to client:
transmission order of requested objects based on client-specified object priority.
divide objects into frames, schedule frames to mitigate HOL(Head Of Line) blocking
head-of-line (HOL) blocking: small object may have to wait for transmission behind large object(s):因为 TCP 是字节流协议,TCP 层必须保证收到的字节数据是完整且有序的,如果序列号较低的 TCP 段在网络传输中丢失了,即使序列号较高的 TCP 段已经被接收了,应用层也无法从内核中读取到这部分数据,从 HTTP 视角看,就是请求被阻塞了。
HTTP1.1: introduced multiple, pipelined GETs over single TCP connection
HTTP2: transmission order of requested objects based on client-specified object priority (not necessarily FCFS)
E-mail
一个电子邮件系统由三部分组成:用户代理、邮件服务器以及邮件协议。 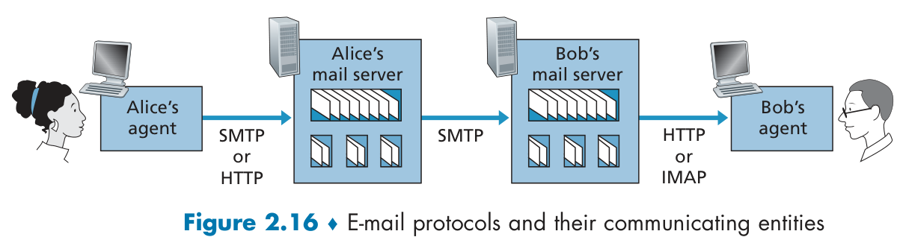
mail servers
mailbox contains incoming messages for user
message queue of outgoing (to be sent) mail message
邮件协议包含发送协议和读取协议,发送协议常用 SMTP,读取协议常用 POP3 和 IMAP。
SMTP vs HTTP:
HTTP: client pull | SMTP: client push
both have ASCII command/response interaction, status codes
HTTP: each object encapsulated in its own response message
SMTP: multiple objects sent in multipart message
SMTP uses persistent connections
SMTP requires message (header & body) to be in 7-bit ASCII
SMTP server uses CRLF to determine end of message
两种扇出模型:写扇出(也称为推模型)和读扇出(也称为拉模型)。
SMTP 只能发送 ASCII 码,而互联网邮件扩充 MIME 可以发送二进制文件。POP3 的特点是只要用户从服务器上读取了邮件,就把该邮件删除。但最新版本的 POP3 可以不删除邮件。IMAP 协议中客户端和服务器上的邮件保持同步,如果不手动删除邮件,那么服务器上的邮件也不会被删除。
DNS
How DNS works?
TLD:Top-level domain.
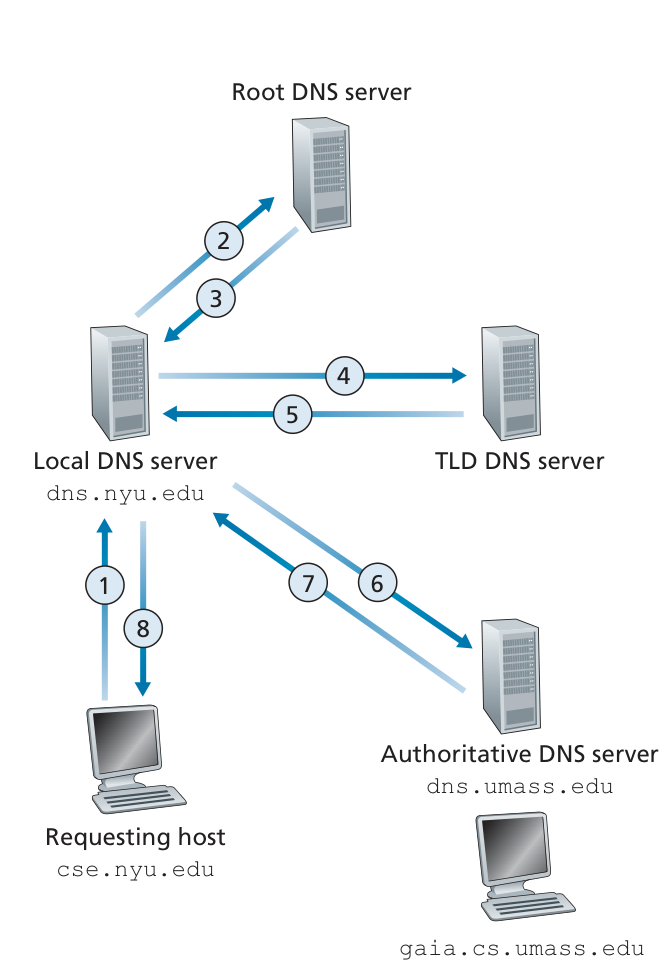
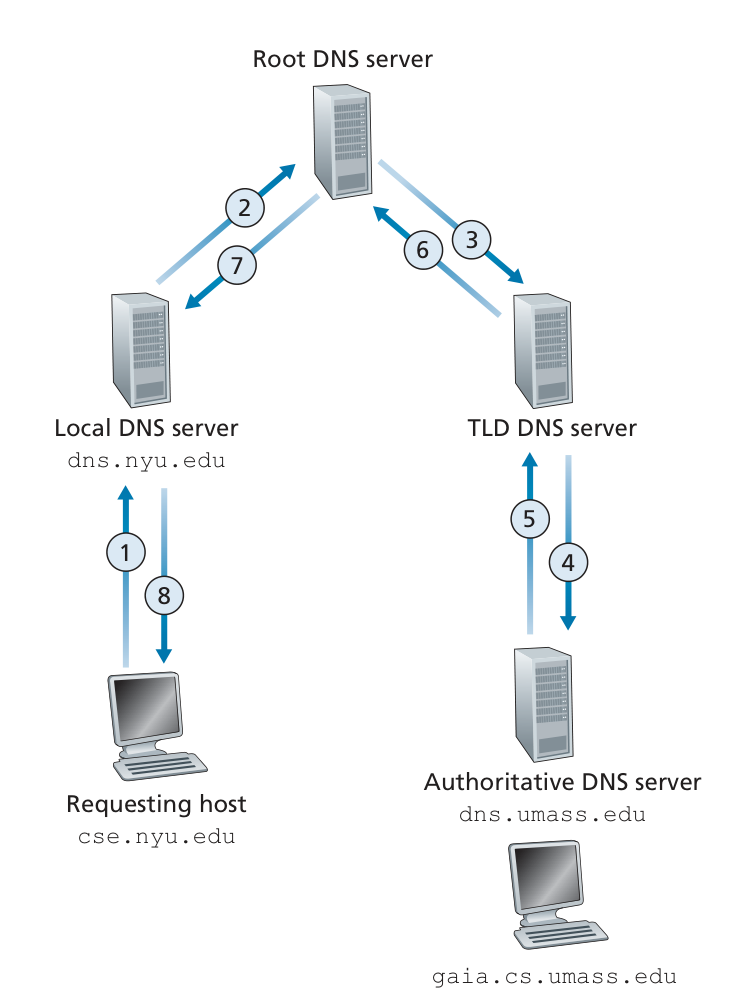
the local DNS server may be on the same LAN as the host; for a residential ISP, it is typically separated from the host by no more than a few routers.
DNS records
(Name, Value, Type, TTL). TTL is the time to live of the resource record.
A
name is hostname ; value is IP address
NS
name is domain ; value is hostname of authoritative name server for this domain
CNAME
name is alias name for some “canonical” (the real) name; value is canonical name
MX
value is name of SMTP mail server associated with name
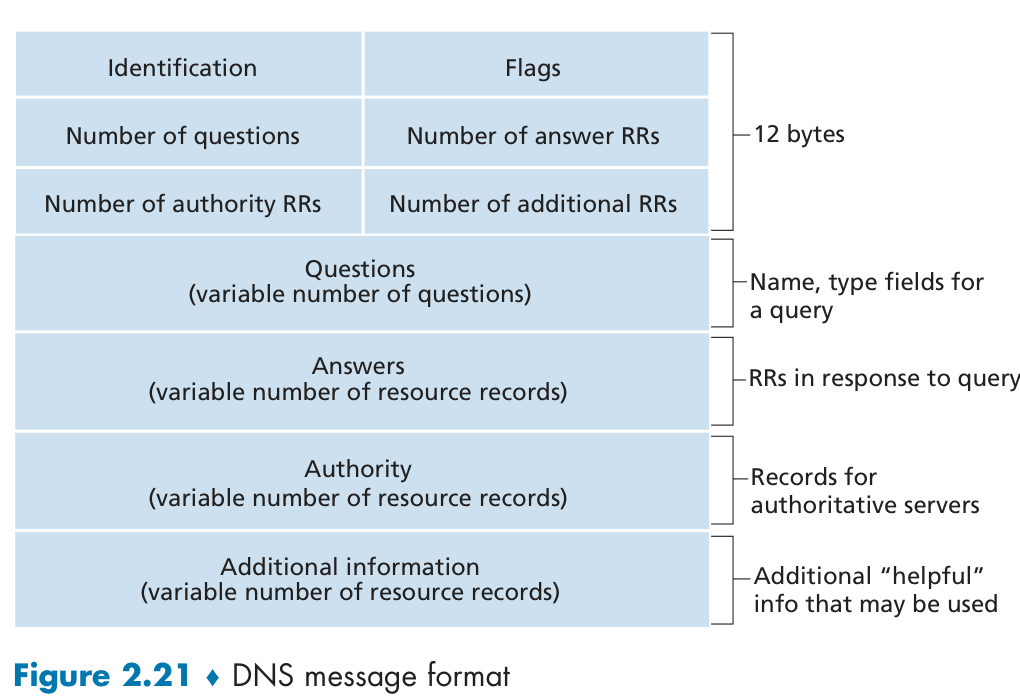
DNS使用什么协议进行传输?
进行区域传送时使用TCP;域名解析时一般使用UDP协议,负载低、响应快、包体小(部分DNS也可以使用TCP,DNS同时占用UDP和TCP端口53)
某些 DNS 服务通过集中方式来路由流量:
防止流量进入维护中的服务器
在不同大小集群间负载均衡
A/B 测试
基于延迟路由
基于地理位置路由
P2P
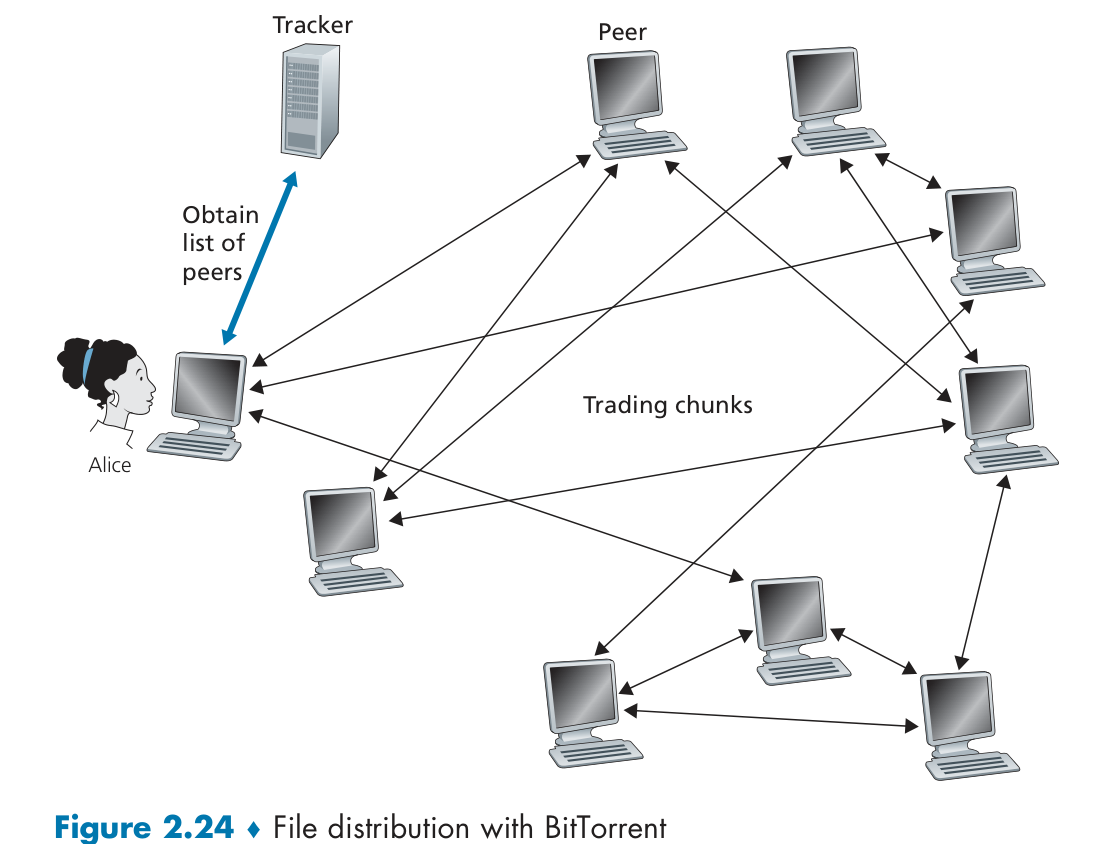
Each torrent has an infrastructure node called a tracker. In deciding which chunks to request, requesting chunks uses a technique called rarest first.
Sending chunks: tit-for-tat, randomly select another peer, starts sending chunks every 30 secs.
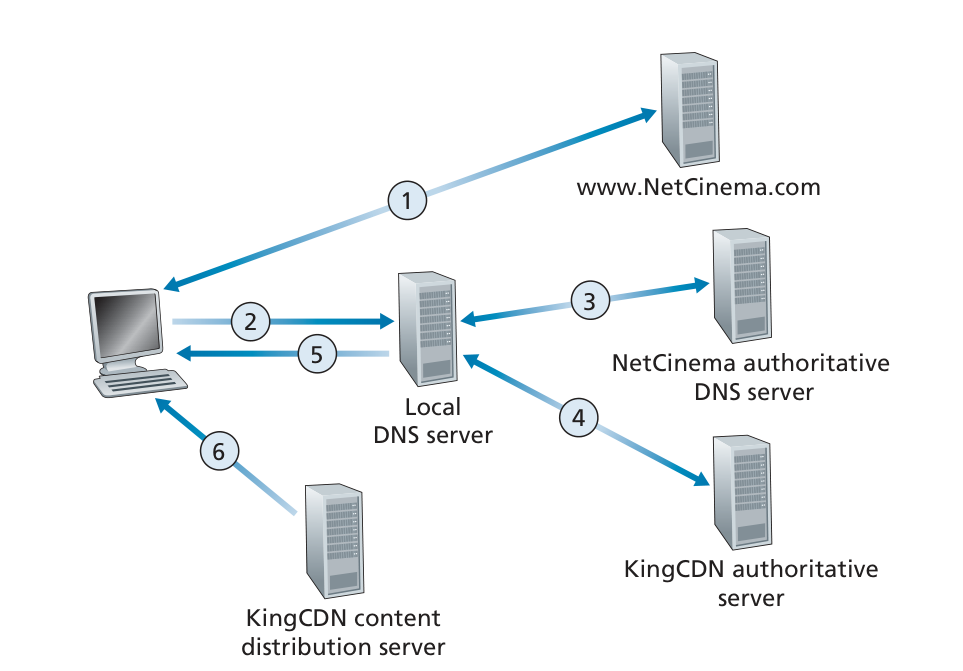
Video Streaming
Streaming video = encoding + DASH + playout buffering
DASH:Dynamic, Adaptive Streaming over HTTP
CDN:内容分发网。store/serve multiple copies of videos at multiple geographically distributed sites.
