静态软件分析-指针分析
Interprocedural Analysis
前面的过程内分析不处理
method call,因此需要过程间分析来提高精度。
call graph(调用图)
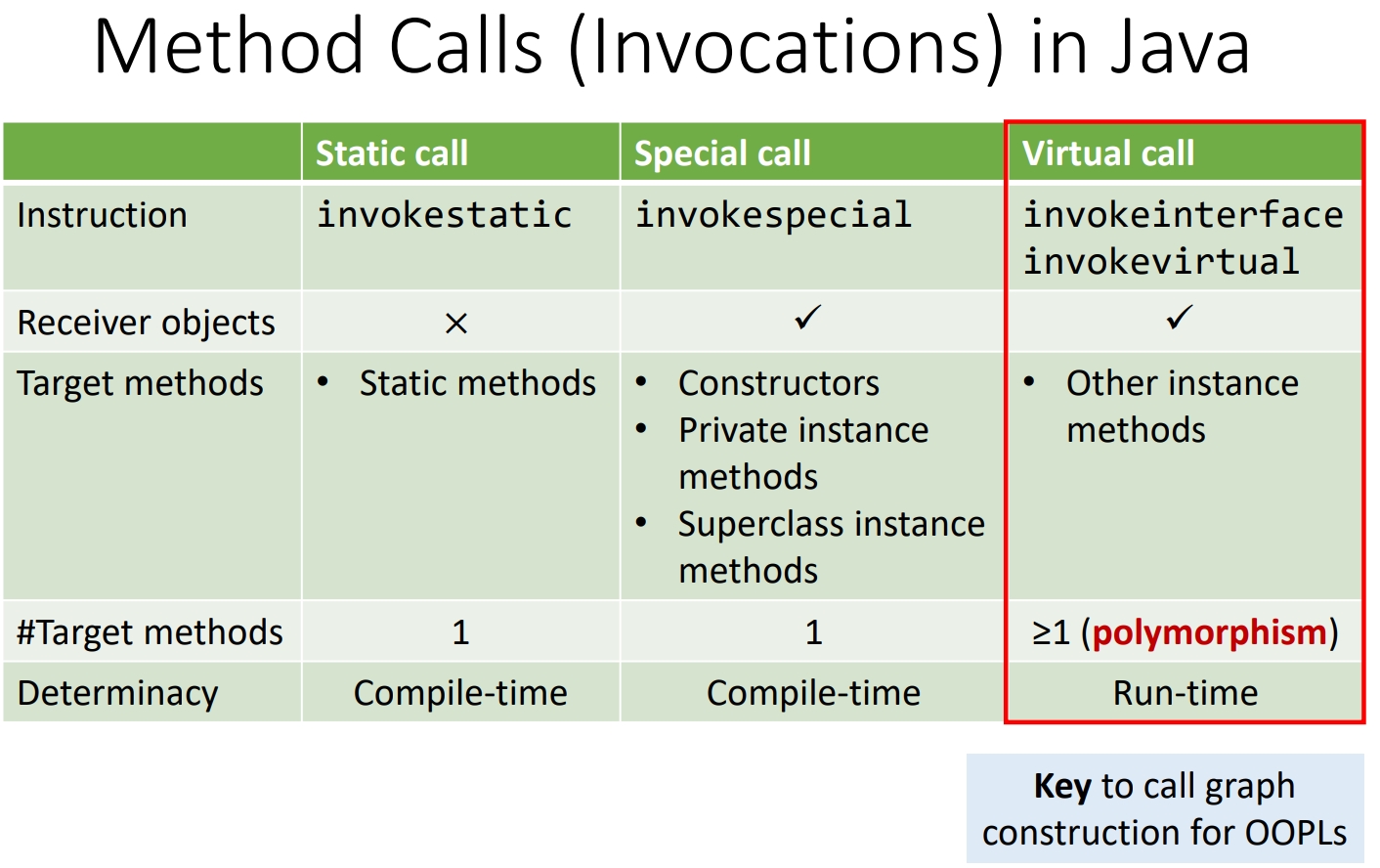
Method Dispatch of Virtual Calls:双亲委派模型?(由receiver object不断向父类寻找匹配的签名)
Two Key Functions

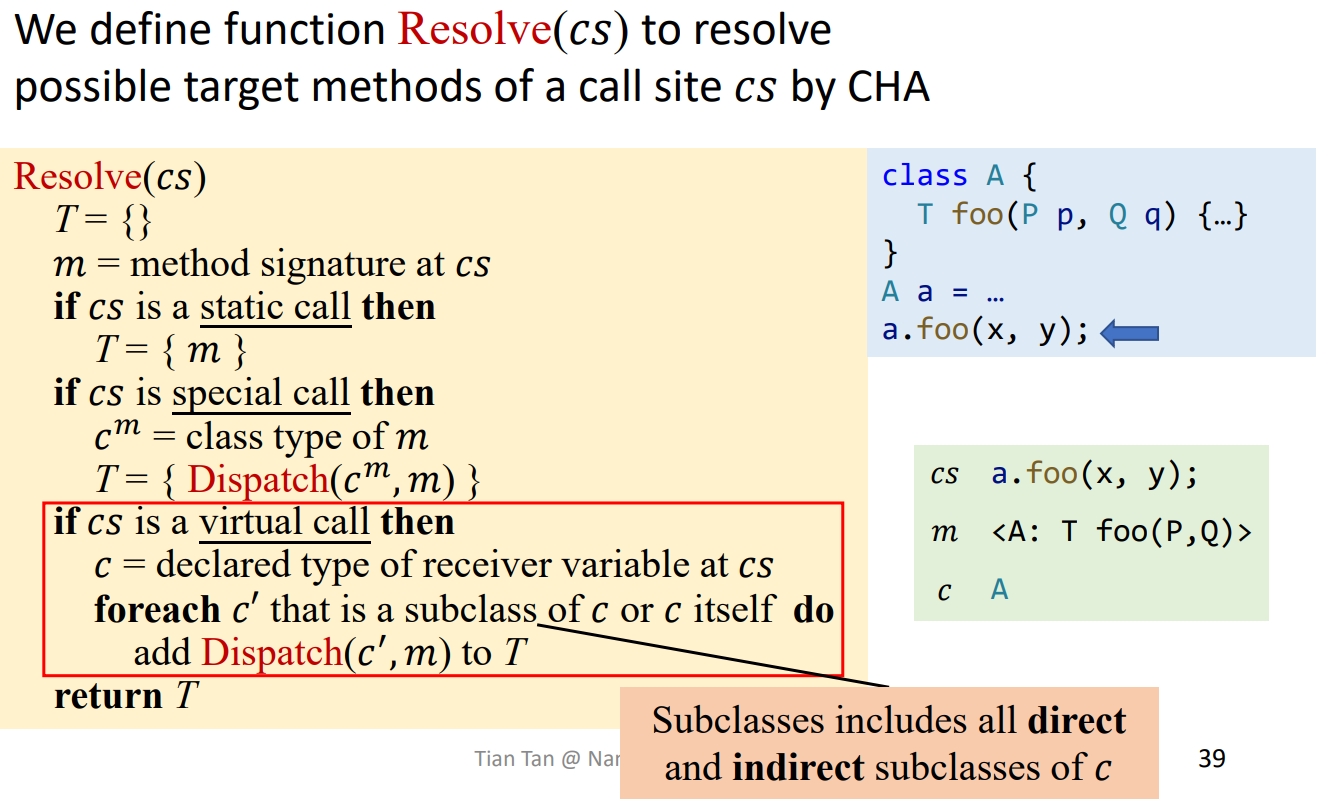
Algorithm
 引入ICFG,表示过程间的调用关系。$CFGs + call& return \ \ edges$
引入ICFG,表示过程间的调用关系。$CFGs + call& return \ \ edges$  算法中,为了节省非左值的传递开销,
算法中,为了节省非左值的传递开销,call site和return site之间的边进行保留,只是kill掉左值,更新成被调用函数的返回值。
Pointer Analysis - Intro
may-analysis points-to relations.,Computes which objects a pointer (variable or field) can point to.
Pointers In Java
Local variable:
xStatic field:
A.fSometimes referred as global variable, like Local variableInstance field:
x.fModeled as an object (pointed by x) with a field fArray element:
a[i]下标访问相关代码块比较复杂,下标一般是变量不是常数等,静态分析的通用做法忽略下标,Modeled as an object (pointed by array) with a single field, say arr, which may point to any value stored in array.