HTTPS = HTTP+加密+认证+完整性保护
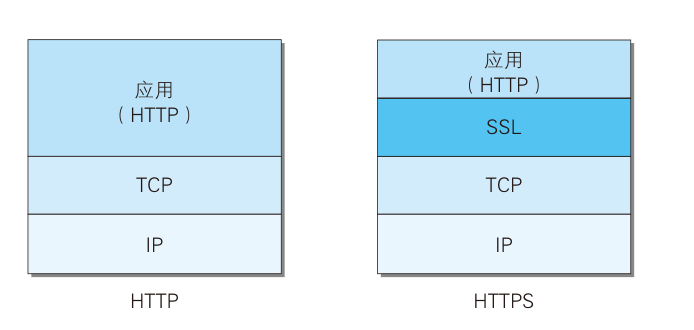
TCP/IP是可能被窃听的网络。HTTP 协议中没有加密机制(明文),加密处理可防止被窃听。加密的对象有:
通信加密。可以通过和 SSL(Secure Socket Layer,安全套接层)或 TLS(Transport Layer Security,安全层传输协议)的组合使用,加密 HTTP 的通信内容。
将通信内容本身加密。把 HTTP 报文里所含的内容进行加密处理。根据密文和公钥,解密原文是技术不支持的。
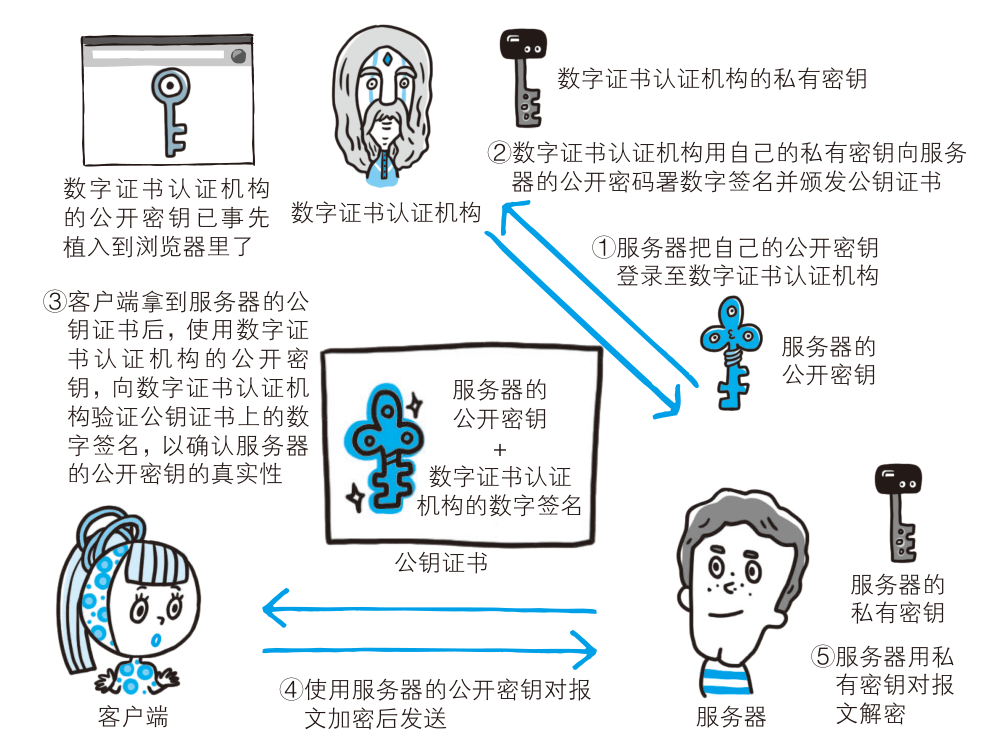
HTTP无法验证通信方的身份,可能遭遇伪装。SSL 还提供了证书,由第三方权威机构CA颁发。
HTTP 协议无法证明通信的报文完整性,常用的是 MD5 和 SHA-1 等散列值校验是否篡改。
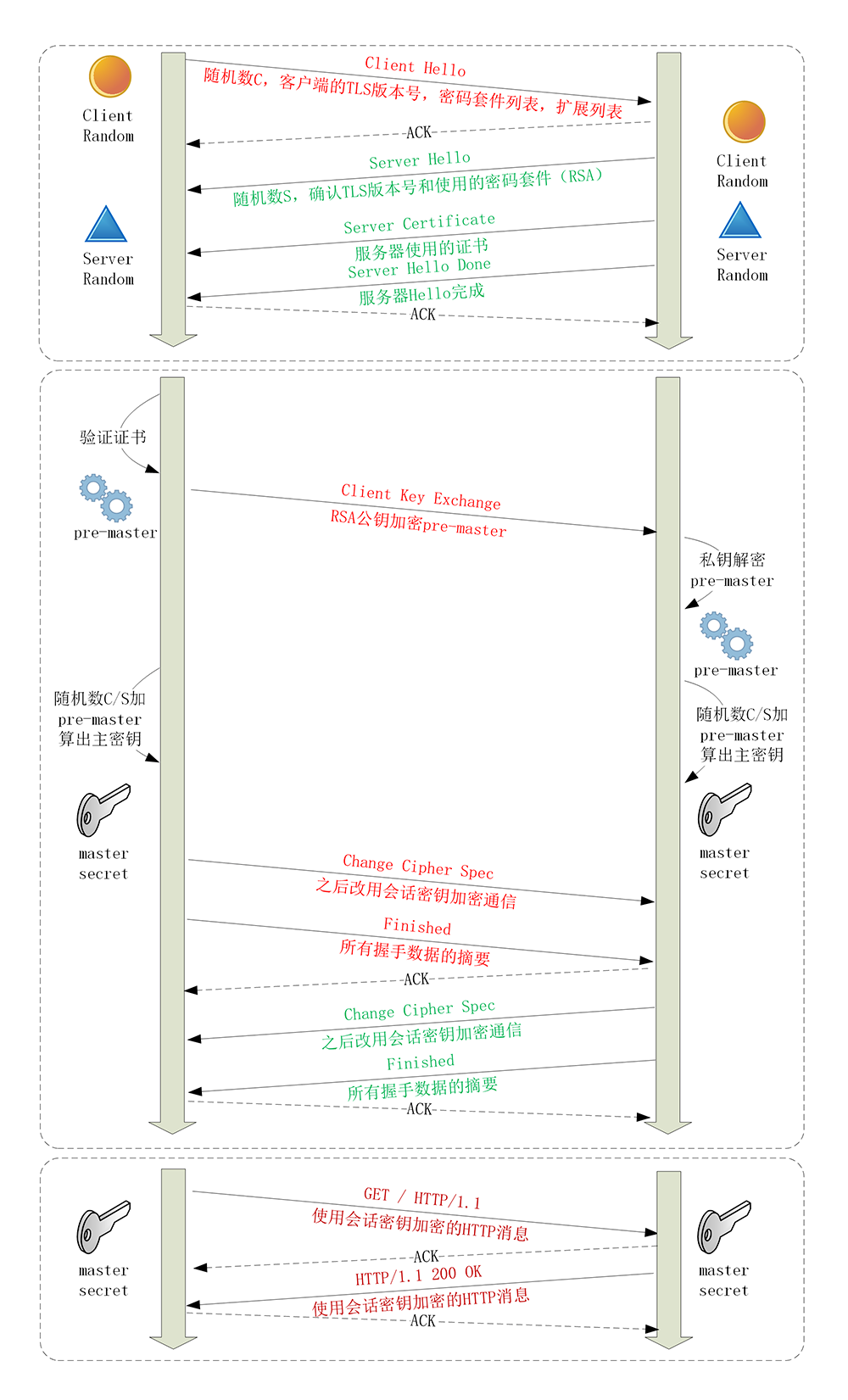
TLS1.2
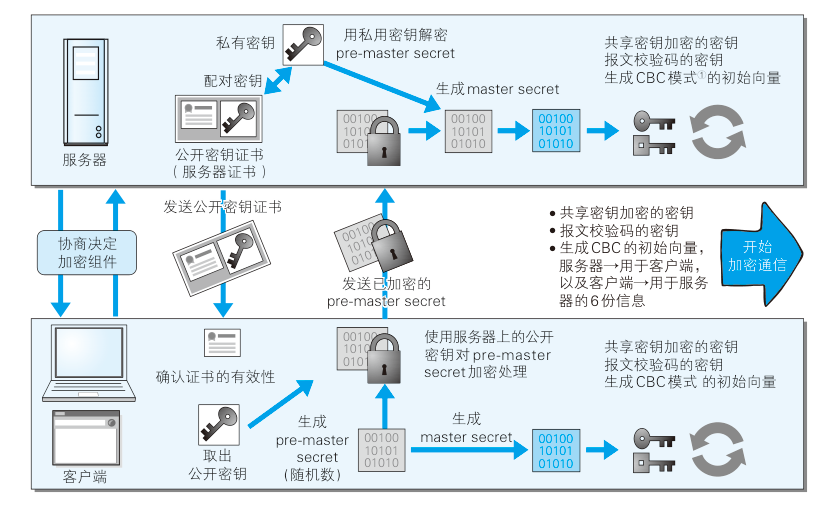
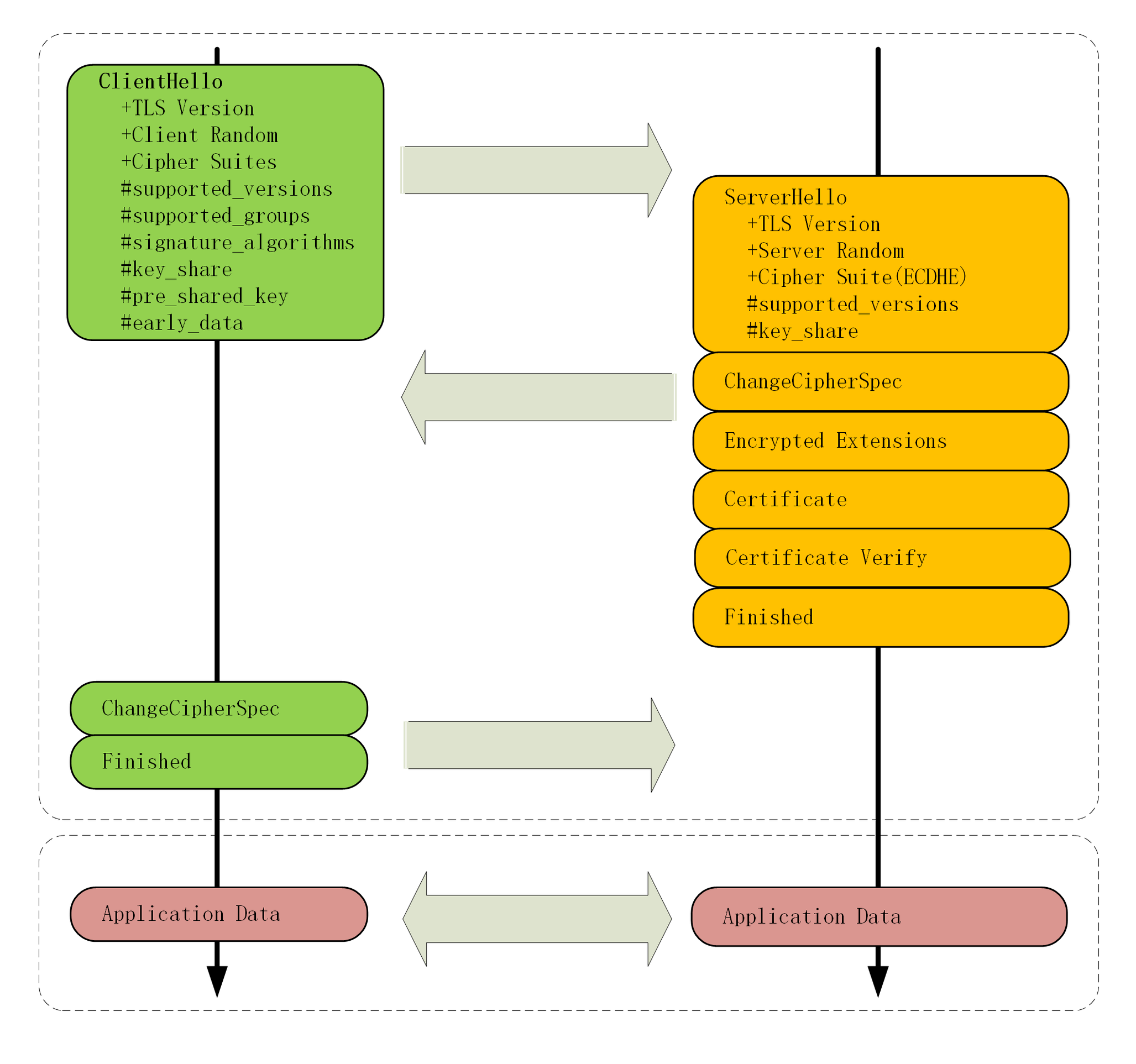
如下图:
客户端发送 C(第一随机数)
服务端发送 S(第二随机数)、CA、公钥
客户端验证证书,DH生成第三随机数(预主密钥),并进行公钥加密发送。
服务器私钥解密预主密钥,现在两方都有C、S、预主密钥,得到主密钥。
说白了,就是先交换了两个随机数,然后由加密算法,在不暴露第三随机数(除非私钥泄漏)的情况下,得到共识的主密钥。
TLS1.3
变化:先验证版本号是否支持拓展。若支持,客户端和服务器就拿到四个共享信息:Client Random和Server Random、Client Params和Server Params,两边就可以各自用 ECDHE(密钥交换算法)算出“Pre-Master”,再用 HKDF(伪随机数函数,HMAC-based Extract-and-Expand Key Derivation Function) 生成主密钥(Master Secret)。在后期的通信中,TLS1.3 里只保留了 AES、ChaCha20 对称加密算法。
认证
HTTP/1.1 使用的认证方式如下:
BASIC 认证(基本认证,extends HTTP/1)
其采用的 Base64 编码方式,不是加密处理,可直接解码;注销不灵活。
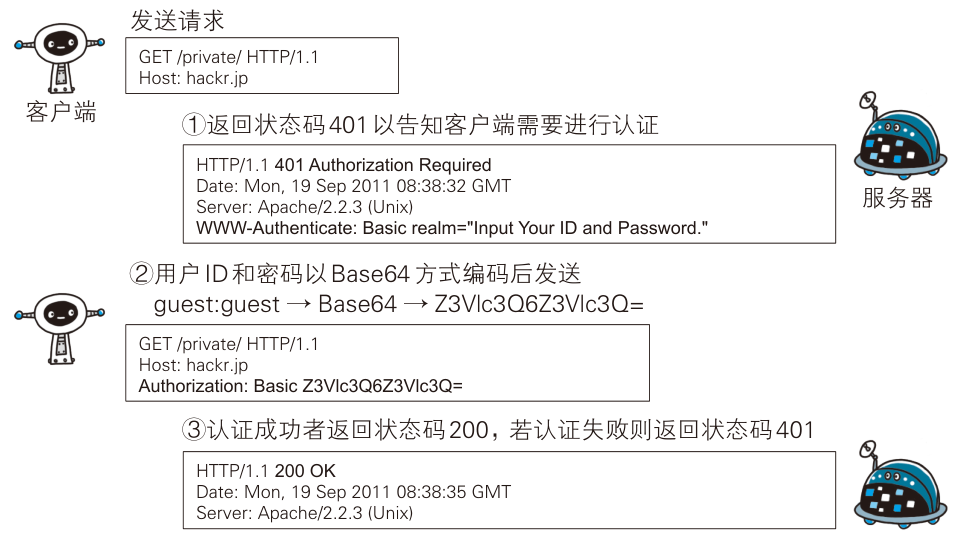
DIGEST 认证(摘要认证, from HTTP/1.1)
不存在防止用户伪装的保护机制,不灵活。

SSL 客户端认证(要钱)
双因素认证:认证过程中不仅需要密码这一个因素,还需要申请认证者提供其他持有信息。
需要事先将客户端证书分发给客户端,且客户端必须安装此证书领取证书内客户端的公钥。
FormBase 认证(基于表单认证,主流)
一般会使用 Cookie 来管理Session(会话)。
账户安全可分为两部分:
Identification:获取你的信息
Authenrazation:确定你有没有权限做这件事情
Transport Layer
Overview
A transport-layer protocol provides for logical communication between application processes running on different hosts, an application’s perspective. (Different network layer: logical communication between hosts)
Two principal Internet transport protocols:
TCP: Transmission Control Protocol
reliable, in-order delivery
congestion control: throttle sender when network overloaded
flow control: sender won't overwhelm receiver
connection-oriented: setup required between client and server processes
does not provide: timing, minimum throughput guarantee, security
UDP: User Datagram Protocol (unreliable between sending and receiving process)
unreliable, unordered delivery
no-frills extension of “best-effort” IP
does not provide: reliability, flow control, congestion control, timing, throughput guarantee, security, or connection setup.
TCP 是面向字节流的协议,UDP 是面向报文的协议. 前者:消息根据发送窗口、拥塞窗口以及当前发送缓冲区的大小等,可能会被分成多个的 TCP 报文,需要定义边界进行划分。 后者:每个 UDP 报文就是一个用户消息的边界。不会对消息进行拆分。
services not available:
delay guarantees
bandwidth guarantees
Multiplexing and Demultiplexing
Multiplexing, demultiplexing: based on segment, datagram header field values
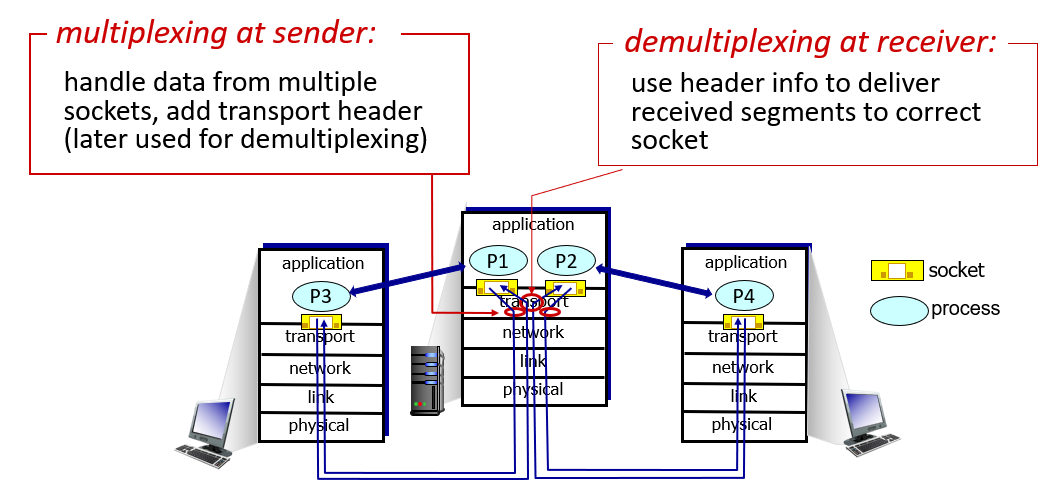
For Connectionless
a UDP socket is fully identified by a two-tuple consisting of a destination IP address and a destination port number.
IP/UDP datagrams with same dest port #, but different source IP addresses and/or source port numbers will be directed to same socket at receiving host.
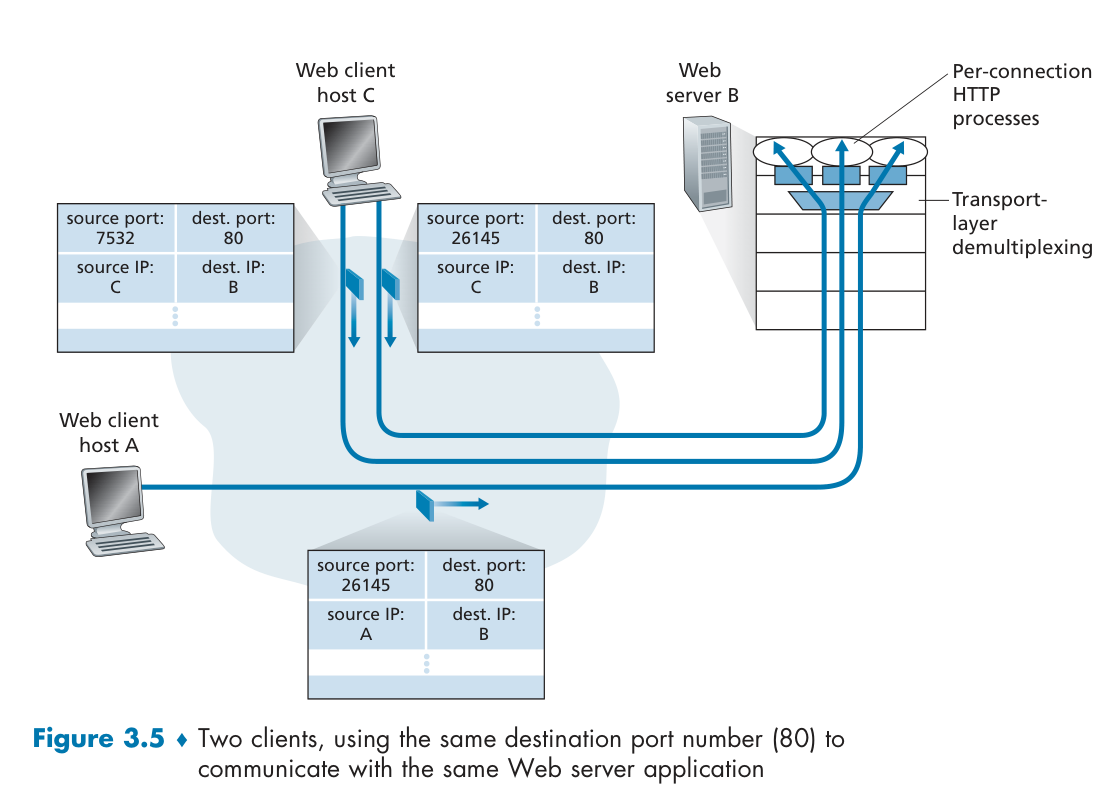
For Connection-Oriented
a TCP socket is identified by a four-tuple: (source IP address, source port number, destination IP address, destination port number). each socket associated with a different connecting client
UDP
UDP use: streaming multimedia apps (loss tolerant, rate sensitive),DNS,SNMP,HTTP/3
Why UDP?
Finer application-level control over what data is sent, and when.
No connection establishment.
No connection state.
Small packet header overhead.
UDP 可以通过广播将数据报发送至子网内的所有设备。这对 DHCP 很有用,因为子网内的设备还没有分配 IP 地址,而 IP 对于 TCP 是必须的。
Segment
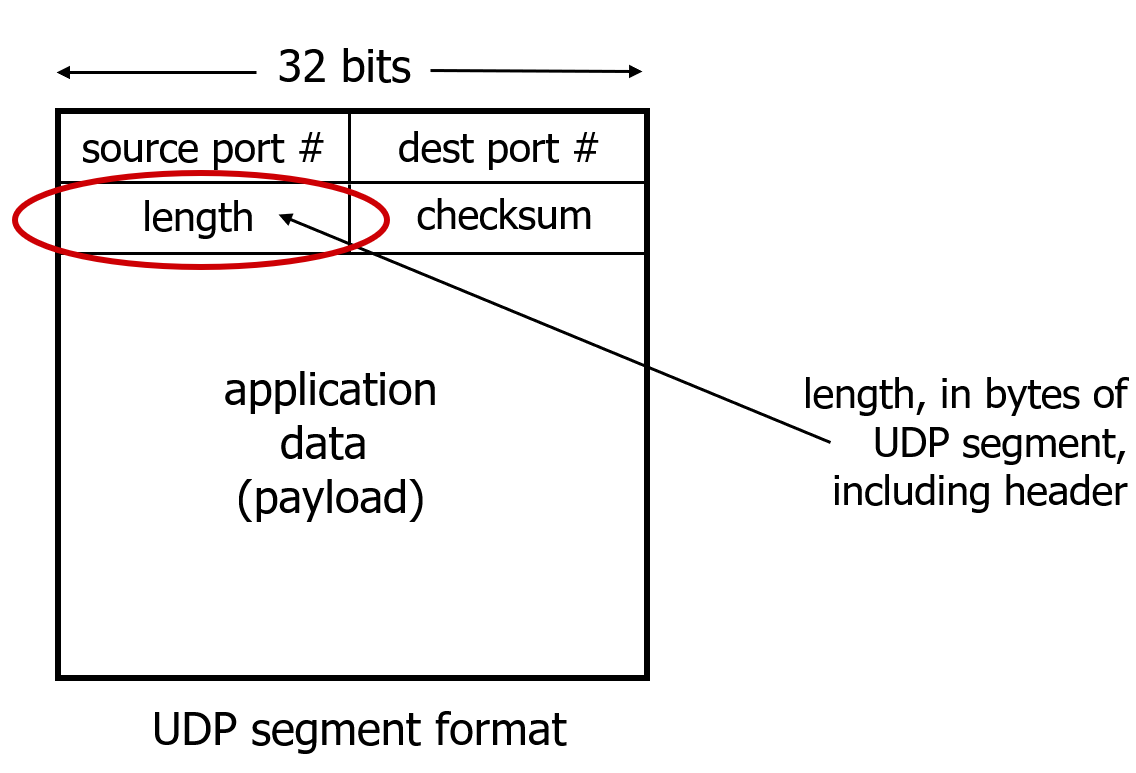
Checksum

At the receiver, all four 16-bit words are added, including the checksum. If no errors are introduced into the packet, then clearly the sum at the receiver will be 1111111111111111. If one of the bits is a 0, then we know that errors have been introduced into the packet.
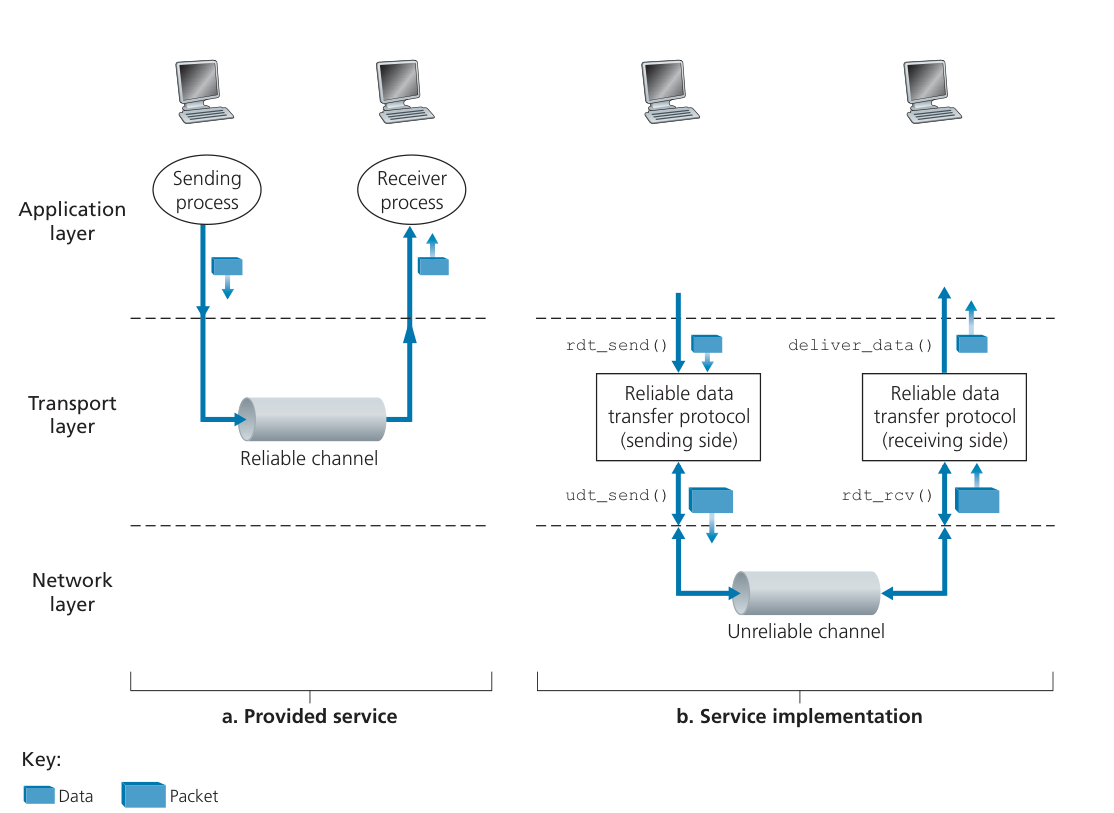
RDT(可靠数据传输)
本部分内容对应北邮PPT链路层的六个协议。
RDT2: channel with Bit Errors
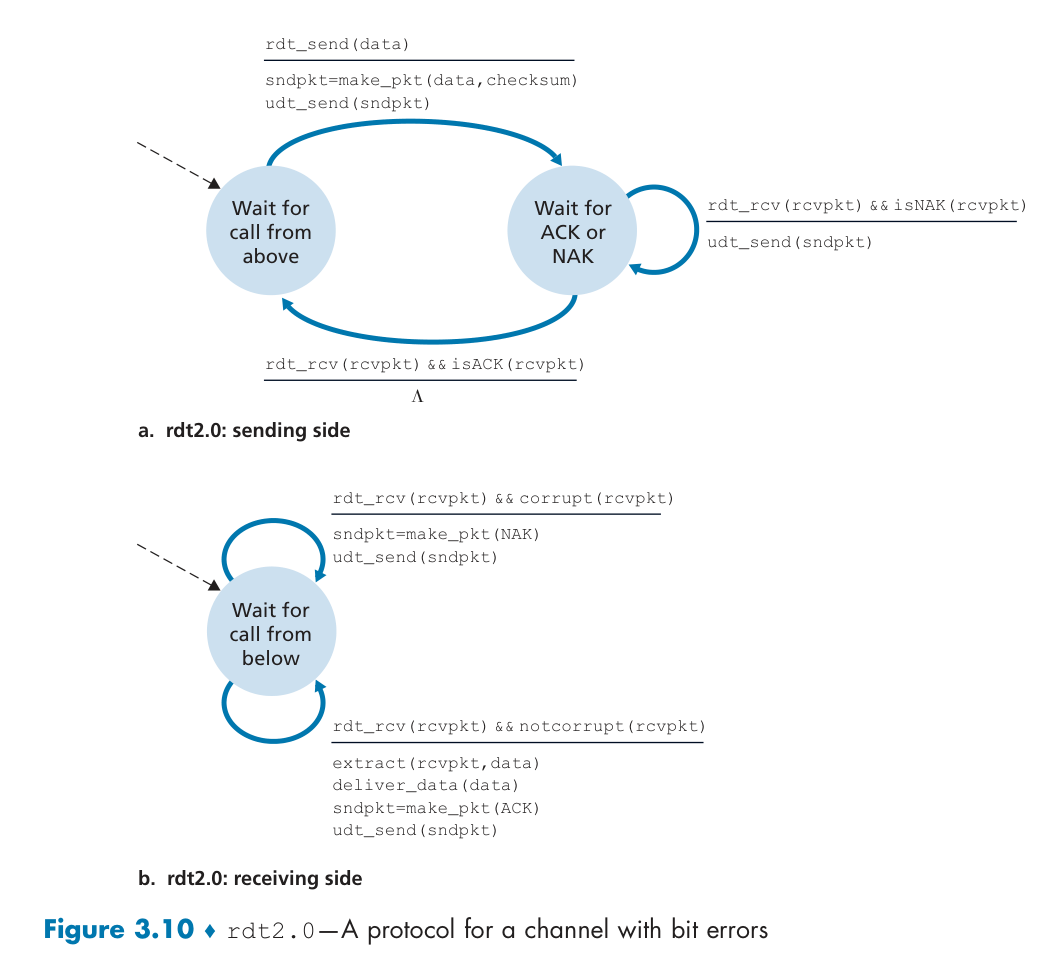
what happens if ACK/NAK corrupted?
retransmit? receiver cannot know - an arriving packet contains new data or is a retransmission.