Key Factors
Heap Abstraction -> How to model heap memory?
 -> A technique is Allocation-site. eg. without iteration, only the site(bounded)
-> A technique is Allocation-site. eg. without iteration, only the site(bounded)Context Sensitivity: separate by different contexts(call), rather than merge.
Flow Sensitivity: Actually we dont respect the exection order of stmts, but maintain a map of points-to relations at the whole program for better performance.
Analysis scope: Whole-program/Demand-driven
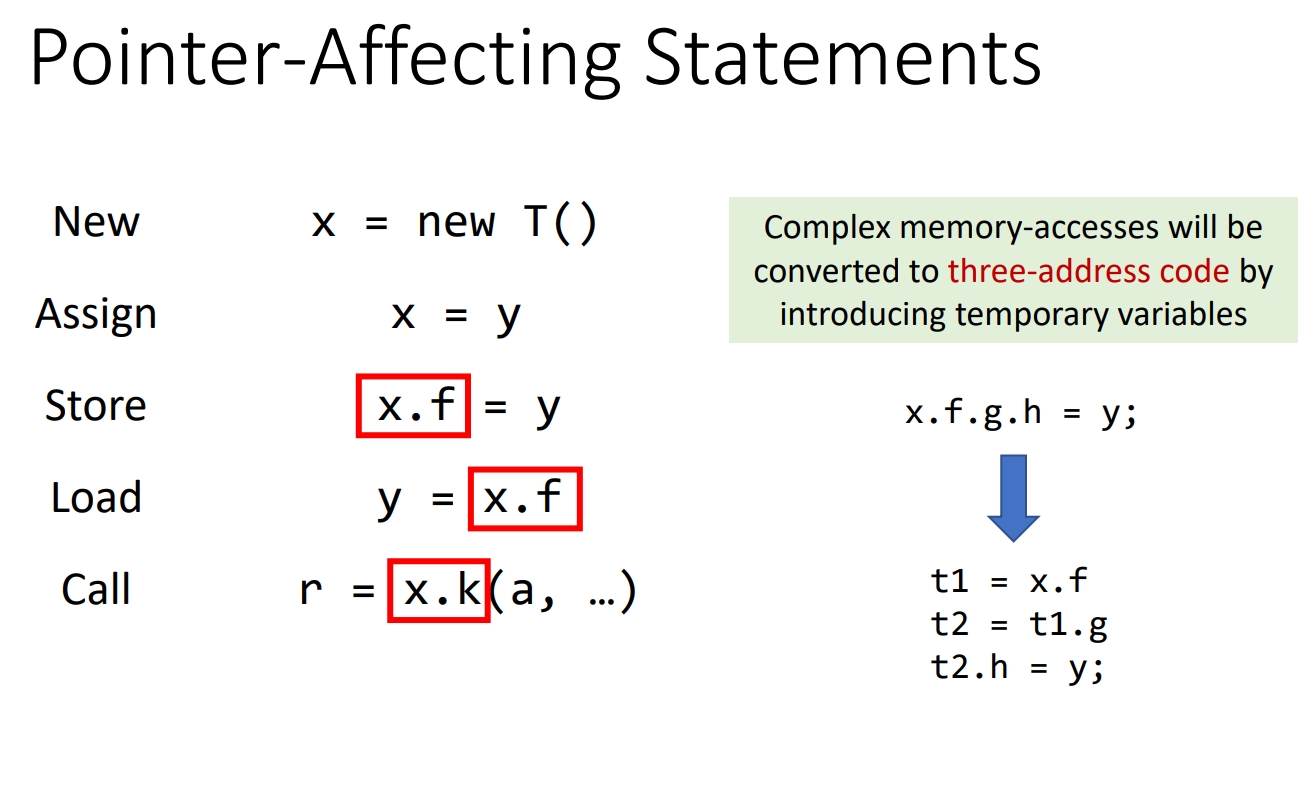
Pointer-Affecting Statements
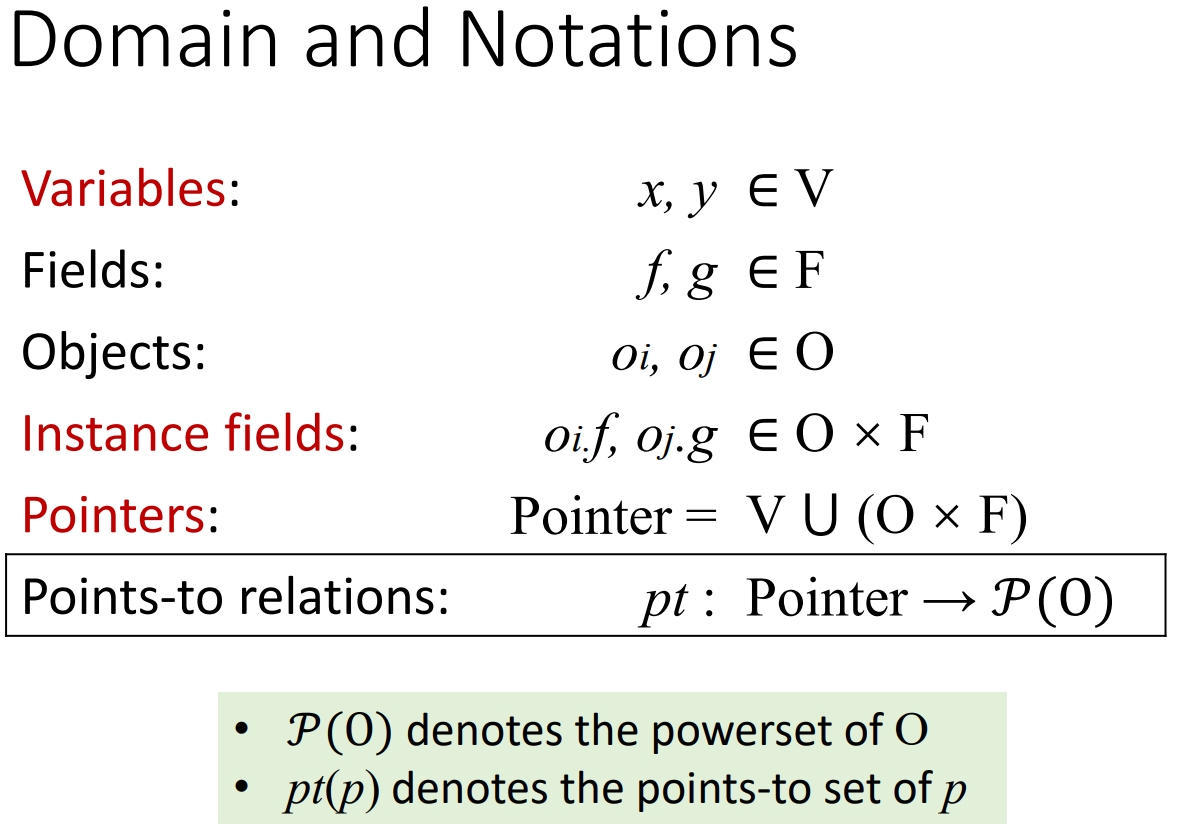
PA-FD.basic
Rule(逻辑推导式)
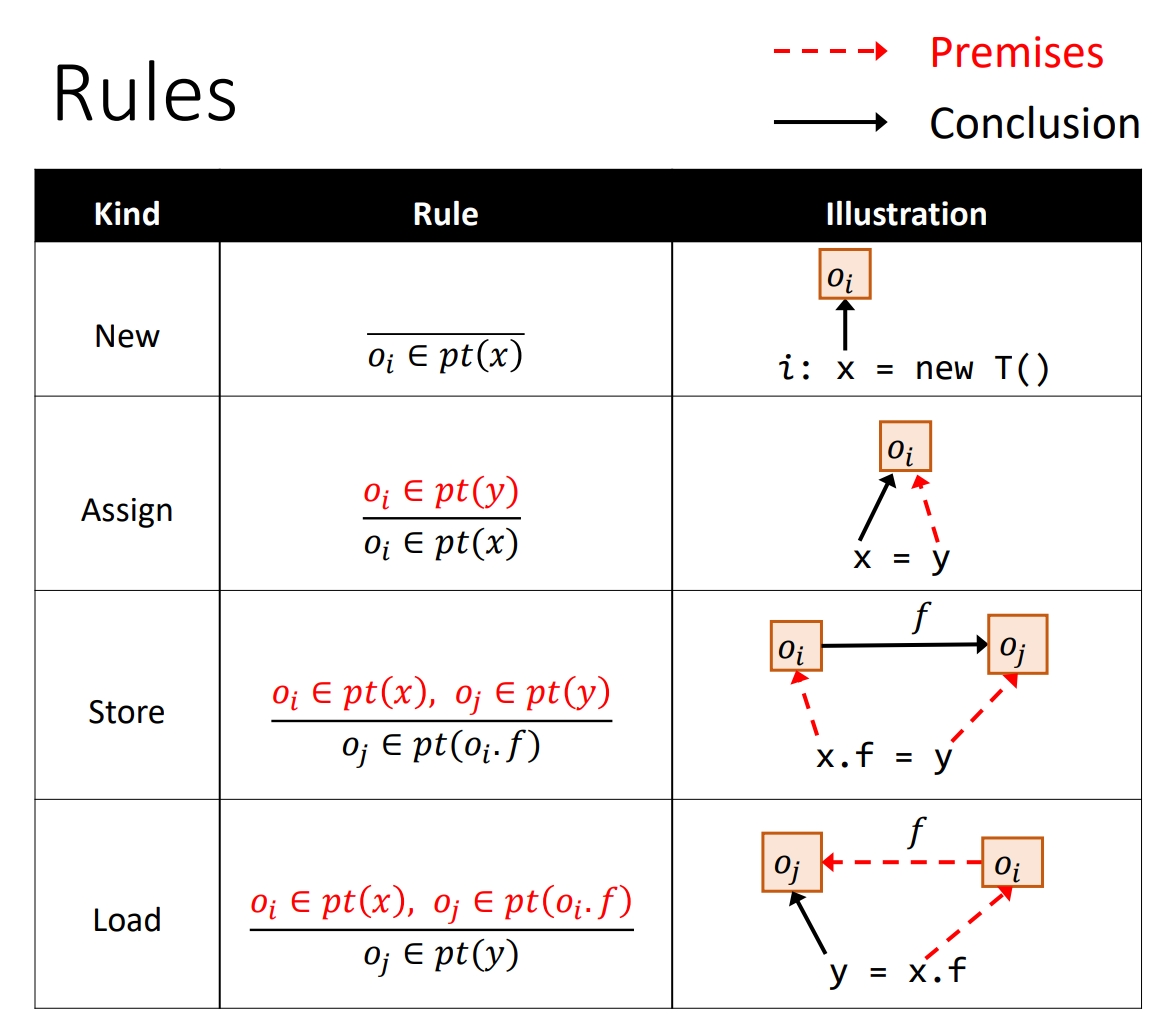
Pointer Flow Graph(PFG)