RDT2.1 Data with sequence number.
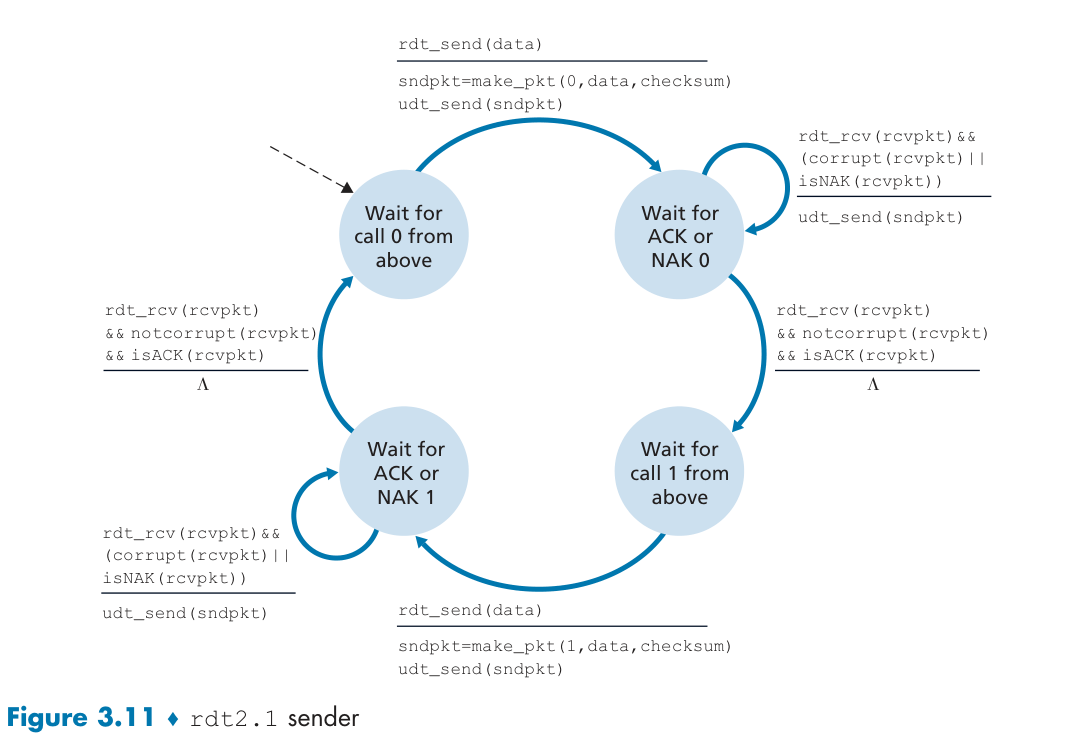
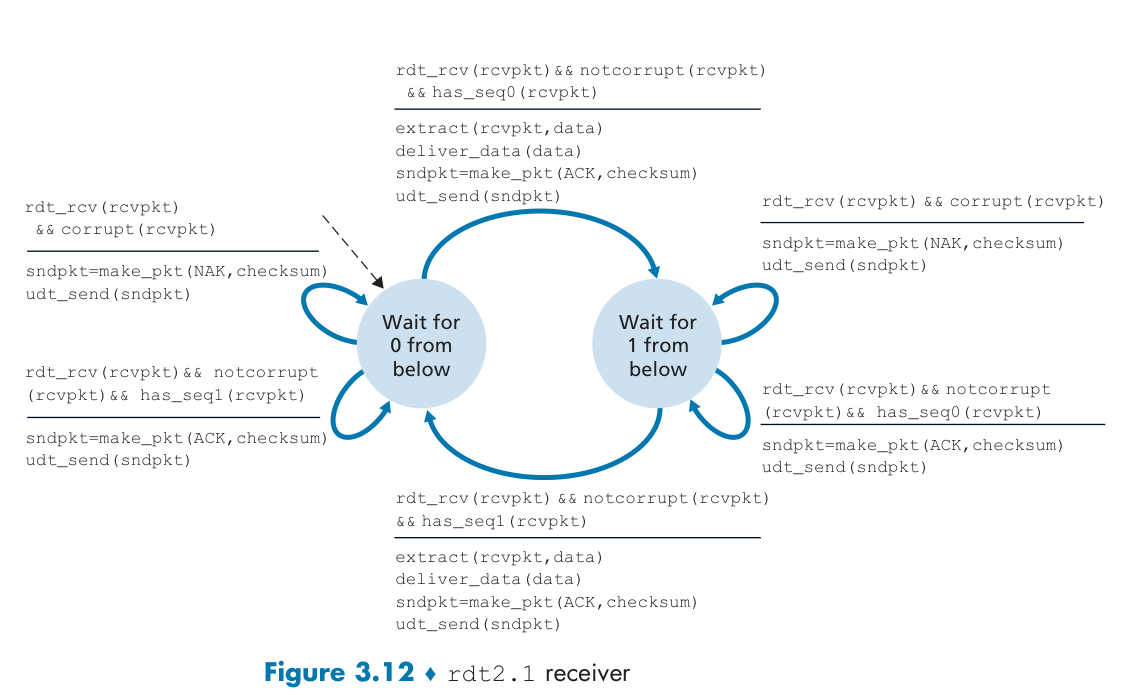
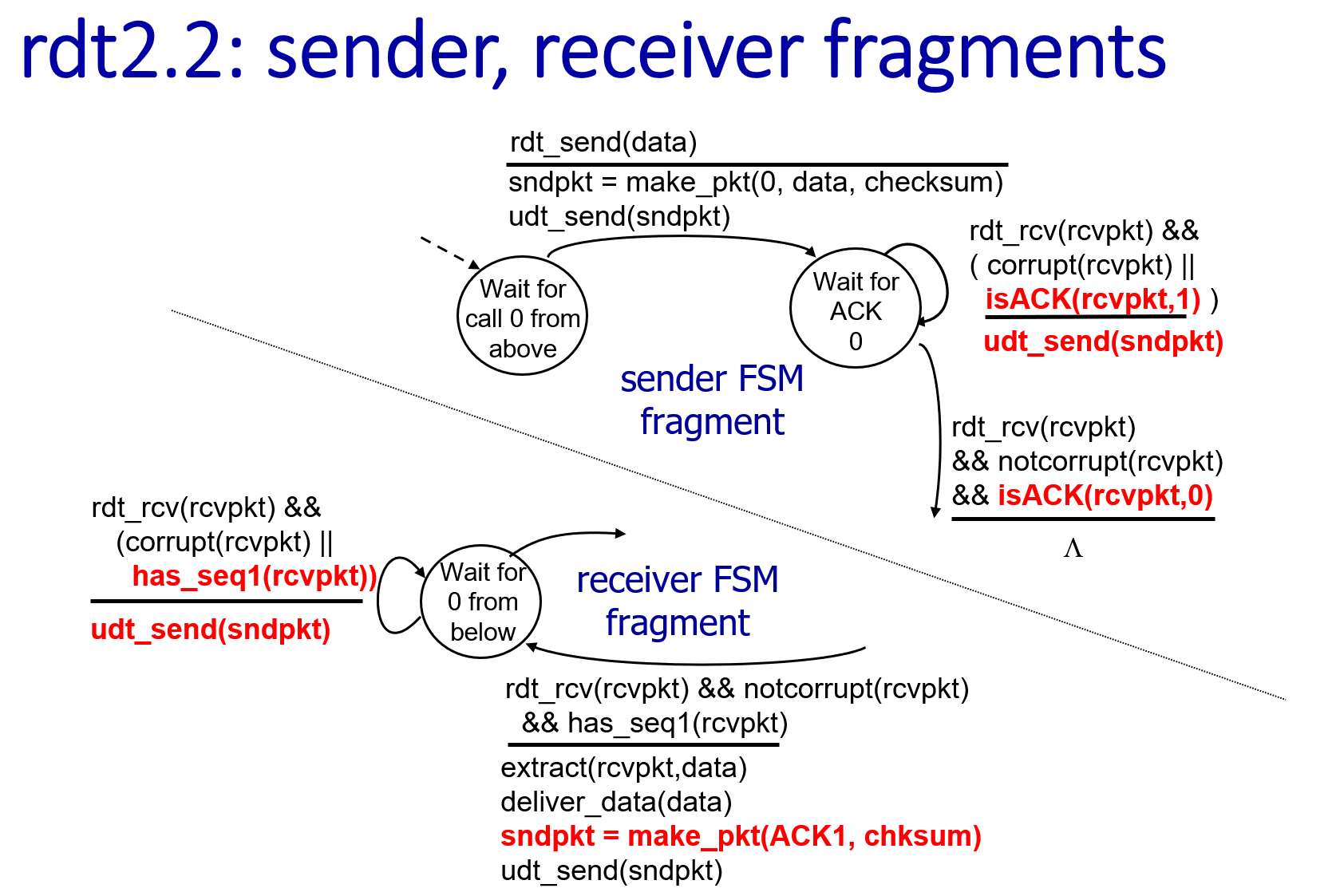
RDT2.2: use ACKs only.
duplicate ACK at sender results in same action as NAK.
RDT3:channel with errors and loss
Implementing a time-based retransmission mechanism requires a countdown timer that can interrupt the sender after a given amount of time has expired.
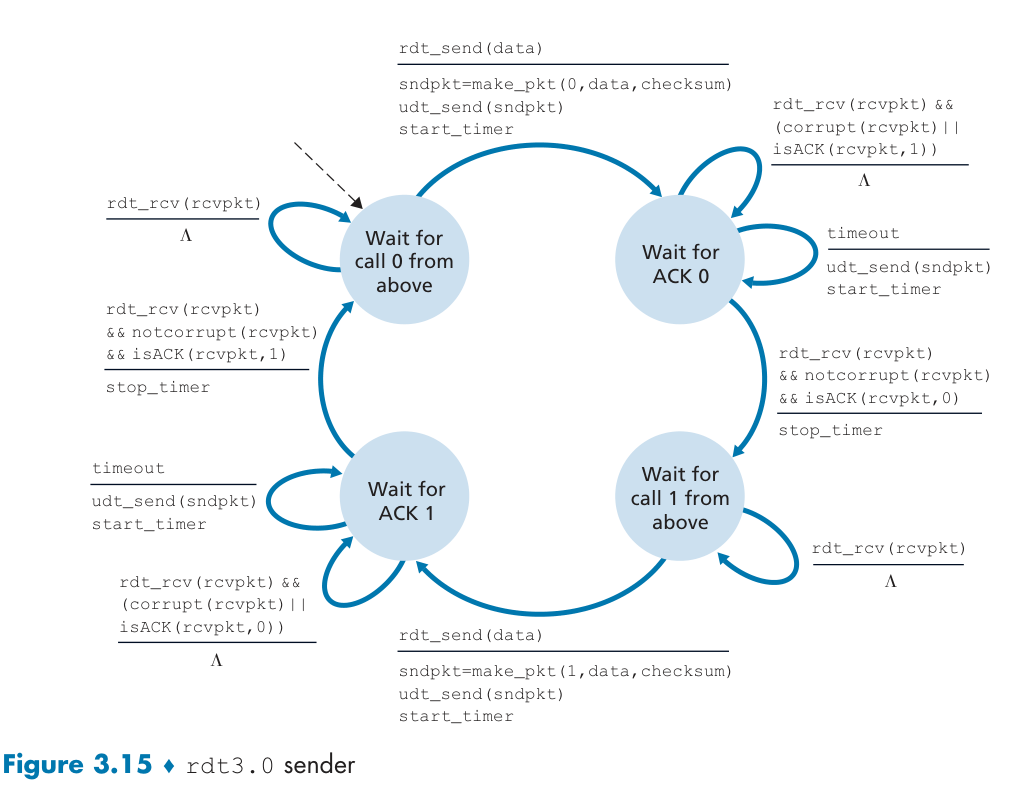
这依旧是一个 stop-and-wait 协议,带宽利用率(性能)不高。
Pipelined Reliable Data Transfer Protocols
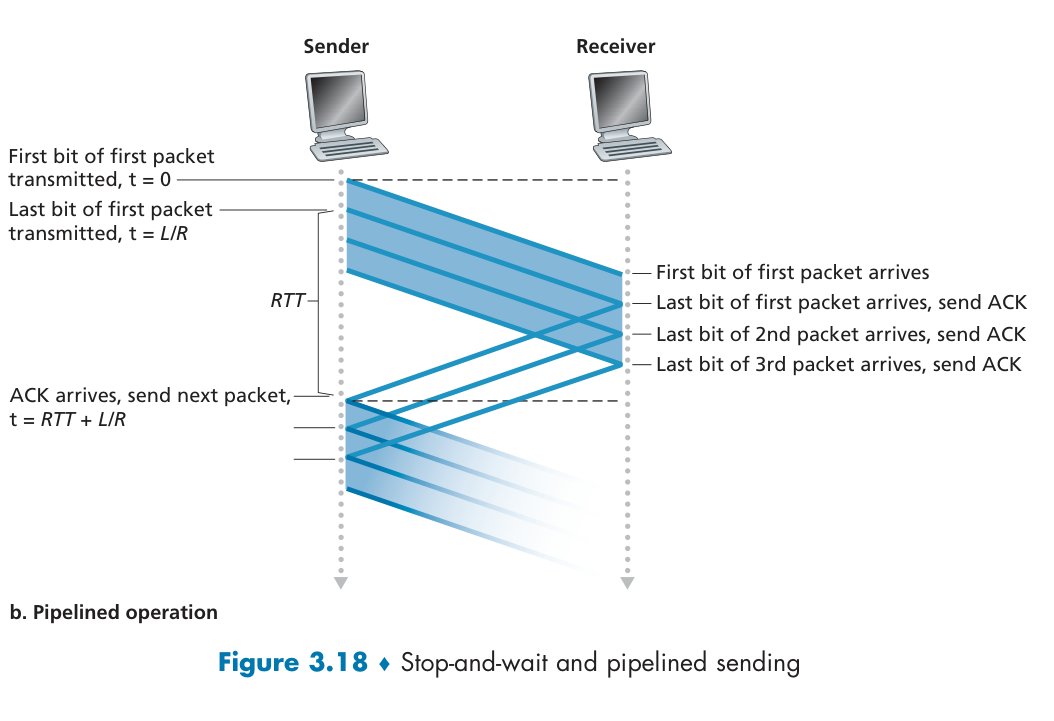
Two basic approaches toward pipelined error recovery can be identified: Go-Back-N and selective repeat.
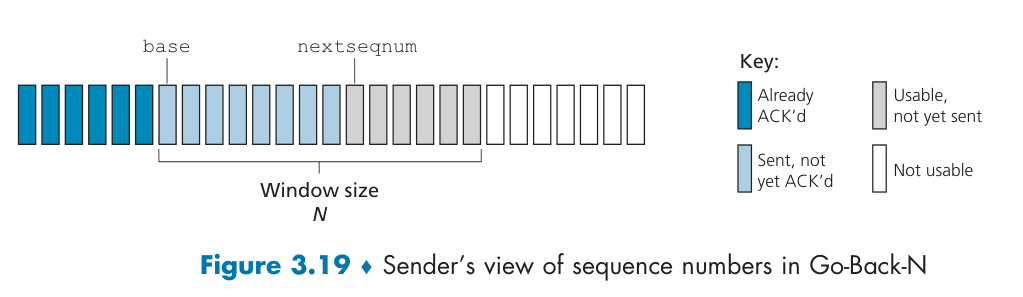
Go - Back - N(GBN)
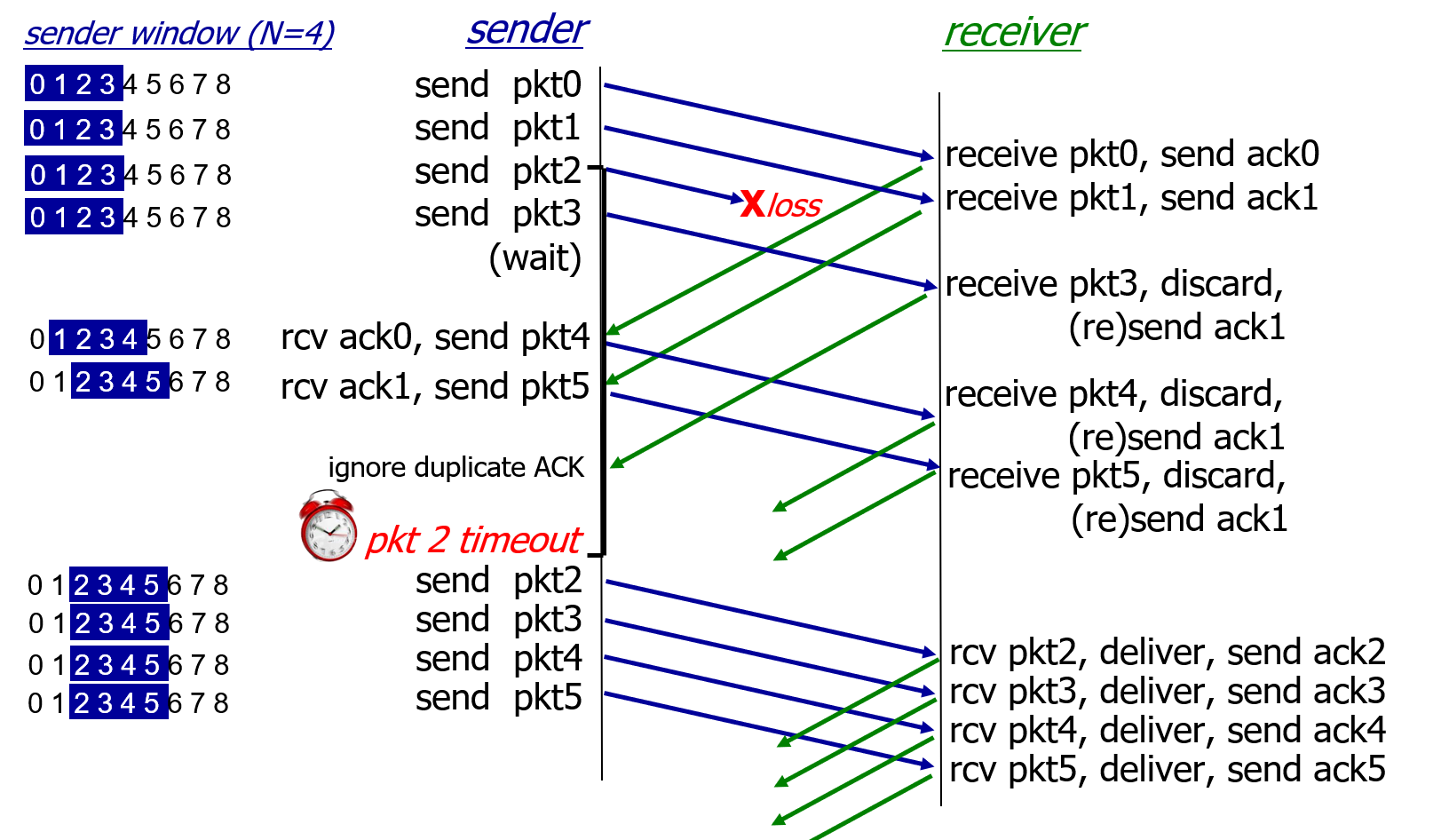
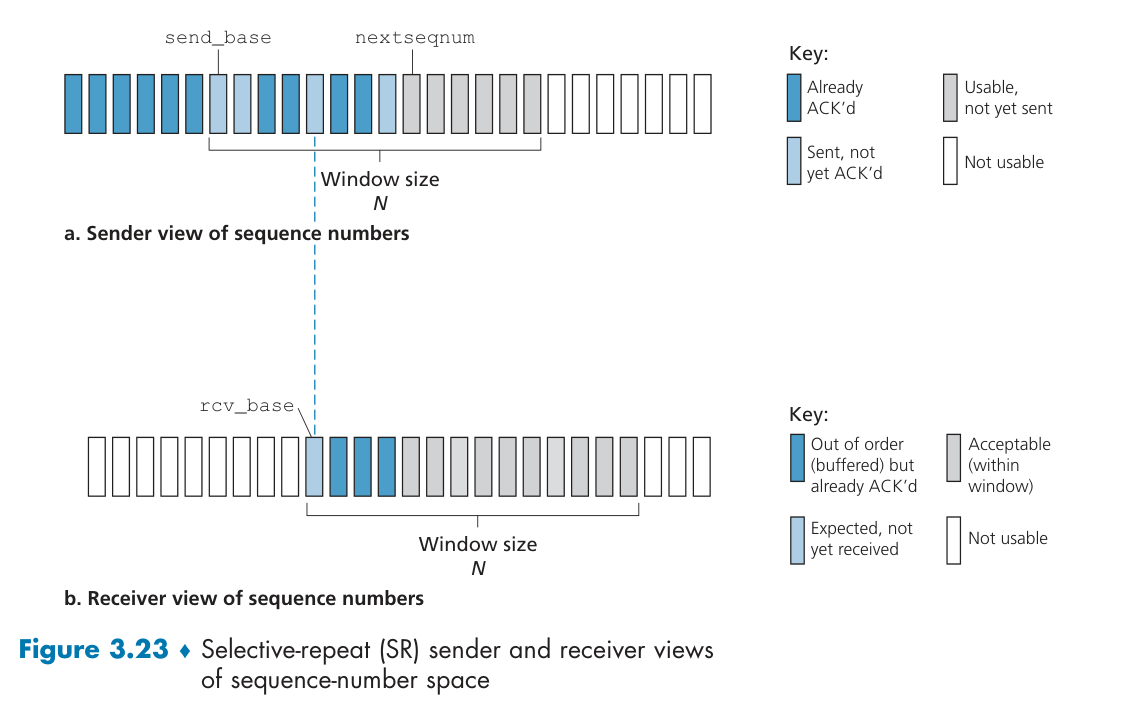
Selective Repeat (SR)
如果ACK未被发送方接收,则须重传将发送方窗口向前移动。
这也是难度所在 :发送方和接收方窗口不完全一致。
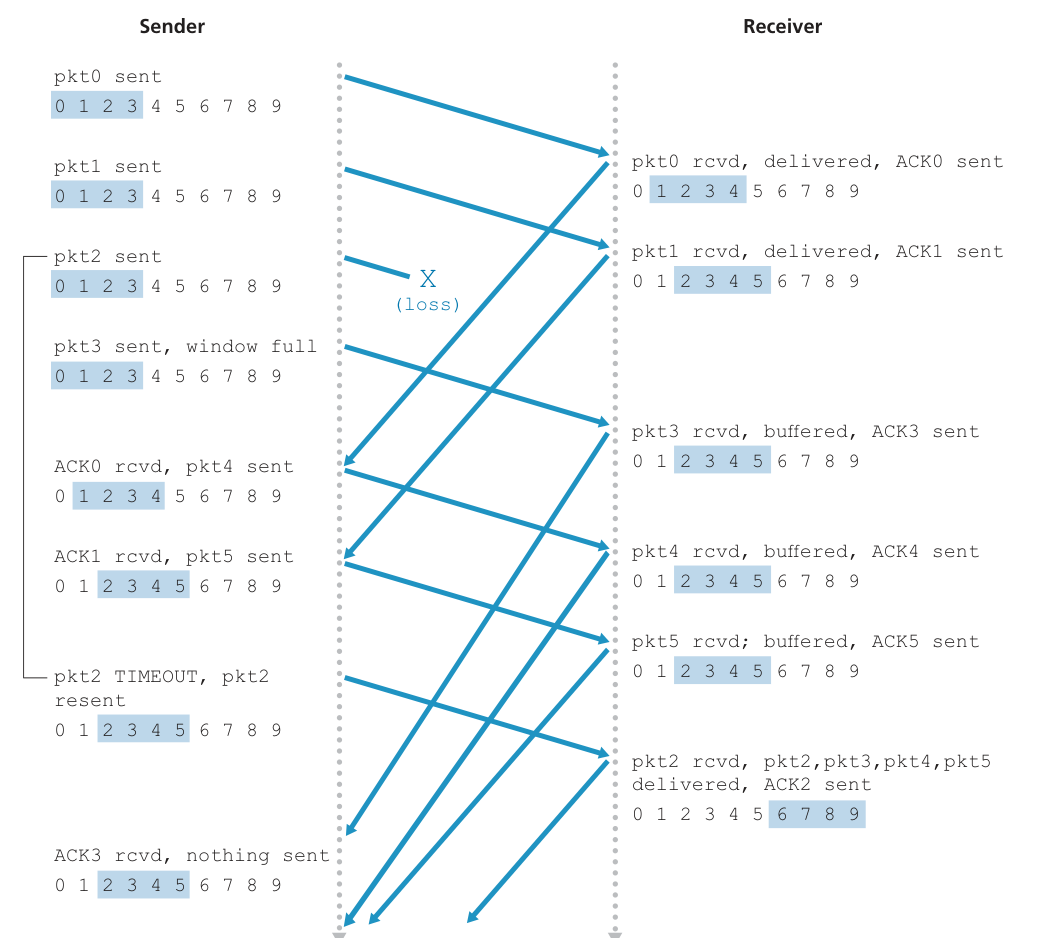
Why checked the left ACK?the sender may not have received an ACK for that packet yet.
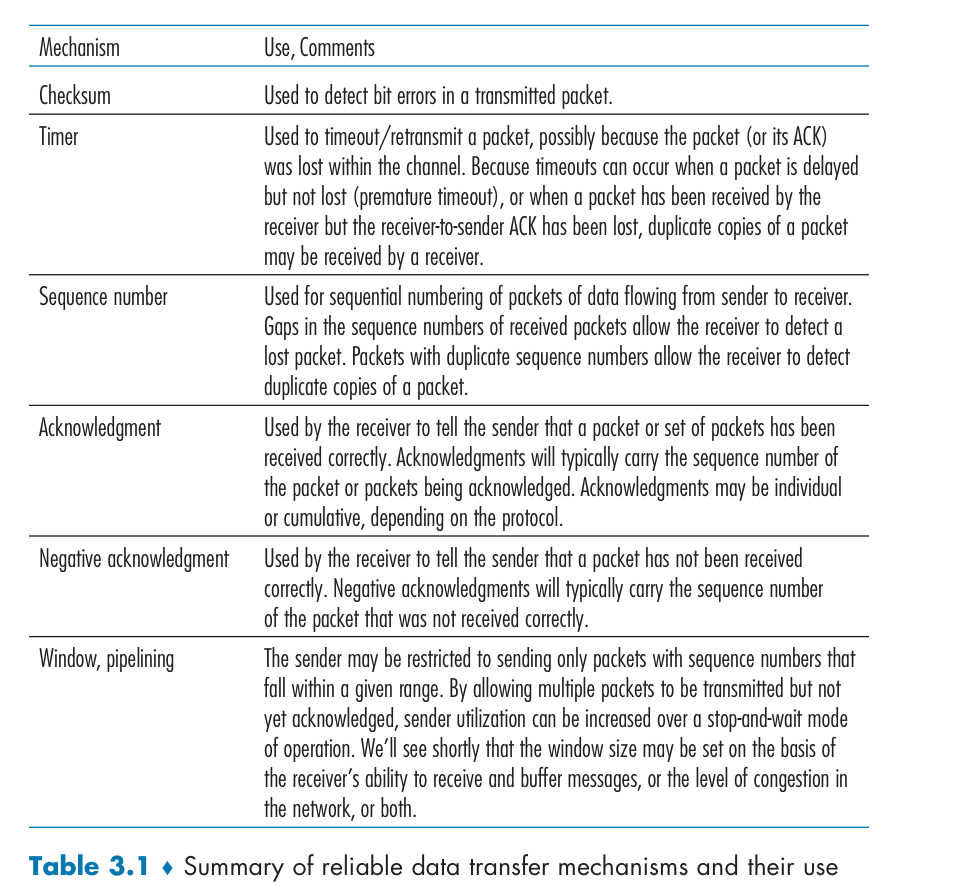
TCP
Why TCP?