其实就是把=理解为<-,构造成指针流图。由此转换成传递闭包的问题。比如说一个对于b的Assign语句,对应的relation map就可以沿着有向边传播。  对于与
对于与field,其预设的$o_{x} \in pt()$是需要在程序里Assign才获得的。Build pointer flow graph (PFG) and Propagate points-to information on PFG is Mutually dependent。 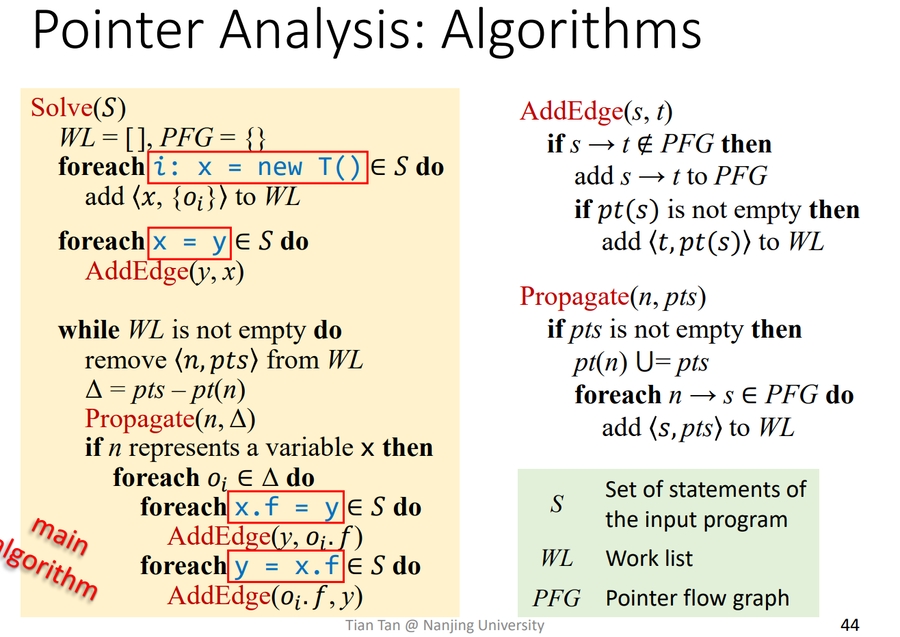
Differential propagation is employed to avoid propagation and processing of redundant points-to information. and no need to propagate them.