TCP是面向连接的,提供可靠交付,有流量控制,拥塞控制,提供全双工通信,面向字节流(把应用层传下来的报文看成字节流,把字节流组织成大小不等的数据块),每一条 TCP 连接只能是点对点的(一对一)。用以下措施保证数据包不被损坏:
每个数据包的序列号和校验码。
确认包和自动重传
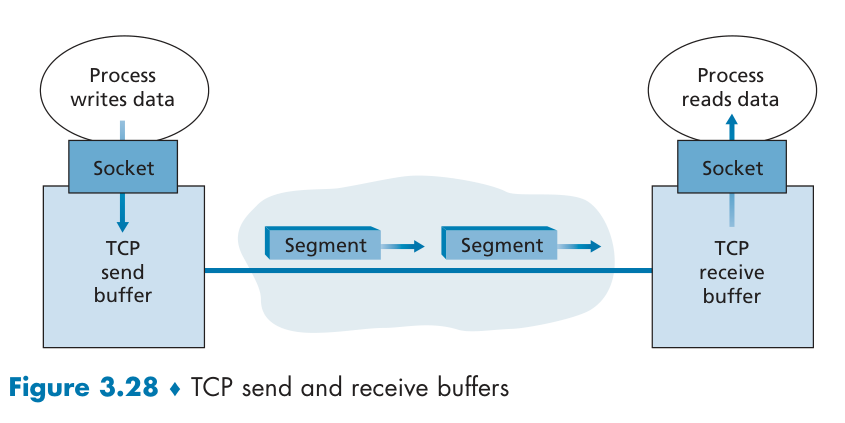
Segment
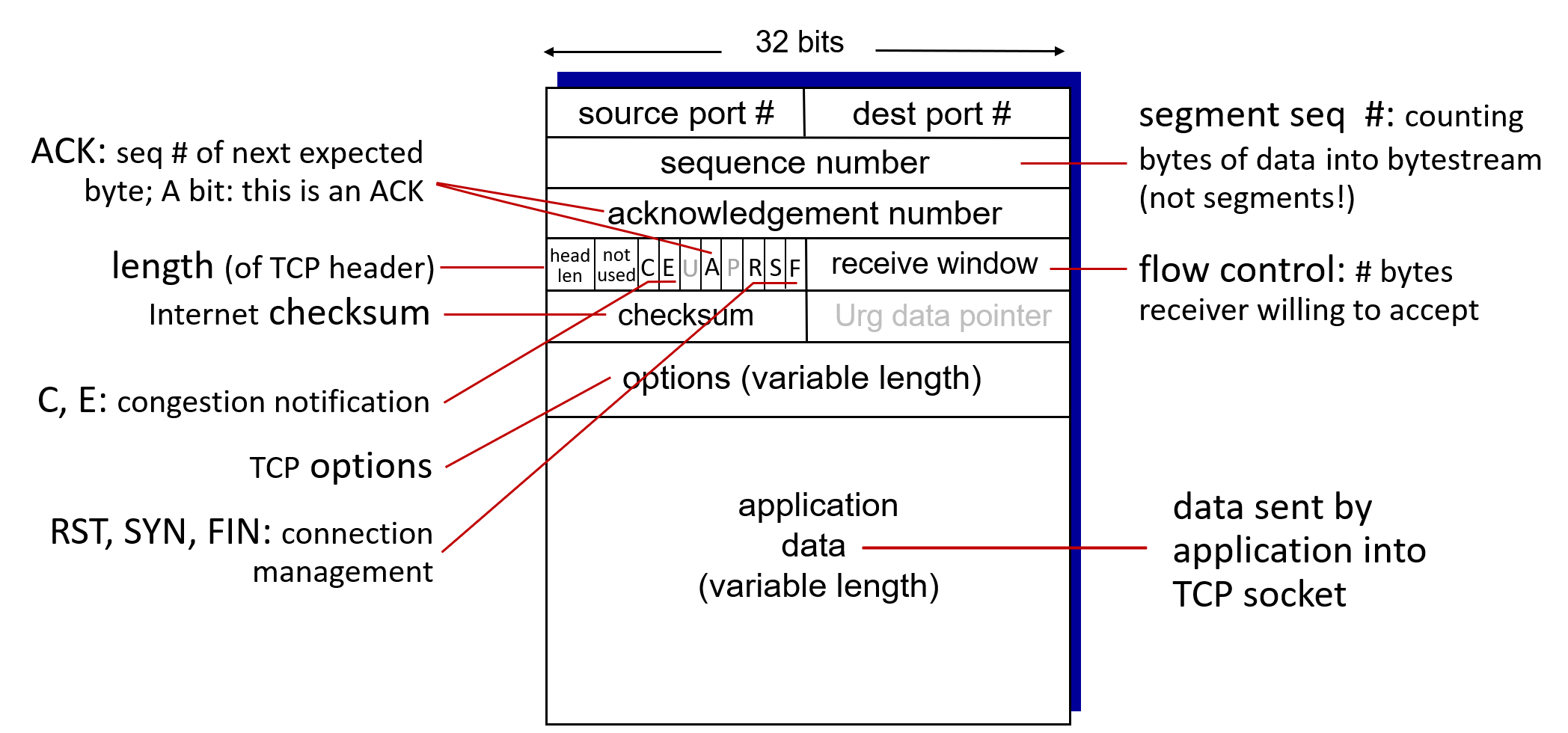
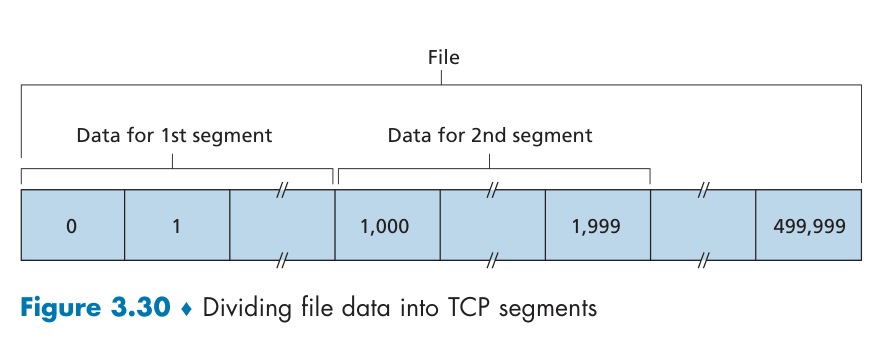
The sequence number for a segment is therefore the byte-stream number of the first byte in the segment.
The ACK number that Receiver puts in its segment is the sequence number of the next byte expecting from Sender.
TCP only acknowledges bytes up to the first missing byte in the stream, TCP is said to provide cumulative acknowledgments.
(术语表)
MTU:一个网络包的最大长度,以太网中一般为1500字节;用于限制数据链路层的payloadMSS:除去 IP 和 TCP 头部之后,一个网络包所能容纳的 TCP 数据的最大长度;RTO: 重传计时器
RTT
The connection’s round-trip time (RTT) is the time from when a segment is sent until it is acknowledged.
TCP通过EWMA(指数加权移动平均. exponential weighted moving average )维护一个RTT均值。建议取值 $\alpha = 0.125$
$EstimatedRTT = (1 – \alpha)\times EstimatedRTT + \alpha\times SampleRTT$
同时维护DevRTT(RTT偏差),即当前SampleRTT与EstimatedRTT的差值。一般取$\beta = 0.25$
DevRTT=(1–β)DevRTT+β∣SampleRTT–EstimatedRTT∣
于是得到超时间隔:
$TimeoutInterval = EstimatedRTT + 4 \times DevRTT$
Reliable Data Transfer
面向事件的处理方案。以下:
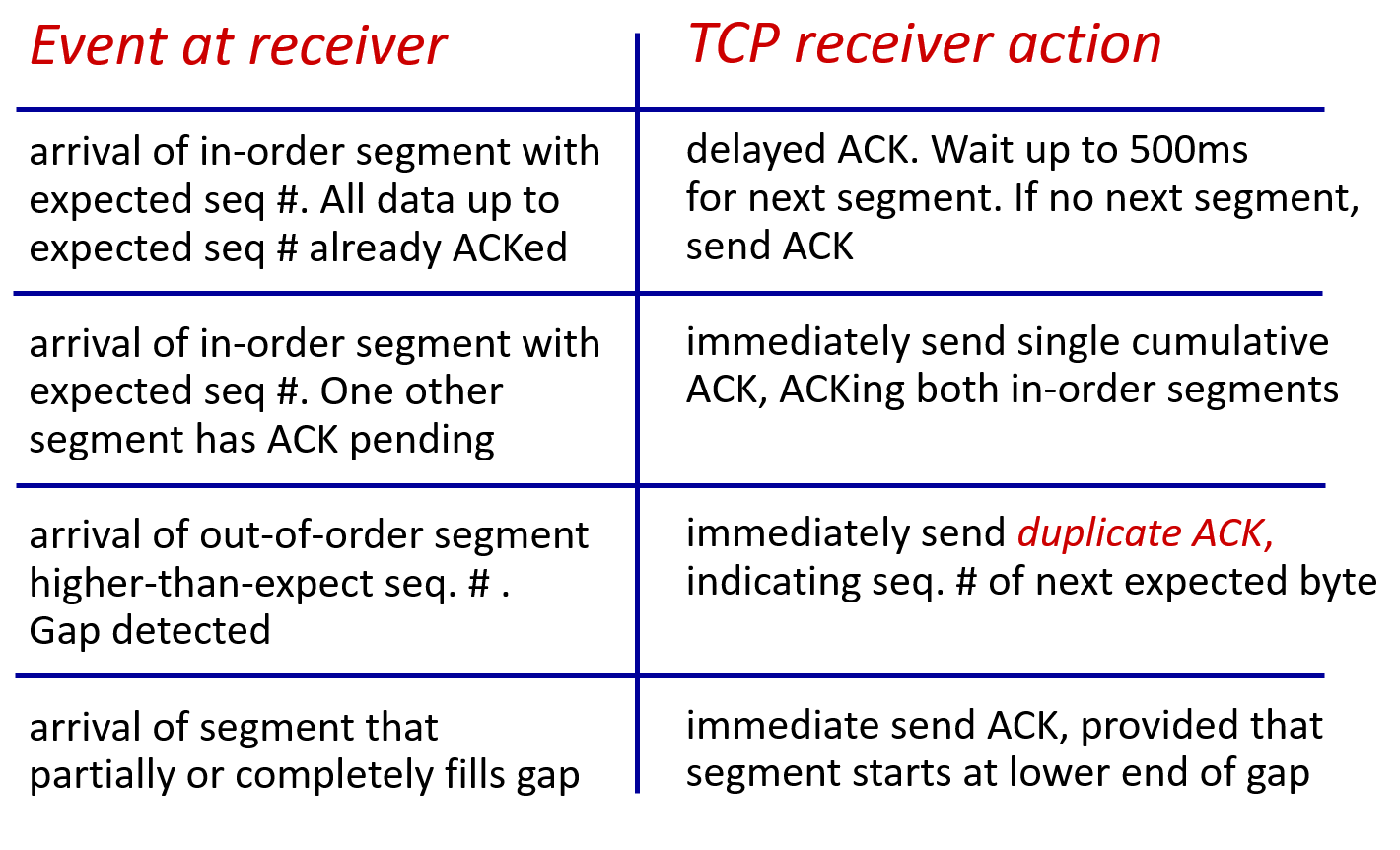
e,g. scenario
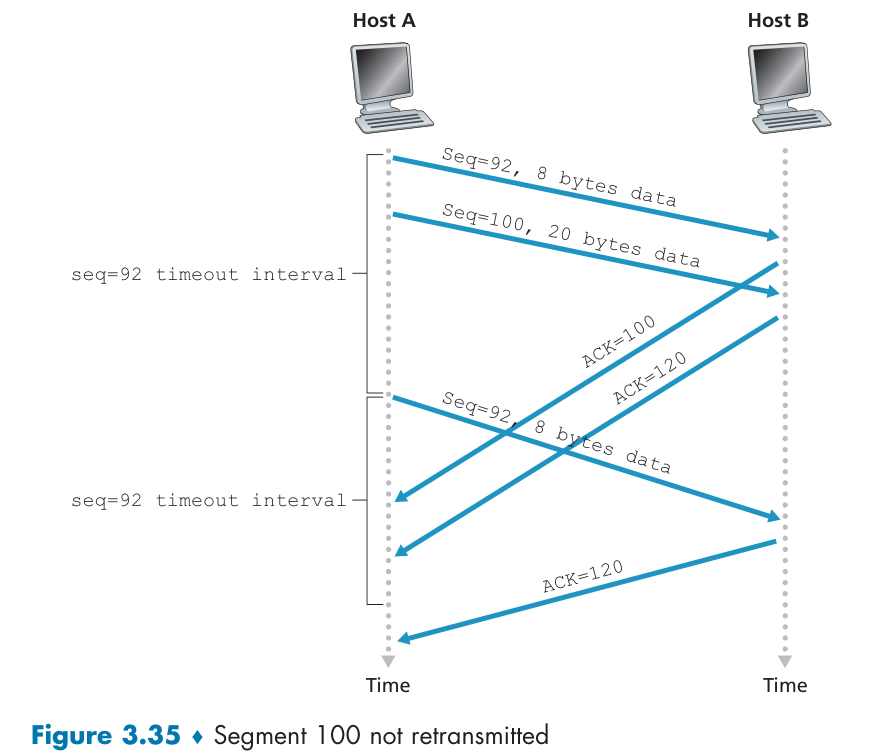
Fast retransmit(不用等计时器)
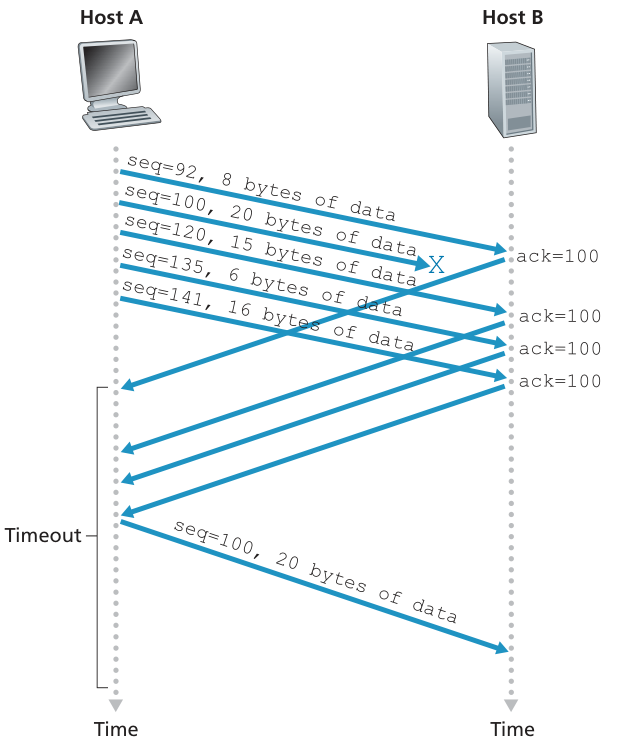
Why 3?
Flow Control
buffer and window
TCP provides flow control by having the sender maintain a variable called the receive window. TCP receiver “advertises” free buffer space in rwnd field in TCP header ,guarantees receive buffer will not overflow.
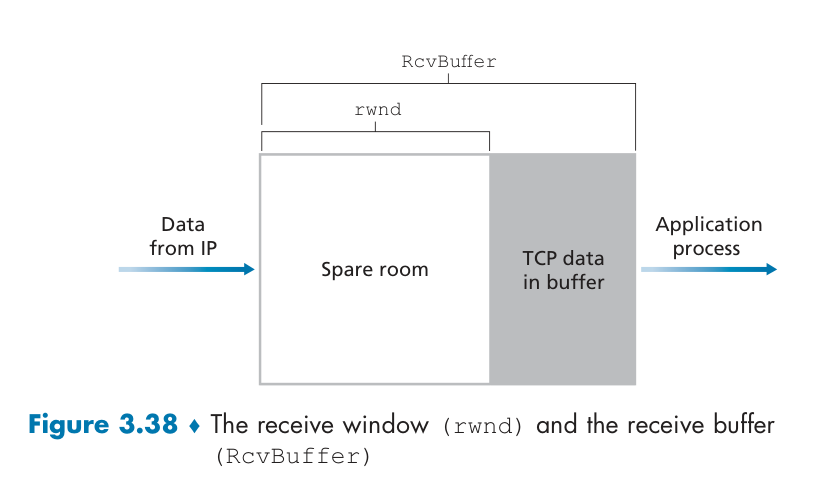
假设接收缓冲区已满(rwnd = 0)。若向接收方发送rwnd = 0报文丢失,而TCP只有在有数据要发送或者有应答要发送时才会向主机发送一个段。因此,发送方永远不会知道接收缓冲区中已经清空了一些缓冲区(被阻塞)。为解决这个问题,要求发送方在的接收窗口为零时继续发送窗口探测报文进行确认。
窗口综合征
接收方忙碌使得发送方的发送窗口过小时,则会导致小包降低网络传输效率的问题。为解决这一问题,可让接收方不通告小窗口给发送方、让发送方避免发送小包。
解决前者(低能窗口综合症)的Clark算法解决方案:接收方发送窗口更新段的条件:「窗口大小」大于 min( MSS,缓存空间 / 2 缓冲区一半为空)。否则,通告窗口为 0 .
解决后者(糊涂窗口综合征)的Nagle算法解决方案:发送第一块数据并缓冲剩余的数据;不再发送数据除非满足下面条件之一:发送出去的数据段被确认,缓冲数据填满半个窗口或达到MSS。
TCP Connection Management
3-way handshake
why not 2?无法防止历史连接的建立。
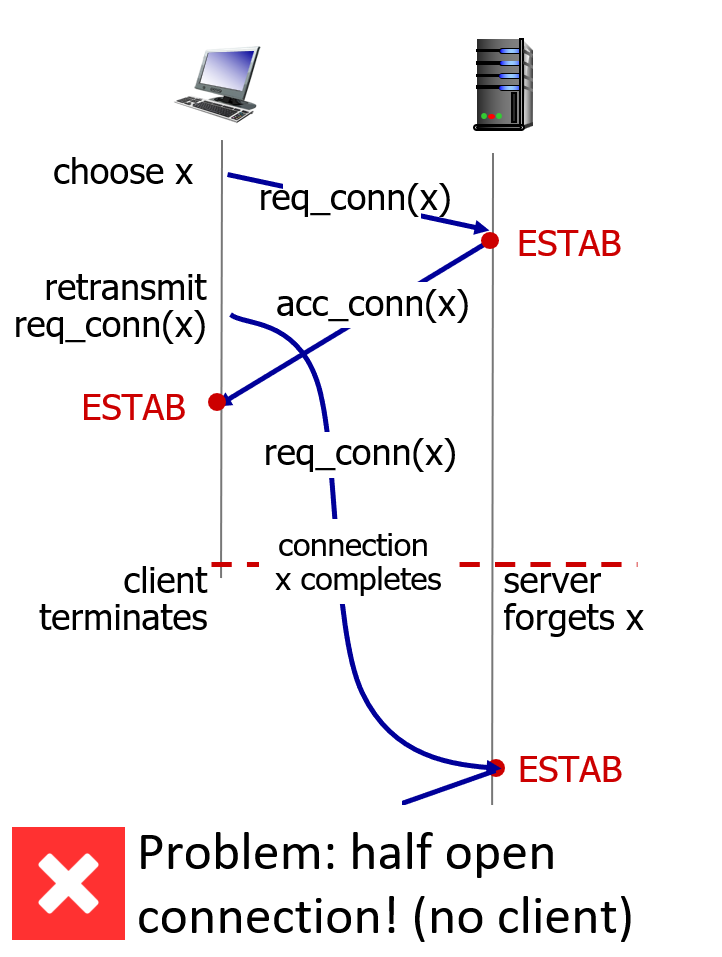
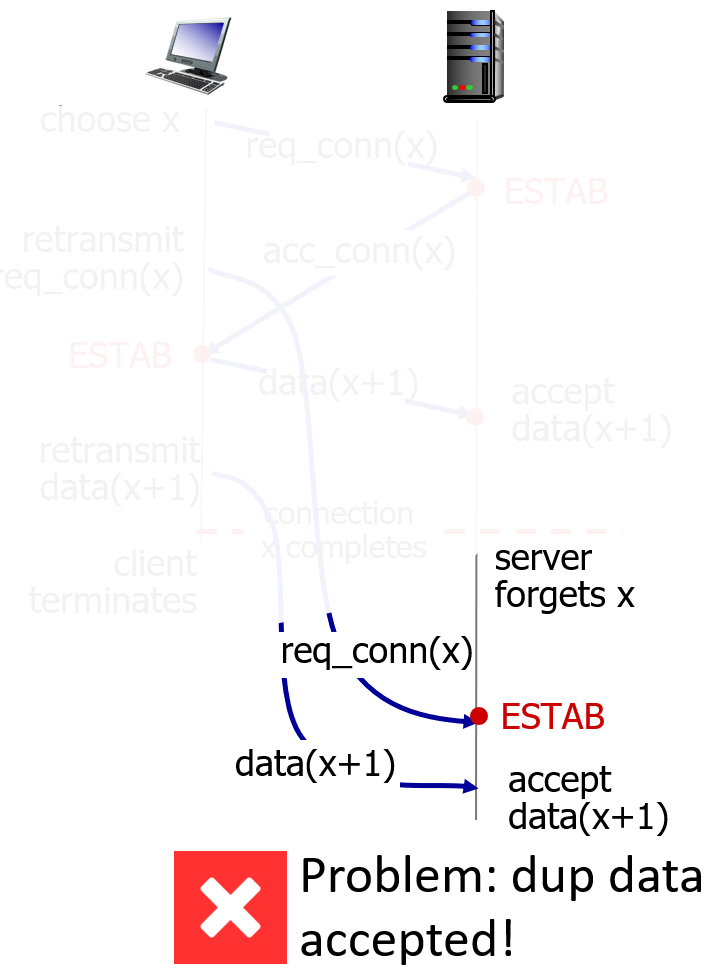
I can’t “see” other side
delay->reordering?
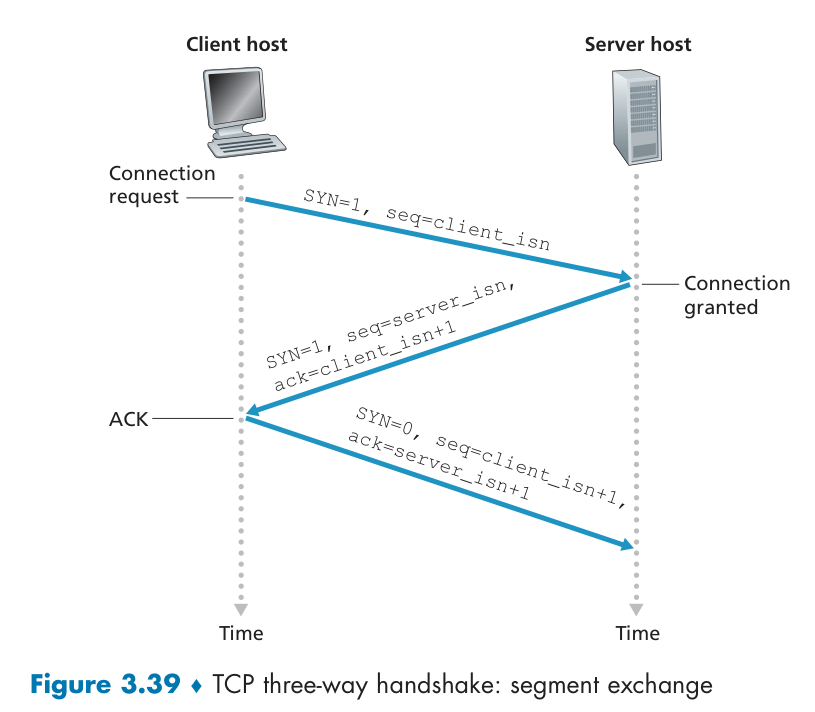
The client-side TCP first sends a special TCP segment - SYN segment to the server-side TCP.(SYNbit = 1)
the server extracts the TCP SYN segment from the datagram, allocates the TCP buffers and variables to the connection, and sends a connection-granted segment - SYNACK segment to the client TCP.
Upon receiving the SYNACK segment, the client also allocates buffers and variables to the connection.
seq是一个含时间戳的随机算法,随机生成,以大概率降低历史报文的接收。同时也防止黑客伪造的相同序列号的 TCP 报文被对方接收,安全。
补充知识:半连接队列(SYN Queue)和全连接队列(accept Q)
服务器收到SYN请求会存储到SYN Q,收到第三次握手的ACK后,添加到AC Q
SYN洪泛攻击
通过SYN Cookie缓解。
四次挥手
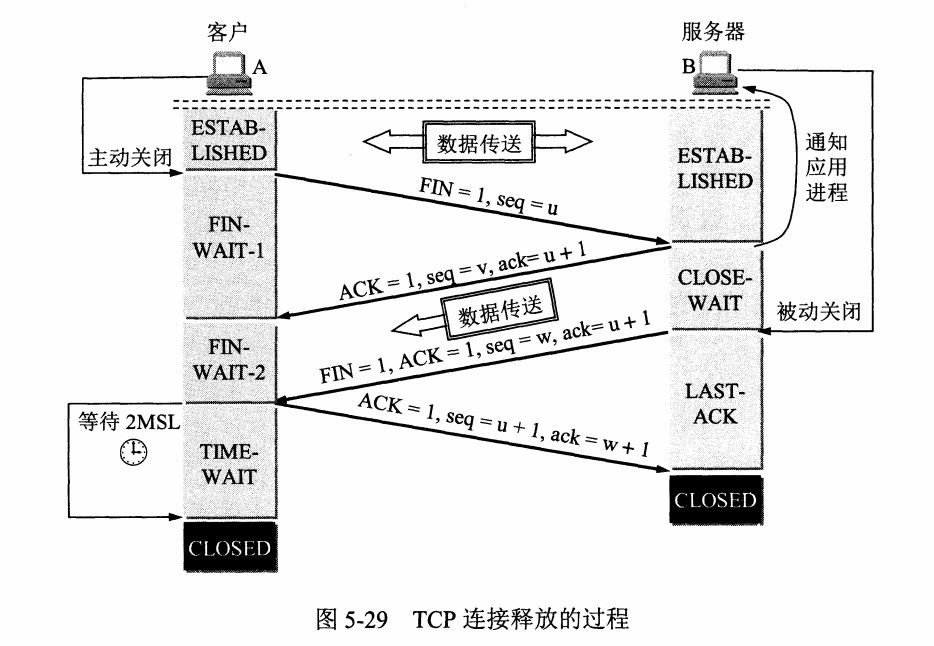
Why 4? Fin表示客户端不再发送数据,服务器返回ACK后可能依旧有待发送数据,处理后发送Fin
为什么最后需要Time wait 2MSL?防止旧连接的ACK包 、确保双工连接关闭。
Principles of Congestion Control
若对网络中某一资源的请求超过了所能提供的可用部分,网络的性能(吞吐量、时延等)就要变差。这种情况就叫拥塞。
拥塞的代价:
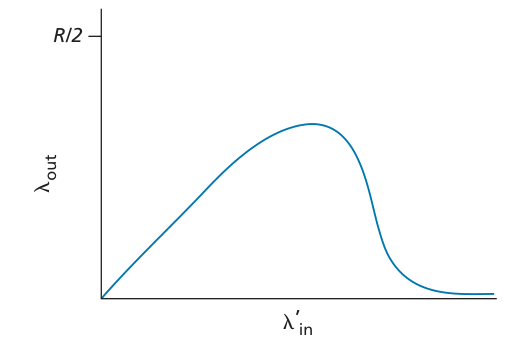
(queueing) delay increases as capacity approached
loss/retransmission decreases effective throughput
un-needed duplicates further decreases effective throughput
upstream transmission capacity / buffering wasted for packets lost downstream
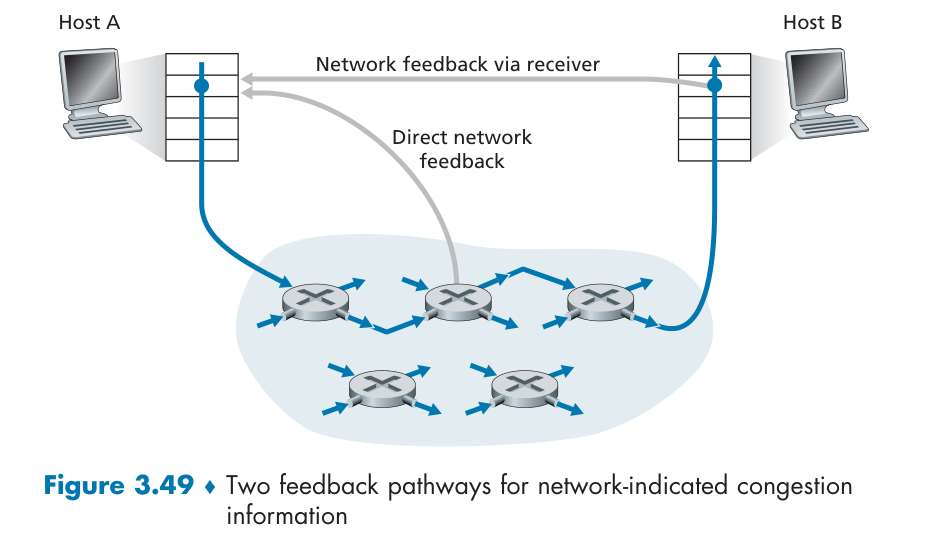
How to solve? Feedback.
TCP Congestion Control
Classic TCP Congestion Control
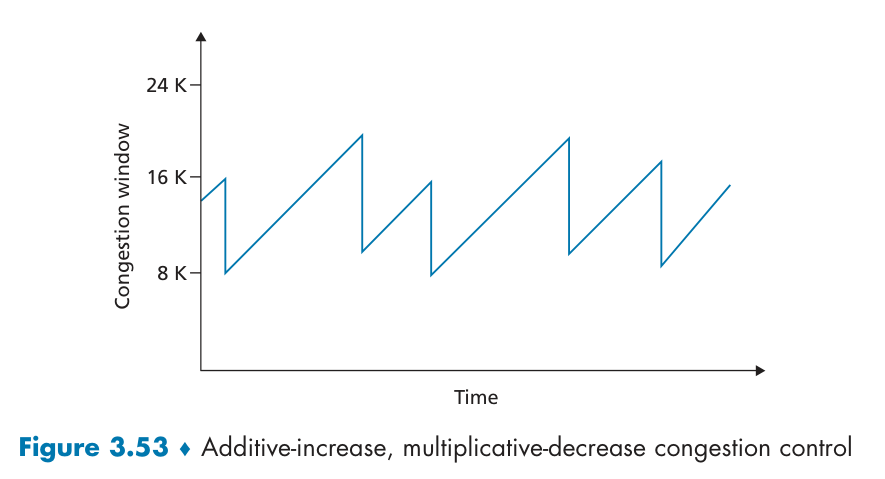
AIMD:Additive Increase and Multiplicative Decrease
A lost segment implies congestion, and hence, the TCP sender’s rate should be decreased when a segment is lost.