PA-FD with method call
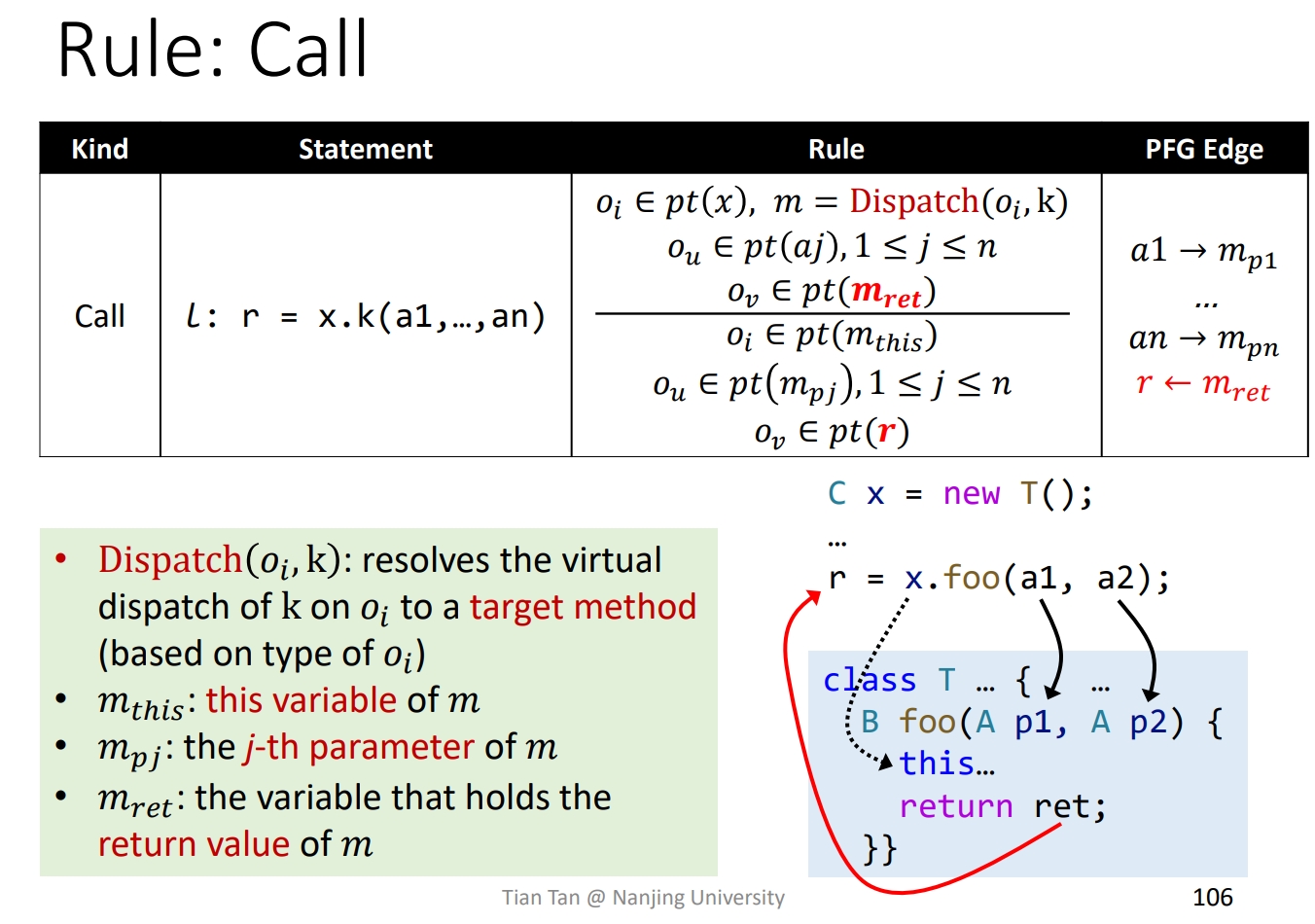
A4:类层次结构分析与过程间常量传播
需要使用一个函数的工具,不一定需要从一个实例出发调用,而可能Static utility比如:
CallGraphs.getCallKind(callSite)就无需new。先捋清楚一些类间关系:
Invoke(callsite): 这相当于
DefStmt的一个范式。(来自于A5)
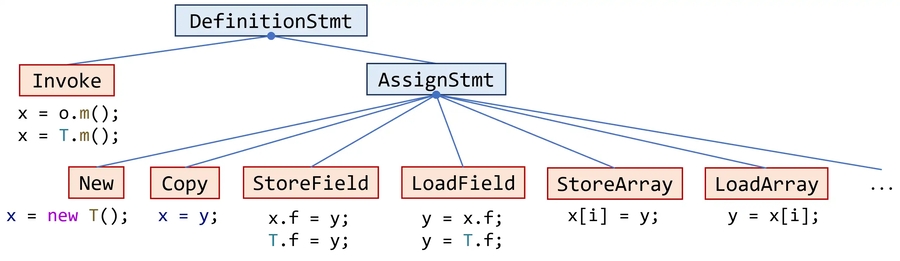
对于一个语句
b = a.m(...)来说,b是result,a.m(...)是InvokeExp。f(...) {...; b = a.m(...); ...;},在这里f(...)是b = a.m(...)的container。如果想获得
a的类型,不是到InvokeExp里面找,而是到MethodRef里面找。