An acknowledged segment indicates that the network is delivering the sender’s segments to the receiver, and hence, the sender’s rate can be increased when an ACK arrives for a previously unacknowledged segment.
Bandwidth probing.
How AIMD?
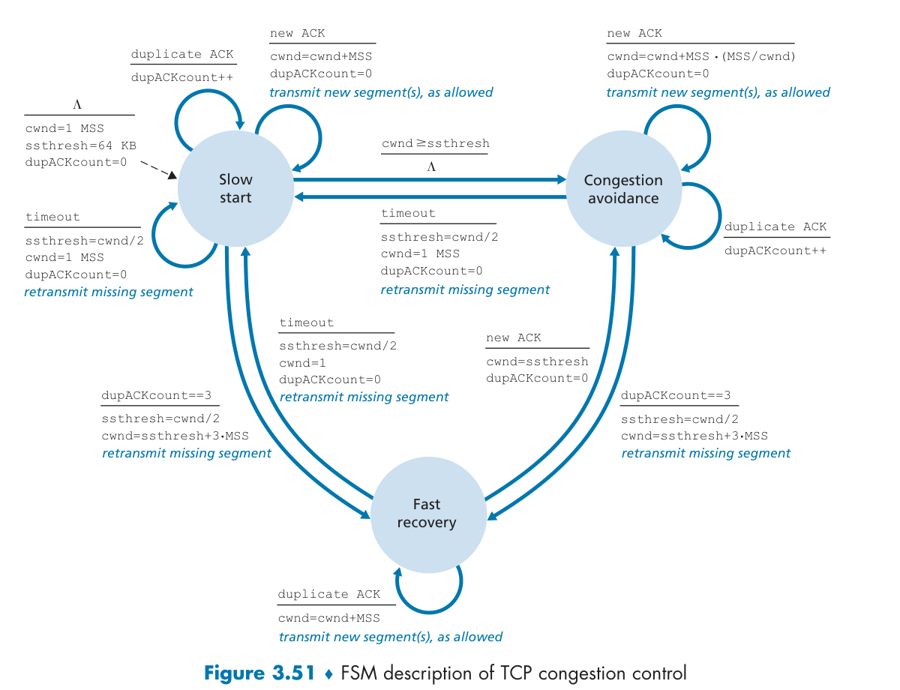
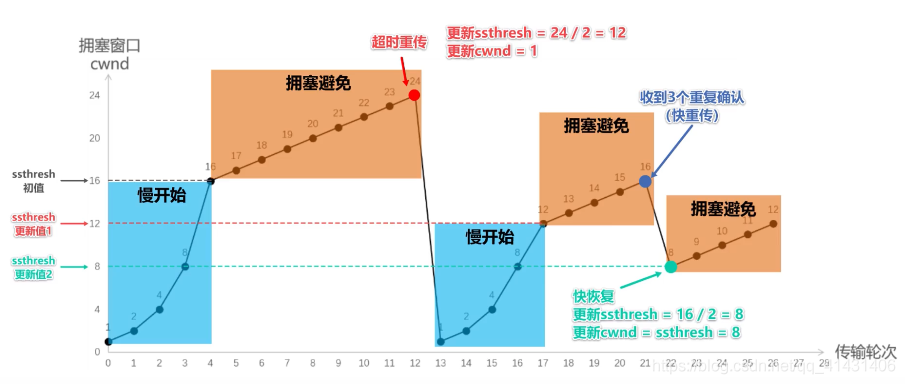
Slow Start
when connection begins, increase rate exponentially until first loss event.
initially cwnd = 1 MSS, double cwnd every RTT done (every ACK received).
when should this exponential growth end? loss, cwnd >= ssthresh, three duplicated ACK then fast retransmit.
ssthresh:“慢启动阈值”,默认为64KB
ssthresh is half the value of cwnd when congestion was last detected.
Congestion Avoidance
因为已经接近临界了,TCP 变得保守,increases the value of cwnd by just a single MSS every RTT, 直到发现拥塞。
Fast Recovery
In fast recovery, the value of cwnd is increased by 1 MSS for every duplicate ACK received for the missing segment that caused TCP to enter the fast-recovery state.
重传DACKs指定的数据包,如果再收到DACKs,那么cwnd大小增加一,如果收到新的ACK(重传成功),退出快速恢复算法。将cwnd设置为ssthresh,然后进入拥塞避免算法。
Better AIMD
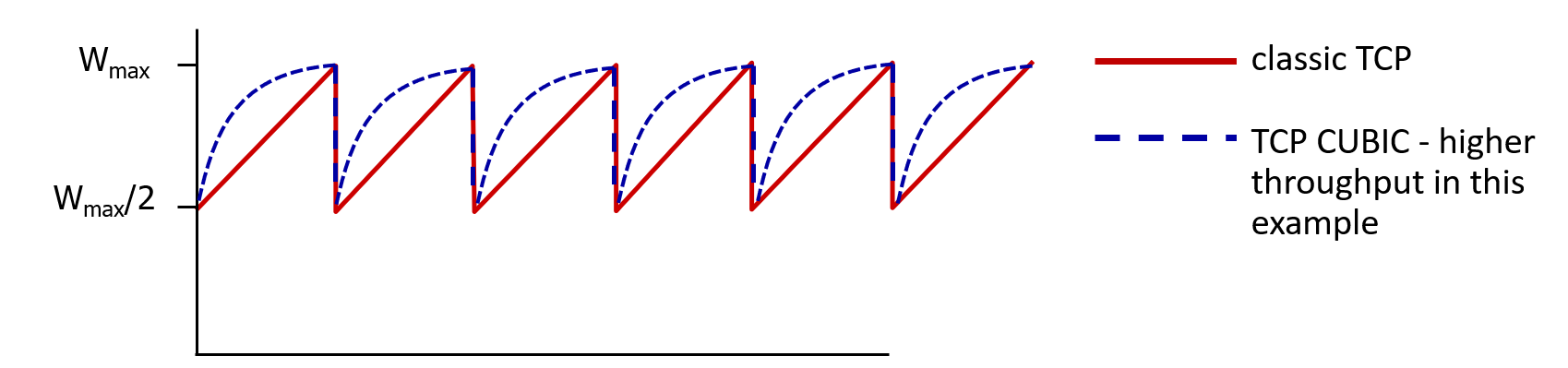
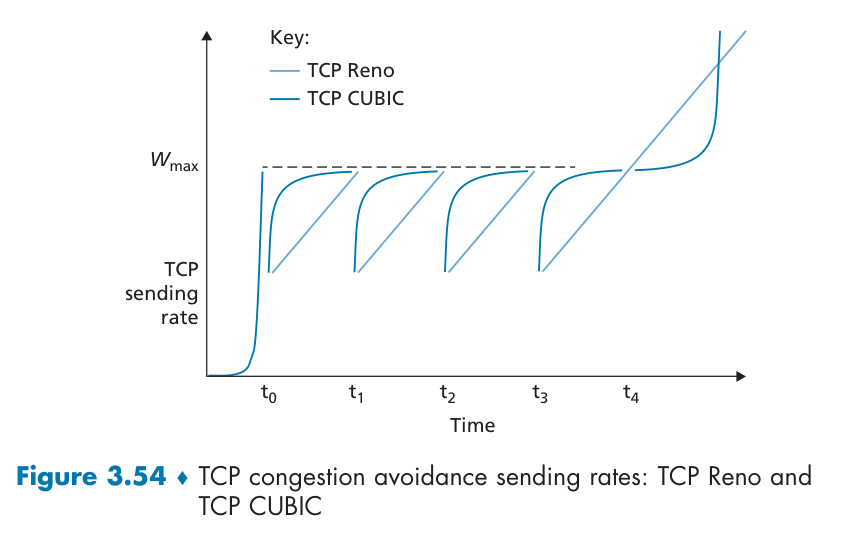
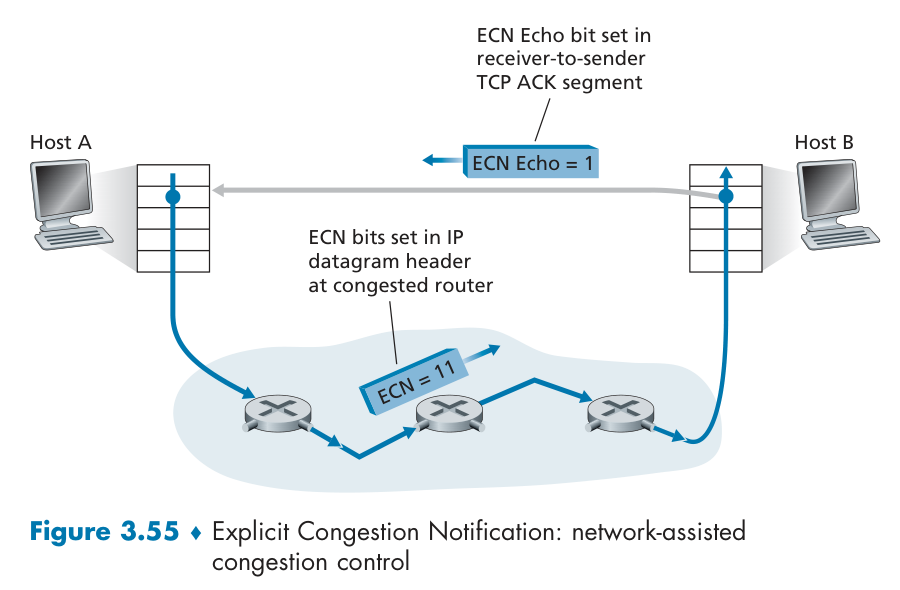
网络辅助拥塞控制
基于延迟的拥塞控制:Keep the pipe just full, but no fuller
$RTT_{min}$ : minimum observed RTT (uncongested path) uncongested throughput with congestion window cwnd is cwnd /$RTT_{min}$
Fairness
Yes.
congestion avoidance: additive increase
loss: decrease window by factor of 2
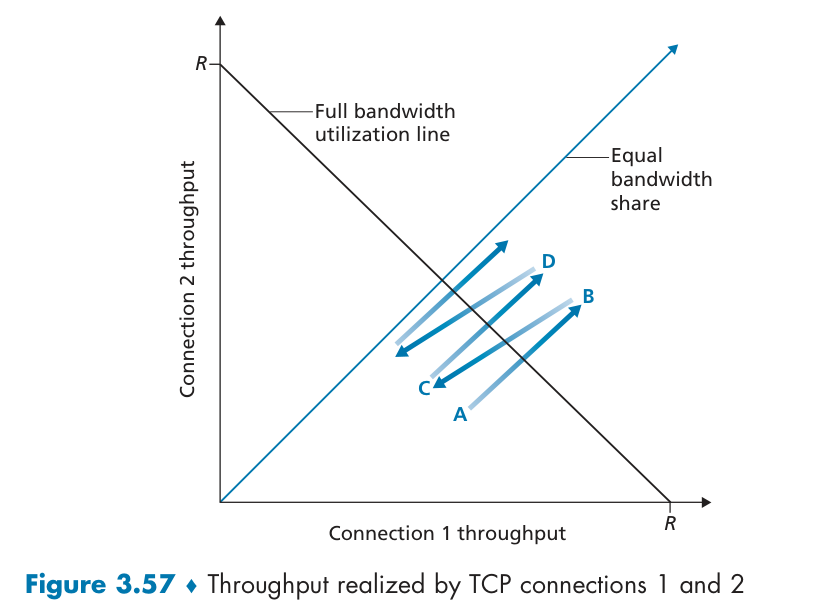
When running over UDP, applications at a constant rate and occasionally lose packets, rather than reduce their rates to “fair” levels at times of congestion and not lose any packets.
web browsers help us when multiple parallel connections, e.g.:
link of rate R with 9 existing connections
•new app asks for 1 TCP, gets rate R/10
•new app asks for 11 TCPs, gets R/2
QUIC
Quick UDP Internet Connections Protocol's major features:
Connection-Oriented and Secure.
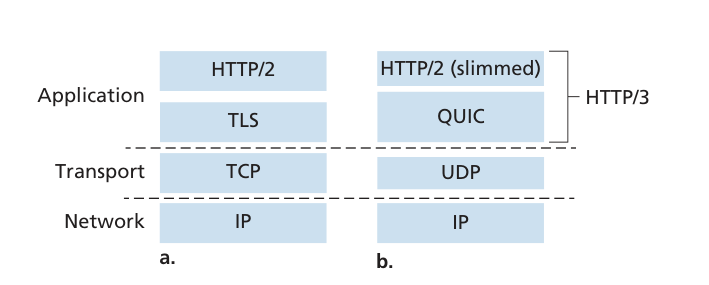
QUIC in application layer Streams. QUIC allows several different application-level “streams” to be multiplexed through a single QUIC connection and establish fast(1 handshake).
Reliable, TCP-friendly congestion-controlled data transfer.
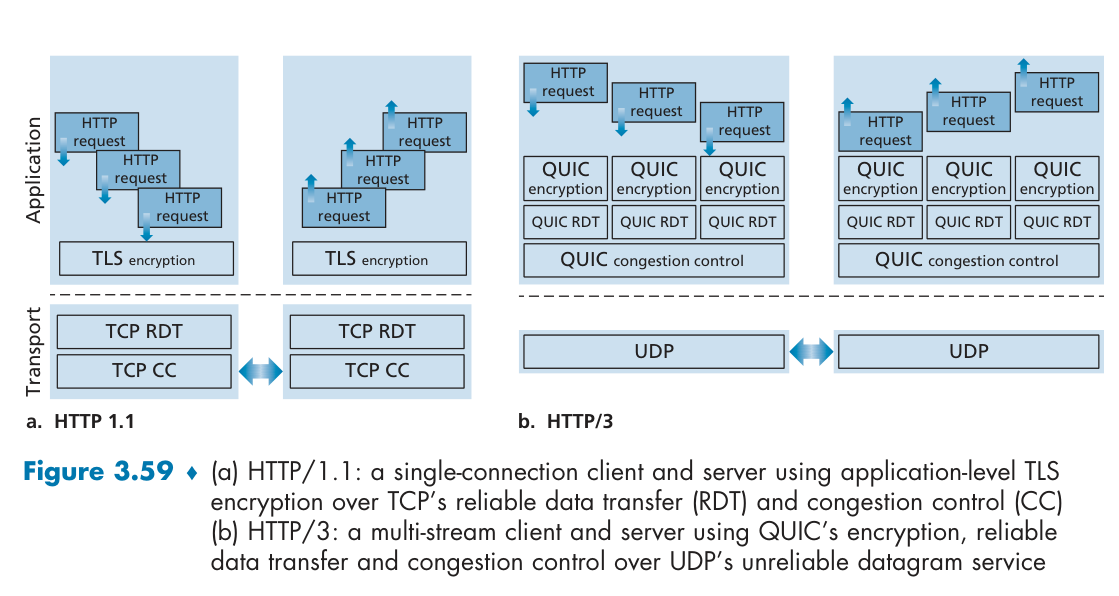
a lost UDP segment only impacts those streams whose data was carried in that segment
参考:
《图解HTTP》
小林coding
最后更新于