m是一个函数签名,但是T是方法的集合。那怎么才能通过签名获得方法呢?注意上面说的,不要找到container去了,答案是通过签名的getDeclaringClass()获得类信息,再通过类信息获得JMethod对象。
Node:与site的关系是..
请注意代码实现与注释规约的一致性。
为了DEBUG相应的模块,你可以看一下Assignment的使用方式。
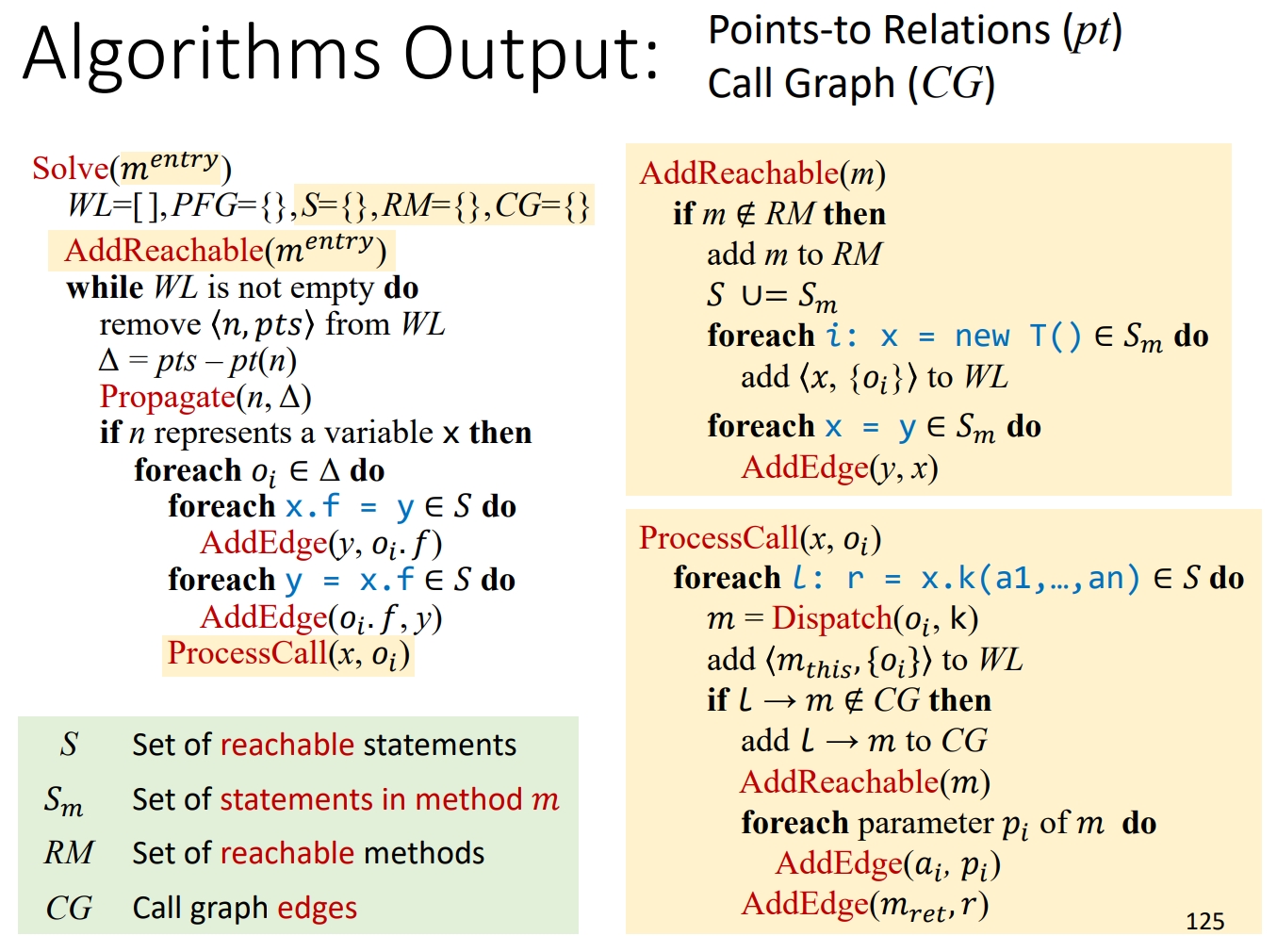
A5:非上下文敏感指针分析
前置知识
LoadField和StoreField同时表示实例和静态字段的 load 和 store。这两个类也提供了isStatic()方法来检查一个LoadField/StoreField语句是 load/store 静态字段还是实例字段。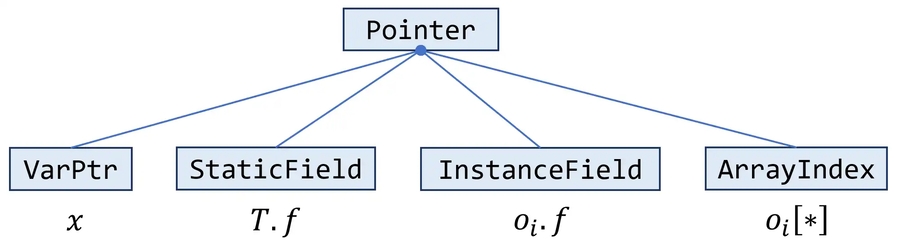
访问者模式
在 addReachable() 中,对于不同种类的语句,你需要使用不同的逻辑来处理。实现这种需求的一个合理方式是访问者模式。Tai-e 的 IR 天然支持访问者模式。具体来说,Tai-e 提供了 pascal.taie.ir.stmt.StmtVisitor 类,这是所有 Stmt 访问者的通用接口,它为所有种类的语句都声明了访问操作。另外,Stmt 的非抽象子类都实现了 accept(StmtVisitor) 方法,因此它们可以回调来自具体访问者的访问操作。
在 Solver 中,我们为 Stmt 访问者提供了代码框架(即内部类 StmtProcessor),并在 initialize() 中创建了它的实例,并将该实例存在字段 stmtProcessor 中。如果你选择通过访问者模式实现 addReachable() 的逻辑,那么你应该在类 stmtProcessor 中实现相关的 visit(…) 方法,并使用它来处理可达方法中的语句。在这次作业中,visit(…) 方法的返回值被忽略,因此你在实现 visit(…) 方法时只需要返回 null。
Thx:https://github.com/RicoloveFeng/SPA-Freestyle-Guidance
最后更新于
这有帮助吗?